(Press-News.org) SAN FRANCISCO, CA—October 8, 2012—Using animal models, scientists at the Gladstone Institutes have discovered how a protein deficiency may be linked to frontotemporal dementia (FTD)—a form of early-onset dementia that is similar to Alzheimer's disease. These results lay the foundation for therapies that one day may benefit those who suffer from this and related diseases that wreak havoc on the brain.
As its name implies, FTD is a fatal disease that destroys cells, or neurons, that comprise the frontal and temporal lobes of the brain—as opposed to Alzheimer's which mainly affects brain's memory centers in the hippocampus. Early symptoms of FTD include personality changes, such as increased erratic or compulsive behavior. Patients later experience difficulties speaking and reading, and often suffer from long-term memory loss. FTD is usually diagnosed between the ages of 40 and 65, with death occurring within 2 to 10 years after diagnosis. No drug exists to slow, halt or reverse the progression of FTD.
A new study led by Gladstone Senior Investigator Robert V. Farese, Jr., MD, offers new hope in the fight against this and other related conditions. In the latest issue of the Journal of Clinical Investigation, available today online, Dr. Farese and his team show how a protein called progranulin prevents a class of cells called microglia from becoming "hyperactive." Without adequate progranulin to keep microglia in check, this hyperactivity becomes toxic, causing abnormally prolonged inflammation that destroys neurons over time—and leads to debilitating symptoms.
"We have known that a lack of progranulin is linked to neurodegenerative conditions such as FTD, but the exact mechanism behind that link remained unclear," said Dr. Farese, who is also a professor at the University of California, San Francisco (UCSF), with which Gladstone is affiliated. "Understanding the inflammatory process in the brain is critical if we are to develop better treatments not only for FTD, but for other forms of brain injury such as Parkinson's disease, Huntington's disease and multiple sclerosis (MS)—which are likely also linked to abnormal microglial activity."
Microglia—which are a type of immune cells that reside in the CNS—normally secrete progranulin. Early studies on traumatic CNS injury found that progranulin accumulates at the injury site alongside microglia, suggesting that both play a role in injury response. So, Dr. Farese and his team designed a series of experiments to decipher the nature of the relationship between progranulin and microglia.
First, the team generated genetically modified mice that lack progranulin. They then monitored how the brains of these mice responded to toxins, comparing this reaction to a control group.
"As expected, the toxin destroys neurons in both sets of mice—but the progranulin-deficient mice lost twice as many neurons as the control group," said Lauren Herl Martens, a Gladstone and UCSF graduate student and the study's lead author. "This showed us that progranulin is crucial for neuron survival. We then wanted to see whether a lack of progranulin itself would injure these cells—even in the absence of toxins."
In a petri dish, the researchers artificially prevented microglia from secreting progranulin and monitored how these modified microglia interacted with neurons. They observed that a significantly greater number of neurons died in the presence of the progranulin-deficient microglia when compared to unmodified microglia.
Other experiments revealed the process' underlying mechanism. Microglia are the CNS's first line of defense. When the microglia sense toxins or injury, they trigger protective inflammation—which can become toxic to neurons if left unchecked. Dr. Farese's team discovered that progranulin works by tempering the microglia's response, thereby minimizing inflammation. Without progranulin, the microglia are unrestricted—and induce prolonged and excessive inflammation that leads to neuron damage—and can contribute to the vast array of symptoms that afflict sufferers FTD and other fatal forms of brain disease.
"However, we found that boosting progranulin levels in microglia reduced inflammation—keeping neurons alive and healthy in cell culture," explained Dr. Farese. "Our next step is to determine if this method could also work in live animals. We believe this to be a therapeutic strategy that could, for example, halt the progression of FTD. More broadly, our findings about progranulin and inflammation could have therapeutic implications for devastating neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer's, Parkinson's and MS."
INFORMATION:
Other scientists who participated in this research at Gladstone include Sami Barmada, PhD, Ping Zhou, MD, Li Gan, PhD and Steve Finkbeiner, MD, PhD. Funding came from a variety of sources, including the Consortium for Frontotemporal Dementia Research, the ALS Association and the National Institutes of Health.
About the Gladstone Institutes
Gladstone is an independent and nonprofit biomedical-research organization dedicated to accelerating the pace of scientific discovery and innovation to prevent, treat and cure cardiovascular, viral and neurological diseases. Gladstone is affiliated with the University of California, San Francisco.
Gladstone scientists identify biological mechanism that plays key role in early-onset dementia
Findings explain how protein deficiency contributes to neurodegenerative disease
2012-10-08
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
New study reveals bitter taste receptors regulate the upper respiratory defense system
2012-10-08
PHILADELPHIA – A new study from a team of researchers at the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania, the Monell Chemical Senses Center, and the Philadelphia VA Medical Center, reveals that a person's ability to taste certain bitter flavors is directly related to their ability to fight off upper respiratory tract infections, specifically chronic sinus infections. The new research is published in the latest edition of the Journal of Clinical Investigation.
Most humans experience five types of tastes: sweet, salty, sour, bitter, and savory. The ...
Study finds nearly 50% of retail firewood infested with insects
2012-10-08
A new study published in the Journal of Economic Entomology reports that live insects were found in 47% of firewood bundles purchased from big box stores, gas stations and grocery stores in Colorado, New Mexico, Utah and Wyoming.
Untreated firewood can harbor pathogens and destructive insects such as the emerald ash borer, the Asian longhorned beetle, bark beetles and others, and transport them to uninfested areas. Furthermore, the risk of moving insects in untreated firewood is high, the authors found, because insects emerged up to 558 days from the purchase date of ...
Smallest and fastest-known RNA switches provide new drug targets
2012-10-08
ANN ARBOR, Mich.—A University of Michigan biophysical chemist and his colleagues have discovered the smallest and fastest-known molecular switches made of RNA, the chemical cousin of DNA. The researchers say these rare, fleeting structures are prime targets for the development of new antiviral and antibiotic drugs.
Once believed to merely store and relay genetic information, RNA is now known to be a cellular Swiss Army knife of sorts, performing a wide variety of tasks and morphing into myriad shapes.
Over the past decade, researchers have determined that most of the ...
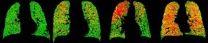
Breathe in, breathe out: New way of imaging lungs could improve COPD diagnosis and treatment
2012-10-08
ANN ARBOR, Mich. — A new approach to lung scanning could improve the diagnosis and treatment of a lung disease that affects approximately 24 million Americans and is the country's third-highest cause of death.
In a new paper published online in Nature Medicine, a team from the University of Michigan Medical School reports on a technique called parametric response mapping, or PRM. They used PRM to analyze computed tomography, or CT, scans of the lungs of patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, known as COPD, who took part in the national COPDGene study funded ...
UCLA researchers discover that the sleeping brain behaves as if it's remembering something
2012-10-08
UCLA researchers have for the first time measured the activity of a brain region known to be involved in learning, memory and Alzheimer's disease during sleep. They discovered that this part of the brain behaves as if it's remembering something, even under anesthesia, a finding that counters conventional theories about memory consolidation during sleep.
The research team simultaneously measured the activity of single neurons from multiple parts of the brain involved in memory formation. The technique allowed them to determine which brain region was activating other areas ...
Genome-wide study identifies 8 new susceptibility loci for atopic dermatitis
2012-10-08
Researchers at the RIKEN Center for Genomic Medicine (CGM) and their colleagues have identified 8 new loci associated with susceptibility to atopic dermatitis in the Japanese population. The findings, which appear in the journal Nature Genetics, advance our understanding of the genetic basis of the skin disorder, which affects millions of children and adults around the world.
Atopic dermatitis (often called ecszema) is a chronic, relapsing inflammatory skin condition affecting as much as one-fifth of children and 1-3% of adults in industrialized countries. Those with ...
Discovery of gatekeeper nerve cells explains the effect of nicotine on learning and memory
2012-10-08
Swedish researchers at Uppsala University have, together with Brazilian collaborators, discovered a new group of nerve cells that regulate processes of learning and memory. These cells act as gatekeepers and carry a receptor for nicotine, which can explain our ability to remember and sort information.
The discovery of the gatekeeper cells, which are part of a memory network together with several other nerve cells in the hippocampus, reveal new fundamental knowledge about learning and memory. The study is published today in Nature Neuroscience.
The hippocampus is an ...
Stanford researchers show oil palm plantations are clearing carbon-rich tropical forests in Borneo
2012-10-08
Expanding production of palm oil, a common ingredient in processed foods, soaps and personal care products, is driving rainforest destruction and massive carbon dioxide emissions, according to a new study led by researchers at Stanford and Yale universities.
The study, published online Oct. 7 in the journal Nature Climate Change, shows that deforestation for the development of oil palm plantations in Indonesian Borneo is becoming a globally significant source of carbon dioxide emissions.
Plantation expansion is projected to contribute more than 558 million metric tons ...
A novel oncogenic network specific to liver cancer initiation
2012-10-08
Researchers headed by Erwin Wagner, the Director of the BBVA Foundation-CNIO Cancer Cell Biology Programme at the Spanish National Cancer Research Centre (CNIO), have deciphered how a stress-inducible gene regulator, AP-1, controls the survival of liver tumor-initiating cells. These results, published in the online edition of Nature Cell Biology, could provide new preventive strategies and identify potentially targetable molecules to prevent liver cancer.
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) causes more than 500,000 deaths per year worldwide. While patients with chronic hepatitis ...
Gene variant linked with reduced lung cancer risk
2012-10-08
A variant in a gene involved with inflammation and the immune response is linked with a decreased risk of lung cancer. That is the finding of an analysis published early online in CANCER, a peer-reviewed journal of the American Cancer Society. The results add to the growing body of literature implicating these processes in the development of lung cancer.
Meredith Shiels, PhD, MHS and Anil Chaturvedi, PhD, of the National Cancer Institute in Rockville, MD, and their colleagues analyzed 1,429 variants in inflammation- and immunity-related genes from 378 patients with lung ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
$3.4 million grant to improve weight-management programs
Higher burnout rates among physicians who treat sickle cell disease
Wetlands in Brazil’s Cerrado are carbon-storage powerhouses
Brain diseases: certain neurons are especially susceptible to ALS and FTD
Father’s tobacco use may raise children’s diabetes risk
Structured exercise programs may help combat “chemo brain” according to new study in JNCCN
The ‘croak’ conundrum: Parasites complicate love signals in frogs
Global trends in the integration of traditional and modern medicine: challenges and opportunities
Medicinal plants with anti-entamoeba histolytica activity: phytochemistry, efficacy, and clinical potential
What a releaf: Tomatoes, carrots and lettuce store pharmaceutical byproducts in their leaves
Evaluating the effects of hypnotics for insomnia in obstructive sleep apnea
A new reagent makes living brains transparent for deeper, non-invasive imaging
Smaller insects more likely to escape fish mouths
Failed experiment by Cambridge scientists leads to surprise drug development breakthrough
Salad packs a healthy punch to meet a growing Vitamin B12 need
Capsule technology opens new window into individual cells
We are not alone: Our Sun escaped together with stellar “twins” from galaxy center
Scientists find new way of measuring activity of cell editors that fuel cancer
Teens using AI meal plans could be eating too few calories — equivalent to skipping a meal
Inconsistent labeling and high doses found in delta-8 THC products: JSAD study
Bringing diabetes treatment into focus
Iowa-led research team names, describes new crocodile that hunted iconic Lucy’s species
One-third of Americans making financial trade-offs to pay for healthcare
Researchers clarify how ketogenic diets treat epilepsy, guiding future therapy development
PsyMetRiC – a new tool to predict physical health risks in young people with psychosis
Island birds reveal surprising link between immunity and gut bacteria
Research presented at international urology conference in London shows how far prostate cancer screening has come
Further evidence of developmental risks linked to epilepsy drugs in pregnancy
Cosmetic procedures need tighter regulation to reduce harm, argue experts
How chaos theory could turn every NHS scan into its own fortress
[Press-News.org] Gladstone scientists identify biological mechanism that plays key role in early-onset dementiaFindings explain how protein deficiency contributes to neurodegenerative disease