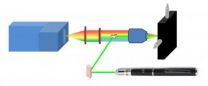
(Press-News.org) WASHINGTON, Oct. 9, 2012—By using an ordinary green laser pointer, the kind commonly found in offices and college lecture halls, an Israeli research team has developed a new and highly portable Raman spectrometer that can detect extremely minute traces of hazardous chemicals in real time. The new sensor's compact design makes it an excellent candidate for rapid field deployment to disaster zones and areas with security concerns. The researchers will present their findings at Laser Science XXVIII—the American Physical Society Division of Laser Science's Annual Meeting—collocated with the Optical Society's (OSA) Annual Meeting, Frontier in Optics (FiO), taking place in Rochester, N.Y. next week.
Raman spectrometers rely on highly focused beams of light at precise wavelengths to illuminate small samples of materials. Very sensitive detectors then study the spectra of light that has been re-emitted, or scattered, by the sample. Most of this scattered light retains its original frequency or color, but a very small percentage of that light is shifted ever so slightly to higher or lower wavelengths, depending on the unique vibrational modes of the sample being studied. By comparing the shifted and the original wavelengths, it's possible to determine the precise chemicals present in the sample.
The researchers brought this capability down to size by constructing their Raman spectrometer using a low-power and low-cost commercial green laser pointer. The green laser's relatively short wavelength helped to improve the detection of the inherently weak Raman signal. The spectrometer also has the capability to first scan the entire sample optically, sweeping from side to side, to locate individual particles of interest – a task usually performed by large and cumbersome Raman microscopes.
"Since the overall system is modular, compact, and can be readily made portable, it can be easily applied to the detection of different compounds and for forensic examination of objects that are contaminated with drugs, explosives, and particularly explosive residues on latent fingerprints," said Ilana Bar, a researcher with the Department of Physics at Ben-Gurion University of the Negev in Israel. "With proper investment this system could be deployed quite quickly as a consumer product." Other members of the research team include Itamar Malka, Alona Petrushansky, and Salman Rosenwaks.
Presentation LTh3I.3, "Detection of Explosives and Latent Fingerprint Residues Utilizing Laser Pointer Based Raman Spectroscopy," takes place Thursday, Oct. 18 at 2:30 p.m. EDT at the Rochester Riverside Convention Center in Rochester, N.Y.
INFORMATION:
EDITOR'S NOTE: An image showing a schematic of the system is available to members of the media upon request. Contact Angela Stark, astark@osa.org.
PRESS REGISTRATION: A press room for credentialed press and analysts will be located in the Rochester Riverside Convention Center, Sunday through Thursday, Oct. 14-18. Those interested in obtaining a press badge for FiO should contact OSA's Angela Stark at 202.416.1443 or astark@osa.org. A full list of meeting highlights for press is available on the FiO website: http://www.frontiersinoptics.com/home/media-center/conference-news/optics-and-photonics-technology-leaders,-researche/
About the Meeting
Frontiers in Optics (FiO) 2012 is the Optical Society's (OSA) 96th Annual Meeting and is being held together with Laser Science XXVIII, the annual meeting of the American Physical Society (APS) Division of Laser Science (DLS). The two meetings unite the OSA and APS communities for five days of quality, cutting-edge presentations, fascinating invited speakers and a variety of special events spanning a broad range of topics in optics and photonics—the science of light—across the disciplines of physics, biology and chemistry. FiO 2012 will also offer a number of Short Courses designed to increase participants' knowledge of a specific subject in the optical sciences while offering the experience of insightful teachers. An exhibit floor featuring leading optics companies will further enhance the meeting. More information at http://www.FrontiersinOptics.org.
About OSA
Uniting more than 180,000 professionals from 175 countries, the Optical Society (OSA) brings together the global optics community through its programs and initiatives. Since 1916 OSA has worked to advance the common interests of the field, providing educational resources to the scientists, engineers and business leaders who work in the field by promoting the science of light and the advanced technologies made possible by optics and photonics. OSA publications, events, technical groups and programs foster optics knowledge and scientific collaboration among all those with an interest in optics and photonics. For more information, visit http://www.osa.org.
From lectures to explosives detection: Laser pointer identifies dangerous chemicals in real-time
2012-10-10
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Satiation hormone could increase risk of diabetes, heart attack and breast cancer in women
2012-10-10
The findings have been presented in a study from Lund University in Sweden, published in the Journal of the American Medical Association.
"It was surprising to find such a clear link to the risk of type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular disease as well as to breast cancer. Obesity is a common risk factor for all three conditions, but the connection with neurotensin is not explained by obesity or other known risk factors", says Professor Olle Melander from the Department of Clinical Sciences at Lund University, who is also a consultant at Skåne University Hospital.
"This ...
UAB researchers develop an advanced computer simulator to manage hospital emergencies
2012-10-10
Researchers of the group High Performance Computing for Efficient Applications and Simulation (HPC4EAS) of the Department of Computer Architecture and Operating Systems of the Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona (UAB), in collaboration with the team at the Emergency Services Unit at Hospital de Sabadell (Parc Taulí Healthcare Corporation), have developed an advanced computer simulator to help in decision-making processes (DSS, or decision support system) which could aid emergency service units in their operations management.
The model was designed based on real data provided ...
Collaborative efforts develop AIUM Practice Guideline
2012-10-10
The American Institute of Ultrasound in Medicine (AIUM) is pleased to announce the collaborative development of the AIUM Practice Guideline for the Performance of a Focused Reproductive Endocrinology and Infertility Scan. Indications for an ultrasound examination for a focused reproductive endocrinology and infertility scan include but are not limited to monitoring of ovulation induction and ovarian stimulation.
The American College of Nurse-Midwives, American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists, American College of Osteopathic Obstetricians and Gynecologists, ...
Loss of protective heart failure protein linked to critical limb ischemia
2012-10-10
PHILADELPHIA— Restoring diminished levels of a protein shown to prevent and reverse heart failure damage could also have therapeutic applications for patients with critical limb ischemia (CLI), suggests a new preclinical study published online October 9 in Circulation Research from researchers at the Center for Translational Medicine at Thomas Jefferson University .
Low levels of the protein S100A1 have been linked to congestive heart failure and high blood pressure, and now appear to be associated with critical lower limb ischemia, a condition found in type 2 diabetic ...
Does immune dysfunction contribute to schizophrenia?
2012-10-10
Philadelphia, PA, October 10, 2012 – A new study reinforces the finding that a region of the genome involved in immune system function, called the major histocompatibility complex (MHC), is involved in the genetic susceptibility to schizophrenia.
Schizophrenia is among the most disabling psychiatric disorders. Approximately 80% of the risk for developing schizophrenia is heritable, but there has been slow progress in identifying genetic variation that contributes to the risk for schizophrenia.
The current paper contributes to this growing literature by identifying ...
Living near livestock may increase risk of acquiring MRSA
2012-10-10
People who live near livestock or in livestock farming communities may be at greater risk of acquiring, Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), according to a new study led by an international team of researchers from the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health, the Dutch Institute for Public Health and the Environment (RIVM) and VU University Medical Center in Amsterdam. A comparison of livestock density, place of residence and existing information on risk factors found that regional density of livestock is an important risk factor for nasal carriage ...
Study shows small fish can play a big role in coastal carbon cycle
2012-10-10
A study in the current issue of Scientific Reports, a new online journal from the Nature Publishing Group, shows that small forage fish like anchovies can play an important role in the "biological pump," the process by which marine life transports carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and surface ocean into the deep sea—where it contributes nothing to current global warming.
The study, by Dr. Grace Saba of Rutgers University and professor Deborah Steinberg of the Virginia Institute of Marine Science, reports on data collected during an oceanographic expedition to the California ...
Applying information theory to linguistics
2012-10-10
CAMBRIDGE, Mass. -- The majority of languages — roughly 85 percent of them — can be sorted into two categories: those, like English, in which the basic sentence form is subject-verb-object ("the girl kicks the ball"), and those, like Japanese, in which the basic sentence form is subject-object-verb ("the girl the ball kicks").
The reason for the difference has remained somewhat mysterious, but researchers from MIT's Department of Brain and Cognitive Sciences now believe that they can account for it using concepts borrowed from information theory, the discipline, invented ...
A problem shared is a problem halved
2012-10-10
The experience of being bullied is particularly detrimental to the psychological health of school girls who don't have social support from either adults or peers, according to a new study by Dr. Martin Guhn and colleagues from the University of British Columbia in Canada. In contrast, social support from adults or peers (or both) appears to lessen the negative consequences of bullying in this group, namely anxiety and depression. The work is published online in Springer's Journal of Happiness Studies.
Guhn and his team looked at whether the combination of high levels ...
Research reveals more about spatial memory problems associated with Alzheimer's
2012-10-10
Researchers at Western University have created a mouse model that reproduces some of the chemical changes in the brain that occur with Alzheimer's, shedding new light on this devastating disease. Marco Prado, Vania Prado and their colleagues at the Schulich School of Medicine & Dentistry's Robarts Research Institute, looked at changes related to a neurotransmitter or chemical messenger, named acetylcholine (ACh), and the kinds of memory problems associated with it. The research is now published online by PNAS.
The researchers, including first author Amanda Martyn, ...