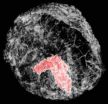
(Press-News.org) Like cleaning the lenses of a foggy pair of glasses, scientists are now able to use a technique developed by UCLA researchers and their European colleagues to produce three-dimensional images of breast tissue that are two to three times sharper than those made using current CT scanners at hospitals. The technique also uses a lower dose of X-ray radiation than a mammogram.
These higher-quality images could allow breast tumors to be detected earlier and with much greater accuracy. One in eight women in the United States will be diagnosed with breast cancer during her lifetime.
The research is published the week of Oct. 22 in the early edition of the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
The most common breast cancer screening method used today is called dual-view digital mammography, but it isn't always successful in identifying tumors, said Jianwei (John) Miao, a UCLA professor of physics and astronomy and researcher with the California NanoSystems Institute at UCLA.
"While commonly used, the limitation is that it provides only two images of the breast tissue, which can explain why 10 to 20 percent of breast tumors are not detectable on mammograms," Miao said. "A three-dimensional view of the breast can be generated by a CT scan, but this is not frequently used clinically, as it requires a larger dose of radiation than a mammogram. It is very important to keep the dose low to prevent damage to this sensitive tissue during screening."
Recognizing these limitations, the scientists went in a new direction. In collaboration with the European Synchrotron Radiation Facility in France and Germany's Ludwig Maximilians University, Miao's international colleagues used a special detection method known as phase contrast tomography to X-ray a human breast from multiple angles.
They then applied equally sloped tomography, or EST — a breakthrough computing algorithm developed by Miao's UCLA team that enables high-quality image-reconstruction — to 512 of these images to produce 3-D images of the breast at a higher resolution than ever before. The process required less radiation than a mammogram.
In a blind evaluation, five independent radiologists from Ludwig Maximilians University ranked these images as having a higher sharpness, contrast and overall image quality than 3-D images of breast tissue created using other standard methods.
"Even small details of the breast tumor can be seen using this technique," said Maximilian Reiser, director of the radiology department at Ludwig Maximilians University, who contributed his medical expertise to the research.
The technology commonly used today for mammograms or imaging a patient's bones measures the difference in an X-ray's intensity before and after it passes through the body. But the phase contrast X-ray tomography used in this study measures the difference in the way an X-ray oscillates through normal tissue rather than through slightly denser tissue like a tumor or bone. While a very small breast tumor might not absorb many X-rays, the way it changes the oscillation of an X-ray can be quite large, Miao said. Phase contrast tomography captures this difference in oscillation, and each image made using this technique contributes to the overall 3-D picture.
The computational algorithm EST developed by Miao's UCLA team is a primary driver of this advance. Three-dimensional reconstructions, like the ones created in this research, are produced using sophisticated software and a powerful computer to combine many images into one 3-D image, much like various slices of an orange can be combined to form the whole. By rethinking the mathematic equations of the software in use today, Miao's group developed a more powerful algorithm that requires fewer "slices" to get a clearer overall 3-D picture.
"The technology used in mammogram screenings has been around for more than 100 years," said Paola Coan, a professor of X-ray imaging at Ludwig Maximilians University. "We want to see the difference between healthy tissue and the cancer using X-rays, and that difference can be very difficult to see, particularly in the breast, using standard techniques. The idea we used here was to combine phase contrast tomography with EST, and this combination is what gave us much higher quality 3-D images than ever before."
While this new technology is like a key in a lock, the door will only swing open — bringing high-resolution 3-D imaging from the synchrotron facility to the clinic — with further technological advances, said Alberto Bravin, managing physicist of the biomedical research laboratory at the European Synchrotron Radiation Facility. He added that the technology is still in the research phase and will not be available to patients for some time.
"A high-quality X-ray source is an absolute requirement for this technique," Bravin said. "While we can demonstrate the power of our technology, the X-ray source must come from a small enough device for it to become commonly used for breast cancer screening. Many research groups are actively working to develop this smaller X-ray source. Once this hurdle is cleared, our research is poised to make a big impact on society."
INFORMATION:
These results represent the collaborative efforts of senior authors Miao, Bravin and Coan. Significant contributions were provided by co-first authors Yunzhe Zhao, a recent UCLA doctoral graduate in Miao's laboratory, and Emmanuel Brun, a scientist working with Bravin and Coan. Other co-authors included Zhifeng Huang of UCLA and Aniko Sztrókay, Paul Claude Diemoz, Susanne Liebhardt, Alberto Mittone and Sergei Gasilov of Ludwig Maximilians University.
The research was funded by UC Discovery/Tomosoft Technologies; the National Institute of General Medical Sciences, a division of the National Institutes of Health; and the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft–Cluster of Excellence Munich–Centre for Advanced Photonics.
UCLA is California's largest university, with an enrollment of more than 40,000 undergraduate and graduate students. The UCLA College of Letters and Science and the university's 11 professional schools feature renowned faculty and offer 337 degree programs and majors. UCLA is a national and international leader in the breadth and quality of its academic, research, health care, cultural, continuing education and athletic programs. Six alumni and six faculty have been awarded the Nobel Prize.
For more news, visit the UCLA Newsroom and follow us on Twitter.
Breakthrough technique images breast tumors in 3-D with great clarity, reduced radiation
2012-10-23
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
ONR to dial up faster data for the Marines
2012-10-23
ARLINGTON, Va. - Office of Naval Research (ONR) officials announced a new program Oct. 22 to optimize tactical handheld technology for quick decision-making in the field.
The Exchange of Actionable Information at the Tactical Edge (EAITE) program, designed to sift through data from multiple sources for faster analysis, is among more than a dozen Future Naval Capability (FNC) programs kicking off in fiscal year 2014.
ONR Director of Transition Dr. Thomas Killion explained the need for the program—and how it benefits both the U.S. Navy and industry—during an FNC overview ...
The Generation X report
2012-10-23
ANN ARBOR—Less than half of Generation X adults can identify our home in the universe, a spiral galaxy, according to a University of Michigan report.
"Knowing your cosmic address is not a necessary job skill, but it is an important part of human knowledge about our universe and—to some extent—about ourselves," said Jon D. Miller, author of "The Generation X Report" and director of the Longitudinal Study of American Youth at the U-M Institute for Social Research.
The study, funded by the National Science Foundation since 1986, now includes responses from approximately ...
Combination of Gulf oil and dispersant spell potential trouble for gut microbes
2012-10-23
A study to be published in mBio®, the online open-access journal of the American Society for Microbiology, on Tuesday, October 23, examined whether crude oil from the 2010 Deepwater Horizon oil spill, the dispersant used on it, or a combination of the two might affect the microbes of the human digestive tract. The researchers found that although high concentrations of oil combined with dispersant are detrimental to these helpful microbial communities, the low to undetectable concentrations typically found in Gulf shellfish had no discernable effect.
"The oil and the ...
Highly efficient production of advanced biofuel by metabolically engineered microorganism
2012-10-23
Daejeon, Republic of Korea, October 23, 2012—Fuels including gasoline, diesel, and jet fuel are derived from fossil oil thorough the petroleum refinery processes. Increased concerns over environmental problems and limited fossil resources drive scientists and researchers to turn their attention to developing fossil-free, bio-based processes for the production of fuels from renewable non-food biomass. Utilizing systems metabolic engineering, a Korean research team at the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) has succeeded in demonstrating an optimized ...
Experts call for wildlife conservation network
2012-10-23
BLOOMINGTON, Ind. -- It's time to establish a national network for wildlife conservation, bringing together state, federal and private initiatives to coordinate planning and work toward common goals, 11 prominent wildlife biologists and policy experts write in the journal BioScience.
Vicky Meretsky of Indiana University and her co-authors say established state wildlife programs provide "strong building blocks" for such a network. But they make a forceful argument that national cooperation and coordination are needed to protect at-risk wildlife species and habitat and ...
Scientists build 'mechanically active' DNA material
2012-10-23
Artificial muscles and self-propelled goo may be the stuff of Hollywood fiction, but for UC Santa Barbara scientists Omar Saleh and Deborah Fygenson, the reality of it is not that far away. By blending their areas of expertise, the pair have created a dynamic gel made of DNA that mechanically responds to stimuli in much the same way that cells do. The results of their research were published online in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
"This is a whole new kind of responsive gel, or what some might call a 'smart' material," said Saleh, associate professor ...
Your Credit Report May Be More Important Than Your Credit Score
2012-10-23
When people think about their credit, they often think only of the number that corresponds to their credit score. However, a credit score is simply a bare-bone representation of the information contained in another, potentially more important part of a person's credit profile: his or her credit report.
Context Matters
A credit report can be even more important than a person's credit score because it provides context for the credit score and shows how an individual got to a particular point in their credit history, rather than just a snapshot of where the individual ...
How to Avoid Tax Audits When Running a Small Business
2012-10-23
How to Avoid Tax Audits When Running a Small Business
Contrary to popular misconception, small businesses are frequently targeted by the Internal Revenue Service for tax audits. As anyone who has ever been through a tax audit knows, the experience can be a major ordeal -- even for those who have done nothing wrong. Therefore, small-business owners should take the time to learn about the steps they can take to help protect themselves from the risk of being audited by the IRS.
Keep Business and Personal Accounts Separate
For any small business owner, particularly ...
California DUI Crackdown Nets 95 Arrests in Monterey County
2012-10-23
California DUI Crackdown Nets 95 Arrests in Monterey County
California Highway Patrol officers made 95 arrests in Monterey County recently as part of a recent crackdown on driving under the influence. The 18-day initiative, which ended Labor Day at midnight, was part of a statewide effort to cut down on intoxicated driving during the late summer weeks. The next statewide DUI enforcement effort is scheduled to run during the 2012 winter holiday season from mid-December through New Year's Eve. As California law enforcement increases its focus on DUI enforcement, it is ...
What Florida Parents Should Know About Child Custody and Parenting Plans
2012-10-23
What Florida Parents Should Know About Child Custody and Parenting Plans
In many divorces, one of the most difficult issues to resolve is which parent gets custody of the children and how often the non-custodial parent will get to see the children. Each parent thinks that he or she knows what is best for the children, and the parents do not always agree on what that is. In some cases, the court has to make the final decision when parents cannot reach agreements. Parents in Florida should be aware of how the court makes custody determinations and what goes into a Florida ...