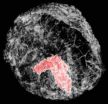
(Press-News.org) New Rochelle, NY, October 22, 2012—New, advanced techniques are needed that can mimic the normal blood supply that feeds natural bone to improve the viability and success of restorative procedures to replace damaged or diseased bone tissue using engineered constructs. A comprehensive review article describing the most promising strategies for vascularization of bone tissue substitutes is published in Tissue Engineering, Part B: Reviews, a peer-reviewed journal from Mary Ann Liebert, Inc. The article is available free online on the Tissue Engineering website.
The lack of an adequate blood supply to engineered bone implants has been a major limiting factor in the ability of these large tissue engineered implants to survive and integrate in the body. Many new strategies for stimulating the growth of new blood vessels and the formation of a vascular network to carry nutrients and oxygen and aid in healing are in development, as presented by Lonnissa H. Nguyen, PhD, and coauthors from Massachusetts Institute of Technology (Cambridge); Brigham and Women's Hospital, Harvard University, and Harvard Medical School (MA); Ecole Polytechnique (Palaiseau, France); Chonnam National University (Gwangju, South Korea); Stanford University (CA); Tohoku University (Sendai, Japan). They describe the different methods and their limitations in the article "Vascularized Bone Tissue Engineering: Approaches for Potential Improvement."
"There is a critical need to develop innovative techniques for tissue vascularization, and the work by Nguyen et al. demonstrates both past successes in the field and future avenues for investigation," says Reviews Co-Editor-in-Chief John P. Fisher, PhD, Professor and Associate Chair, Fischell Department of Bioengineering, University of Maryland, College Park, MD.
###
About the Journal
Tissue Engineering is an authoritative peer-reviewed journal published monthly in print and online in three parts: Part A--the flagship journal; Part B—Reviews; and Part C—Methods. Led by Co-Editors-In-Chief Antonios Mikos, PhD, Louis Calder Professor at Rice University, Houston, TX, and Peter C. Johnson, MD, Vice President, Research and Development, Avery Dennison Medical Solutions of Chicago, IL and President and CEO, Scintellix, LLC, Raleigh, NC, the Journal brings together scientific and medical experts in the fields of biomedical engineering, material science, molecular and cellular biology, and genetic engineering. Tissue Engineering is the official journal of the Tissue Engineering & Regenerative Medicine International Society (TERMIS). Complete tables of content and a sample issue may be viewed online on the Tissue Engineering website.
About the Publisher
Mary Ann Liebert, Inc. is a privately held, fully integrated media company known for establishing authoritative peer-reviewed journals in many promising areas of science and biomedical research, including Stem Cells and Development, Human Gene Therapy and HGT Methods, and Advances in Wound Care. Its biotechnology trade magazine, Genetic Engineering & Biotechnology News (GEN), was the first in its field and is today the industry's most widely read publication worldwide. A complete list of the firm's 70 journals, books, and newsmagazines is available on the Mary Ann Liebert Inc. website.
Mary Ann Liebert, Inc. 140 Huguenot St., New Rochelle, NY 10801-5215 www.liebertpub.com
Phone: (914) 740-2100 (800) M-LIEBERT Fax: (914) 740-2101
Will new methods that increase blood flow to bone implants improve viability of engineered bone tissue?
2012-10-23
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Breakthrough technique images breast tumors in 3-D with great clarity, reduced radiation
2012-10-23
Like cleaning the lenses of a foggy pair of glasses, scientists are now able to use a technique developed by UCLA researchers and their European colleagues to produce three-dimensional images of breast tissue that are two to three times sharper than those made using current CT scanners at hospitals. The technique also uses a lower dose of X-ray radiation than a mammogram.
These higher-quality images could allow breast tumors to be detected earlier and with much greater accuracy. One in eight women in the United States will be diagnosed with breast cancer during her ...
ONR to dial up faster data for the Marines
2012-10-23
ARLINGTON, Va. - Office of Naval Research (ONR) officials announced a new program Oct. 22 to optimize tactical handheld technology for quick decision-making in the field.
The Exchange of Actionable Information at the Tactical Edge (EAITE) program, designed to sift through data from multiple sources for faster analysis, is among more than a dozen Future Naval Capability (FNC) programs kicking off in fiscal year 2014.
ONR Director of Transition Dr. Thomas Killion explained the need for the program—and how it benefits both the U.S. Navy and industry—during an FNC overview ...
The Generation X report
2012-10-23
ANN ARBOR—Less than half of Generation X adults can identify our home in the universe, a spiral galaxy, according to a University of Michigan report.
"Knowing your cosmic address is not a necessary job skill, but it is an important part of human knowledge about our universe and—to some extent—about ourselves," said Jon D. Miller, author of "The Generation X Report" and director of the Longitudinal Study of American Youth at the U-M Institute for Social Research.
The study, funded by the National Science Foundation since 1986, now includes responses from approximately ...
Combination of Gulf oil and dispersant spell potential trouble for gut microbes
2012-10-23
A study to be published in mBio®, the online open-access journal of the American Society for Microbiology, on Tuesday, October 23, examined whether crude oil from the 2010 Deepwater Horizon oil spill, the dispersant used on it, or a combination of the two might affect the microbes of the human digestive tract. The researchers found that although high concentrations of oil combined with dispersant are detrimental to these helpful microbial communities, the low to undetectable concentrations typically found in Gulf shellfish had no discernable effect.
"The oil and the ...
Highly efficient production of advanced biofuel by metabolically engineered microorganism
2012-10-23
Daejeon, Republic of Korea, October 23, 2012—Fuels including gasoline, diesel, and jet fuel are derived from fossil oil thorough the petroleum refinery processes. Increased concerns over environmental problems and limited fossil resources drive scientists and researchers to turn their attention to developing fossil-free, bio-based processes for the production of fuels from renewable non-food biomass. Utilizing systems metabolic engineering, a Korean research team at the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) has succeeded in demonstrating an optimized ...
Experts call for wildlife conservation network
2012-10-23
BLOOMINGTON, Ind. -- It's time to establish a national network for wildlife conservation, bringing together state, federal and private initiatives to coordinate planning and work toward common goals, 11 prominent wildlife biologists and policy experts write in the journal BioScience.
Vicky Meretsky of Indiana University and her co-authors say established state wildlife programs provide "strong building blocks" for such a network. But they make a forceful argument that national cooperation and coordination are needed to protect at-risk wildlife species and habitat and ...
Scientists build 'mechanically active' DNA material
2012-10-23
Artificial muscles and self-propelled goo may be the stuff of Hollywood fiction, but for UC Santa Barbara scientists Omar Saleh and Deborah Fygenson, the reality of it is not that far away. By blending their areas of expertise, the pair have created a dynamic gel made of DNA that mechanically responds to stimuli in much the same way that cells do. The results of their research were published online in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
"This is a whole new kind of responsive gel, or what some might call a 'smart' material," said Saleh, associate professor ...
Your Credit Report May Be More Important Than Your Credit Score
2012-10-23
When people think about their credit, they often think only of the number that corresponds to their credit score. However, a credit score is simply a bare-bone representation of the information contained in another, potentially more important part of a person's credit profile: his or her credit report.
Context Matters
A credit report can be even more important than a person's credit score because it provides context for the credit score and shows how an individual got to a particular point in their credit history, rather than just a snapshot of where the individual ...
How to Avoid Tax Audits When Running a Small Business
2012-10-23
How to Avoid Tax Audits When Running a Small Business
Contrary to popular misconception, small businesses are frequently targeted by the Internal Revenue Service for tax audits. As anyone who has ever been through a tax audit knows, the experience can be a major ordeal -- even for those who have done nothing wrong. Therefore, small-business owners should take the time to learn about the steps they can take to help protect themselves from the risk of being audited by the IRS.
Keep Business and Personal Accounts Separate
For any small business owner, particularly ...
California DUI Crackdown Nets 95 Arrests in Monterey County
2012-10-23
California DUI Crackdown Nets 95 Arrests in Monterey County
California Highway Patrol officers made 95 arrests in Monterey County recently as part of a recent crackdown on driving under the influence. The 18-day initiative, which ended Labor Day at midnight, was part of a statewide effort to cut down on intoxicated driving during the late summer weeks. The next statewide DUI enforcement effort is scheduled to run during the 2012 winter holiday season from mid-December through New Year's Eve. As California law enforcement increases its focus on DUI enforcement, it is ...