(Press-News.org) Three years ago University of Tennessee, Knoxville, researchers helped to discover water on the surface of the moon. Now, they are piecing together the origin of that water: solar wind.
A new study confirms solar wind as a source for water embedded in the lunar surface.
Solar wind is the continuous flow of charged particles from the sun. Scientists have speculated it to be responsible for water on the surface of the moon.
Last year Larry Taylor, distinguished professor in the Department of Earth and Planetary Sciences, confirmed comets as the source for water inside the moon. This year, Yang Liu, research assistant professor, and Taylor have confirmed solar wind as the source for water on the outside—by depositing positively charged hydrogen atoms, or protons, onto its surface, allowing it to combine with the moon's oxygen to create water.
"When those protons hit the lunar surface with enough force, they break apart oxygen bonds in soil materials to join together and form water," said Liu. "This does not happen on Earth because our atmosphere and magnetic field protect us from being bombarded by these protons, but the moon lacks this protection."
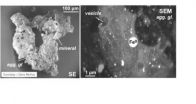
The researchers used lunar samples from three Apollo missions, including one brought back by Neil Armstrong, analyzing something called an agglutinate. An agglutinate, which resembles "dirty Swiss cheese," is a unique product of space weathering in the lunar regolith, the crushed materials on the moon's surface. The agglutinate was chosen because it consisted of products suspected to contain hydrogen. The researchers used infrared spectroscopy to confirm the presence of hydroxyl (OH). Then they used secondary ion mass spectrometry to obtain the amount of hydroxyl and the origins of the hydrogen.
The researchers discovered that most of the water in the agglutinates came from solar wind. Confirming the solar-wind- induced hydroxyl emphasizes the possibility of finding water on the surface of other similar airless bodies.
"This means water likely exists on Mercury and on the asteroids such as Vesta or Eros further within our solar system," said Liu. "These planetary bodies have very different environments, but all have potential to produce water. The finding also implies solar-wind contributes to water ice in lunar poles."
The research also identifies the largest reservoir for water on the lunar surface since regolith, and thus the corresponding hydroxyl is very widespread. This gives the moon the potential to serve as a habitat and gas station in the sky.
"The hydroxyl in such a volumetrically large reservoir is a valuable resource," said Taylor. "With the cost of $25,000 for taking one pint of water to the moon, water has the potential to be used as rocket fuel as liquid hydrogen or oxygen."
INFORMATION:
Liu and Taylor collaborated with researchers from the California Institute of Technology and the University of Michigan on this study.
University of Tennessee study confirms solar wind as source for moon water
A new study confirms solar wind as a source for water embedded in the lunar surface
2012-10-15
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
LA BioMed's Dr. Virender Rehan studies maternal nicotine's effects on unborn children and asthma
2012-10-15
LOS ANGELES (Oct. 15, 2012) – Currently, there are approximately 25 million people in the United States who suffer from the lifelong effects of asthma – wheezing, breathlessness, tightness in the chest, coughing – and the numbers are rising each year. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), the number of people in the United States diagnosed with asthma grew by 4.3 million from 2001 to 2009. Approximately 1 in 10 children and 1 in 12 adults suffer from asthma; the numbers are even higher among racial/ethnic groups, with 1 in 6 children in the ...
Urgent need for tuberculosis vaccines; experts report progress, obstacles in growing drug resistance
2012-10-15
Contact: Coimbra Sirica
csirica@burnesscommunications.com
44-743-538-4915
Burness Communications
Annmarie Leadman
aleadman@aeras.org
301-332-8252
Aeras
Urgent need for tuberculosis vaccines; experts report progress, obstacles in growing drug resistance
As World Health Organization prepares to release report on global TB incidence, researchers say UK at forefront of efforts to develop critical medical tools
London (October 15, 2012) – Drawing on recent findings of a significant rise in cases of drug-resistant tuberculosis in the UK and globally, top TB researchers ...
Cell growth protein Ras forms a 'pair' on the cell membrane
2012-10-15
Bochum biophysicists in collaboration with the MPI Dortmund have for the first time measured the orientation of the Ras protein bound to the cell membrane. The RUB team combined the use of three biophysical methods - infrared spectroscopy, computer simulations and fluorescence measurements - and came to the surprising conclusion that two Ras molecules form a pair to take an upright position on the membrane. It was previously assumed, based on computer simulations, that the protein is located horizontally on the membrane as single molecule. Ras is the central "switch" for ...
Traditional courtyards: an example of eco-efficiency for architects
2012-10-15
Researchers from the University of Seville (Spain) have used mathematical tools to assess what has been known for centuries: the temperature inside the typical Mediterranean courtyard is cooler than that of the street. Though seemingly common sense, understanding such information in detail helps to save energy and money, which is the objective of eco-efficient buildings.
The inhabitants of Mediterranean regions have known for centuries that during the summer their courtyards are cooler than the street. "Why then put air conditioning extractor units on rooftops or outer ...
Exposure to 'Prestige' fuel causes short-term damage to rat DNA
2012-10-15
An experiment carried out on rodents exposed to fuel similar to that of the Prestige tanker oil spill – which took place nearly a decade ago – shows that inhalation of the fuel causes damage to genetic material. According to the study, led by the University of A Coruña, the results could be used in relation to people who carry out the industrial cleaning of coasts.
On 19 November, it will be ten years since the sinking of the Prestige, which caused one of Spain's largest ecological disasters. The oil spill reached the coasts of Galicia and the rest of the Cantabrian coast, ...
Replicating risk genes in bipolar disorder
2012-10-15
Philadelphia, PA, October 15, 2012 – One of the biggest challenges in psychiatric genetics has been to replicate findings across large studies.
Scientists at King's College London, Institute of Psychiatry have now performed one of the largest ever genetic replication studies of bipolar affective disorder, with 28,000 subjects recruited from 36 different research centers. Their findings provide compelling evidence that the chromosome 3p21.1 locus contains a common genetic risk for bipolar disorder, the PBRM1 gene.
The locus at 3p21.1 has also been previously associated ...
Soccer scores a health hat trick for hypertensive men
2012-10-15
Playing soccer (football) could be the best way for people with high blood pressure, known as hypertension, to improve their fitness, normalise their blood pressure and reduce their risk of stroke. Research from Universities of Exeter and Copenhagen, and Gentofte University Hospital in Denmark, published today (Monday 15 October 2012) in the journal Medicine and Science in Sports and Exercise, suggests that soccer training prevents cardiovascular disease in middle-aged men with hypertension and is more effective than healthy lifestyle advice currently prescribed by GPs.
After ...
Programs for treating addiction in doctors pose ethical issues
2012-10-15
Philadelphia, Pa. (October 15, 2012) – State physician health programs (PHPs) play a key role in helping doctors with substance abuse problems. But the current PHP system is inconsistent and prone to potential conflicts of interest and ethical issues, according to a review available as publish ahead of print content from the December 2012 issue of Journal of Addiction Medicine, the official journal of the American Society of Addiction Medicine. The journal is published by Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, a part ofWolters Kluwer Health.
In the article, Drs J. Wesley Boyd ...
'Treasure trove' of film records unlocks history of British Cinema
2012-10-15
A film historian at Queen Mary, University of London has been uncovering the secret past of British cinema in a private collection of production records for thousands of films, including such iconic titles as Dr No, The African Queen, and Zulu.
The unique production archive is owned by Film Finances Ltd, underwriters of many major British films made since the 1950s. The company has kept complete documentation for
every production it has guaranteed, including letters, telegrams, shooting schedules, scripts, storyboards and even doctors' certificates.
In 2009, Film Finances ...
New techniques stretch carbon nanotubes, make stronger composites
2012-10-15
Researchers from North Carolina State University have developed new techniques for stretching carbon nanotubes (CNT) and using them to create carbon composites that can be used as stronger, lighter materials in everything from airplanes to bicycles.
By stretching the CNT material before incorporating it into a composite for use in finished products, the researchers straighten the CNTs in the material, which significantly improves its tensile strength – and enhances the stiffness of the composite material and its electrical and thermal conductivity.
State-of-the-art ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Evaluating the effects of hypnotics for insomnia in obstructive sleep apnea
A new reagent makes living brains transparent for deeper, non-invasive imaging
Smaller insects more likely to escape fish mouths
Failed experiment by Cambridge scientists leads to surprise drug development breakthrough
Salad packs a healthy punch to meet a growing Vitamin B12 need
Capsule technology opens new window into individual cells
We are not alone: Our Sun escaped together with stellar “twins” from galaxy center
Scientists find new way of measuring activity of cell editors that fuel cancer
Teens using AI meal plans could be eating too few calories — equivalent to skipping a meal
Inconsistent labeling and high doses found in delta-8 THC products: JSAD study
Bringing diabetes treatment into focus
Iowa-led research team names, describes new crocodile that hunted iconic Lucy’s species
One-third of Americans making financial trade-offs to pay for healthcare
Researchers clarify how ketogenic diets treat epilepsy, guiding future therapy development
PsyMetRiC – a new tool to predict physical health risks in young people with psychosis
Island birds reveal surprising link between immunity and gut bacteria
Research presented at international urology conference in London shows how far prostate cancer screening has come
Further evidence of developmental risks linked to epilepsy drugs in pregnancy
Cosmetic procedures need tighter regulation to reduce harm, argue experts
How chaos theory could turn every NHS scan into its own fortress
Vaccine gaps rooted in structural forces, not just personal choices: SFU study
Safer blood clot treatment with apixaban than with rivaroxaban, according to large venous thrombosis trial
Turning herbal waste into a powerful tool for cleaning heavy metal pollution
Immune ‘peacekeepers’ teach the body which foods are safe to eat
AAN issues guidance on the use of wearable devices
In former college athletes, more concussions associated with worse brain health
Racial/ethnic disparities among people fatally shot by U.S. police vary across state lines
US gender differences in poverty rates may be associated with the varying burden of childcare
3D-printed robotic rattlesnake triggers an avoidance response in zoo animals, especially species which share their distribution with rattlers in nature
Simple ‘cocktail’ of amino acids dramatically boosts power of mRNA therapies and CRISPR gene editing
[Press-News.org] University of Tennessee study confirms solar wind as source for moon waterA new study confirms solar wind as a source for water embedded in the lunar surface