(Press-News.org) AUDIO:
This is a mouse song.
Click here for more information.
Scientists have found the first evidence that the ability to learn vocalizations, a capacity so far believed to be restricted to a handful of bird and mammal species like humans and dolphins, is shared by another species: mice. The new research, published Oct. 10 in the open access journal PLOS ONE by Erich Jarvis and Gustavo Arriaga at Duke University and colleagues, shows for the first time that mice share certain behavioral and brain mechanisms involved in vocal learning with songbirds and humans and can learn new vocal patterns.
Most animals make sounds of some sort, but only a few have the capacity to modify the sequence and pitch of sounds to create songs and speech, collectively referred to as vocal learning. So far, only three groups of birds - parrots, hummingbirds and songbirds - and some mammalian species - humans, whales, dolphins, sea lions, bats and elephants - have shown the behaviors and brain circuits that are considered essential to the process of learned vocalization. Despite decades of research, scientists have yet to find evidence of these behavioral and neurological hallmarks in other species, including those closely related to vocal learners such as non-human primates.
Though the series of ultrasonic vocalizations referred to as mouse 'song' was previously known, this study provides the first evidence that mice can change at least one acoustic feature of these vocalizations based on their social exposure. When two male mice of different strains were housed together, the animals gradually learned to match the pitch of their songs to one another, suggesting a capacity for learning not previously known. The researchers state that this is a limited form of vocal learning, but do not know whether other more complex features, such as syntax and frequency modulation, could be learned.
The researchers found that mice can form some of the necessary connections between different brain regions and the vocal motor neurons to control the sounds they make, a feature so far found in song learning birds and humans. Though the connections are more limited in mice compared to humans or songbirds, Jarvis states, "This is an exciting find, as the presence of direct forebrain control over the vocal neurons may be one of the most critical aspects in the human evolution of speech."
According to the researchers, their discovery was made possible by using modern techniques not previously available. They also clarify that the connections in mice are much more primitive than in songbirds or humans, but they may reveal some of the intermediate steps in the process by which vocalization evolved in advanced vocal learners like songbirds and humans.
INFORMATION:Citation: Arriaga G, Zhou EP, Jarvis ED (2012) Of Mice, Birds, and Men: The Mouse Ultrasonic Song System Has Some Features Similar to Humans and Song-Learning Birds. PLoS ONE 7(10): e46610. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0046610
Financial disclosure: Research was supported by a National Institutes of Health pioneer award DP1 OD000448 and HHMI investigator award to EDJ and an National Science Foundation predoctoral fellowship to GA. The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
Competing Interest Statement: The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
PLEASE LINK TO THE SCIENTIFIC ARTICLE IN ONLINE VERSIONS OF YOUR REPORT (URL goes live after the embargo ends):
http://dx.plos.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0046610
END
Bad news articles in the media increase women's sensitivity to stressful situations, but do not have a similar effect on men, according to a study undertaken by University of Montreal researchers at the Centre for Studies on Human Stress of Louis-H. Lafontaine Hospital. The findings were published today in PLOS One. The women who participated in the study also had a clearer recollection of the information they had learned. "It's difficult to avoid the news, considering the multitude of news sources out there, said lead author Marie-France Marin. "And what if all that news ...
The remarkably well-preserved fossil of an extinct arthropod shows that anatomically complex brains evolved earlier than previously thought and have changed little over the course of evolution. According to University of Arizona neurobiologist Nicholas Strausfeld, who co-authored the study describing the specimen, the fossil is the earliest known to show a brain.
The discovery will be published in the Oct. 11 issue of the journal Nature.
Embedded in mudstones deposited during the Cambrian period 520 million years ago in what today is the Yunnan Province in China, the ...
Researchers have published the first highly detailed description of how neurotensin, a neuropeptide hormone which modulates nerve cell activity in the brain, interacts with its receptor. Their results suggest that neuropeptide hormones use a novel binding mechanism to activate a class of receptors called G-protein coupled receptors (GPCRs).
"The knowledge of how the peptide binds to its receptor should help scientists design better drugs," said Dr. Reinhard Grisshammer, a scientist at the NIH's National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NINDS) and an ...
The well-documented presence of excessive levels of carbon dioxide (CO2) in our atmosphere is causing global temperatures to rise and glaciers and ice caps to melt.
New research, published today, 11 October, in IOP Publishing's Journal of Physics D: Applied Physics, has shown that CO2 molecules may be having a more direct impact on the ice that covers our planet.
Researchers from the Massachusetts Institute for Technology have shown that the material strength and fracture toughness of ice are decreased significantly under increasing concentrations of CO2 molecules, ...
Who we call and how long we speak to them changes with the weather, according to new research by experts at Newcastle University.
Analysing the call patterns of 1.3 million mobile phone users, the team found that in 'uncomfortable' weather – such as very hot, humid, wet or cold weather – call length increased but the number of people we made contact with went down.
Apparently "isolating" ourselves during more unpleasant weather, research lead Dr Santi Phithakkitnukoon said the data showed that we were also more likely to contact our close friends and family than our wider ...
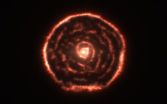
A team using the Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA), the most powerful millimetre/submillimetre telescope in the world, has discovered a surprising spiral structure in the gas around the red giant star R Sculptoris [1][2][3]. This means that there is probably a previously unseen companion star orbiting the star [4]. The astronomers were also surprised to find that far more material than expected had been ejected by the red giant.
"We've seen shells around this kind of star before, but this is the first time we've ever seen a spiral of material coming ...
DURHAM, N.C. -- Guys who imitate Luciano Pavarotti or Justin Bieber to get the girls aren't alone. Male mice may do a similar trick, matching the pitch of other males' ultrasonic serenades. The mice also have certain brain features, somewhat similar to humans and song-learning birds, which they may use to change their sounds, according to a new study.
"We are claiming that mice have limited versions of the brain and behavior traits for vocal learning that are found in humans for learning speech and in birds for learning song," said Duke neurobiologist Erich Jarvis, who ...
PHOENIX, Ariz. — Oct. 10, 2012 — Whole genome sequencing — spelling out all 3 billion letters in the human genome — "is an obvious and powerful method for advancing our understanding of pancreatic cancer," according to a new study from TGen, Mayo Clinic and Scottsdale Healthcare published today.
The Translational Genomics Research Institute (TGen) demonstrated that the use of WGS "represents a compelling solution to obtaining detailed molecular information on tumor biopsies in order to provide guidance for therapeutic selection," concluded the study published by the journal ...
PORTLAND, Ore. – Physician-scientists at Oregon Health & Science University Doernbecher Children's Hospital have demonstrated for the first time that banked human neural stem cells — HuCNS-SCs, a proprietary product of StemCells Inc. — can survive and make functional myelin in mice with severe symptoms of myelin loss. Myelin is the critical fatty insulation, or sheath, surrounding new nerve fibers and is essential for normal brain function.
This is a very important finding in terms of advancing stem cell therapy to patients, the investigators report, because in most ...
Writing in Nature, Nobel Prize-winner Professor Kostya Novoselov and an international team of authors has produced a 'Graphene Roadmap' which for the first time sets out what the world's thinnest, strongest and most conductive material can truly achieve.
The paper details how graphene, isolated for the first time at The University of Manchester by Professor Novoselov and colleague Professor Andre Geim in 2004, has the potential to revolutionise diverse applications from smartphones and ultrafast broadband to anticancer drugs and computer chips.
One key area is touchscreen ...