(Press-News.org) The immune system protects the upper respiratory tract from bacterial infections, but the cues that alert the immune system to the presence of bacteria are not known. In this issue of the Journal of Clinical Investigation, researchers led by Noam Cohen at the University of Pennsylvania demonstrated that the bitter taste receptor T2R38 regulates the immune defense of the human upper airway. Cohen and colleagues found that T2R38 was expressed in the cells that line the upper respiratory tract and could be activated by molecules secreted by Pseudomonas aeruginosa and other bacteria. Additionally, they found that common polymorphisms in the T2R38 gene were correlated with the incidence of bacterial sinus infections. These results demonstrate that genetic variation contributes to individual differences in susceptibility to respiratory infection. In a companion piece, Alice Prince of Columbia University discusses the role of bitter taste receptors in immune defense.
TITLE:
T2R38 taste receptor polymorphisms underlie susceptibility to upper respiratory infection
AUTHOR CONTACT:
Noam Cohen
Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, PA, USA
Phone: 215-823-5800 ext 3892; Fax: 215-349-5977; E-mail: cohenn@uphs.upenn.edu
View this article at: http://www.jci.org/articles/view/64240?key=8713f7c1bd015e43f32d
ACCOMPANYING COMMENTARY
TITLE:
The bitter tast of infection
AUTHOR CONTACT:
Alice S. Prince
Columbia University, New York, NY, USA
Phone: 212/305-4193; Fax: 212-305-2284; E-mail: asp7@columbia.edu
View this article at: http://www.jci.org/articles/view/66182?key=3da926f3262c7c8e0664
### END
Sinusitis: Leaving a bad taste in your mouth
2012-10-08
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Endotrophin links obesity to breast cancer progression
2012-10-08
Fat cells (adipocytes) surround breast tumors and contribute to tumor growth by expressing factors that aid oncogenesis. Col6 is a protein that is highly expressed in adipocytes and its expression is further increased in both obesity and in breast cancer cells. In this issue of the Journal of Clinical Investigation, Phillip Scherer and Jiyoung Park of the University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center report that a portion of the Col6 protein, known as endotrophin, alters the tumor environment to promote tumor growth and metastasis in mice. Mice with reduced endotrophin ...
Use of fresh red blood cells for transfusions for premature infants does not improve outcomes
2012-10-08
CHICAGO – Among premature, very low-birth-weight infants requiring a transfusion, use of fresh red blood cells (RBCs) compared with standard RBC transfusion practice did not improve clinical outcomes that included rates of complications or death, according to a study in the October 10 issue of JAMA. The study is being published early online to coincide with its presentation at the AABB (formerly the American Association of Blood Banks) Annual Meeting.
"Although RBC transfusions are used routinely in acutely ill patients, including those in neonatal intensive care units, ...
Fresh blood not better, clinical trial shows
2012-10-08
October 8, 2012, Ottawa — In a finding that runs counter to commonly held beliefs about fresh being better, a clinical trial published today by the Journal of the American Medical Association shows that acutely ill premature babies who received fresher blood did not fare better than those who received the current standard of care. There was no difference between the two approaches with respect to major organ injury, mortality and infection.
"Before now, most of the literature on the subject suggested that fresh red blood cells are better," says lead author Dr. Dean Fergusson, ...
Gladstone scientists identify biological mechanism that plays key role in early-onset dementia
2012-10-08
SAN FRANCISCO, CA—October 8, 2012—Using animal models, scientists at the Gladstone Institutes have discovered how a protein deficiency may be linked to frontotemporal dementia (FTD)—a form of early-onset dementia that is similar to Alzheimer's disease. These results lay the foundation for therapies that one day may benefit those who suffer from this and related diseases that wreak havoc on the brain.
As its name implies, FTD is a fatal disease that destroys cells, or neurons, that comprise the frontal and temporal lobes of the brain—as opposed to Alzheimer's which mainly ...
New study reveals bitter taste receptors regulate the upper respiratory defense system
2012-10-08
PHILADELPHIA – A new study from a team of researchers at the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania, the Monell Chemical Senses Center, and the Philadelphia VA Medical Center, reveals that a person's ability to taste certain bitter flavors is directly related to their ability to fight off upper respiratory tract infections, specifically chronic sinus infections. The new research is published in the latest edition of the Journal of Clinical Investigation.
Most humans experience five types of tastes: sweet, salty, sour, bitter, and savory. The ...
Study finds nearly 50% of retail firewood infested with insects
2012-10-08
A new study published in the Journal of Economic Entomology reports that live insects were found in 47% of firewood bundles purchased from big box stores, gas stations and grocery stores in Colorado, New Mexico, Utah and Wyoming.
Untreated firewood can harbor pathogens and destructive insects such as the emerald ash borer, the Asian longhorned beetle, bark beetles and others, and transport them to uninfested areas. Furthermore, the risk of moving insects in untreated firewood is high, the authors found, because insects emerged up to 558 days from the purchase date of ...
Smallest and fastest-known RNA switches provide new drug targets
2012-10-08
ANN ARBOR, Mich.—A University of Michigan biophysical chemist and his colleagues have discovered the smallest and fastest-known molecular switches made of RNA, the chemical cousin of DNA. The researchers say these rare, fleeting structures are prime targets for the development of new antiviral and antibiotic drugs.
Once believed to merely store and relay genetic information, RNA is now known to be a cellular Swiss Army knife of sorts, performing a wide variety of tasks and morphing into myriad shapes.
Over the past decade, researchers have determined that most of the ...
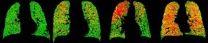
Breathe in, breathe out: New way of imaging lungs could improve COPD diagnosis and treatment
2012-10-08
ANN ARBOR, Mich. — A new approach to lung scanning could improve the diagnosis and treatment of a lung disease that affects approximately 24 million Americans and is the country's third-highest cause of death.
In a new paper published online in Nature Medicine, a team from the University of Michigan Medical School reports on a technique called parametric response mapping, or PRM. They used PRM to analyze computed tomography, or CT, scans of the lungs of patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, known as COPD, who took part in the national COPDGene study funded ...
UCLA researchers discover that the sleeping brain behaves as if it's remembering something
2012-10-08
UCLA researchers have for the first time measured the activity of a brain region known to be involved in learning, memory and Alzheimer's disease during sleep. They discovered that this part of the brain behaves as if it's remembering something, even under anesthesia, a finding that counters conventional theories about memory consolidation during sleep.
The research team simultaneously measured the activity of single neurons from multiple parts of the brain involved in memory formation. The technique allowed them to determine which brain region was activating other areas ...
Genome-wide study identifies 8 new susceptibility loci for atopic dermatitis
2012-10-08
Researchers at the RIKEN Center for Genomic Medicine (CGM) and their colleagues have identified 8 new loci associated with susceptibility to atopic dermatitis in the Japanese population. The findings, which appear in the journal Nature Genetics, advance our understanding of the genetic basis of the skin disorder, which affects millions of children and adults around the world.
Atopic dermatitis (often called ecszema) is a chronic, relapsing inflammatory skin condition affecting as much as one-fifth of children and 1-3% of adults in industrialized countries. Those with ...