(Press-News.org) Sauder School of Business researchers at the University of British Columbia have found that a person's date of birth can affect their climb up the corporate ladder.
The Sauder study shows that only 6.13 per cent of an S&P 500 CEO sample was born in June and only 5.87 per cent of the sample was born in July. By comparison, people born in March and April represented 12.53 per cent and 10.67 per cent of the sample of CEOs.
"Our findings indicate that summer babies underperform in the ranks of CEOs as a result of the 'birth-date effect,' a phenomenon resulting from the way children are grouped by age in school," says Sauder Finance Prof. Maurice Levi, co-author of the study to appear in the December issue of the journal Economics Letters.
In the United States, cut-off dates for school admission fall between September and January. The researchers determined that those CEOs in the sample born between June and July were the youngest in their class during school, and those in March and April were the oldest. This takes into account children born in months close to the cut offs who were held back or accelerated.
"Older children within the same grade tend to do better than the youngest, who are less intellectually developed," explains Levi. "Early success is often rewarded with leadership roles and enriched learning opportunities, leading to future advantages that are magnified throughout life."
Levi and his co-authors, former Sauder PhD students Qianqian Du and Huasheng Gao, investigated the birth-date effect in a sample of 375 CEOs from S&P 500 companies between 1992 and 2009.
"Our study adds to the growing evidence that the way our education system groups students by age impacts their lifelong success," says Prof. Levi. "We could be excluding some of the business world's best talent simply by enrolling them in school too early."
### END
Summer babies less likely to be CEOs: UBC research
2012-10-24
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Blood chromosome differences are linked to pancreatic cancer
2012-10-24
MADISON – A new study shows that a blood marker is linked to pancreatic cancer, according to a study published today by scientists at the University of Wisconsin Carbone Cancer Center and Mayo Clinic.
First author Dr. Halcyon Skinner, assistant professor of population health sciences at the University of Wisconsin School of Medicine and Public Health, says the study is the first time pancreatic cancer risk has been linked to differences in telomeres' length in blood cells.
"This suggests a new avenue to identify those with pancreatic cancer or those at risk of developing ...
Genetic patterns of deep-sea coral provide insights into evolution of marine life
2012-10-24
The ability of deep-sea corals to harbor a broad array of marine life, including commercially important fish species, make these habitat-forming organisms of immediate interest to conservationists, managers, and scientists. Understanding and protecting corals requires knowledge of the historical processes that have shaped their biodiversity and biogeography.
While little is known about these processes, new research described in the journal Molecular Ecology helps elucidate the historical patterns of deep-sea coral migration and gene flow, coincident with oceanic circulation ...
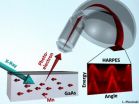
New finding could pave way to faster, smaller electronics
2012-10-24
University of California, Davis, researchers for the first time have looked inside gallium manganese arsenide, a type of material known as a "dilute magnetic semiconductor" that could open up an entirely new class of faster, smaller devices based on an emerging field known as "spintronics."
Materials of this type might be used to read and write digital information not by using the electron's charge, as is the case with today's electronic devices, but by using its "spin."
Understanding the magnetic behavior of atoms is key to designing spintronics materials that could ...
New paper examines shifting gears in the circadian clock of the heart
2012-10-24
A new study conducted by a team of scientists led by Giles Duffield, assistant professor of biological sciences and a member of the Eck Institute for Global Health at the University of Notre Dame focuses on the circadian clock of the heart, and used cultured heart tissue. The results of the new study have implications for cardiovascular health, including daily changes in responses to stress and the effect of long-term rotational shift work.
Previous studies by a research group at the University of Geneva demonstrated a role for glucocorticoids in shifting the biological ...
Droplet response to electric voltage in solids exposed
2012-10-24
DURHAM, N.C. – For the first time, scientists have observed how droplets within solids deform and burst under high electric voltages.
This is important, the Duke University engineers who made the observations said, because it explains a major reason why such materials as insulation for electrical power lines eventually fail and cause blackouts. This observation not only helps scientists develop better insulation materials, but could also lead to such positive developments as "tunable" lenses for eyes.
As the voltage increases, water droplets, or air bubbles, within ...
Analysis of dinosaur bone cells confirms ancient protein preservation
2012-10-24
A team of researchers from North Carolina State University and the Palo Alto Research Center (PARC) has found more evidence for the preservation of ancient dinosaur proteins, including reactivity to antibodies that target specific proteins normally found in bone cells of vertebrates. These results further rule out sample contamination, and help solidify the case for preservation of cells – and possibly DNA – in ancient remains.
Dr. Mary Schweitzer, professor of marine, earth and atmospheric sciences with a joint appointment at the North Carolina Museum of Natural Sciences, ...
NJIT math professor calls Detroit Tigers a favorite to win World Series
2012-10-24
Since the Major League Baseball Division Series and League Championship Series have determined which teams will compete in the World Series, NJIT Math Professor Bruce Bukiet has again analyzed the probability of each team taking the title.
"The Detroit Tigers have a solid advantage over the San Francisco Giants. The Tigers, who surprisingly swept the New York Yankees in four straight games in the American League Championship Series to reach the World Series, have a 58 percent chance of beating the Giants in the best of seven series," he said.
At the season's start, ...
Medical recommendations should go beyond race, scholar says
2012-10-24
EAST LANSING, Mich. — Medical organizations that make race-based recommendations are misleading some patients about health risks while reinforcing harmful notions about race, argues a Michigan State University professor in a new paper published in the journal Preventive Medicine.
While some racial groups are on average more prone to certain diseases than the general population, they contain "islands" of lower risk that medical professionals should acknowledge, said Sean Valles, assistant professor in MSU's Lyman Briggs College and the Department of Philosophy.
For instance, ...
New Jersey's teen driver decals linked with fewer crashes
2012-10-24
A new study from The Children's Hospital of Philadelphia (CHOP) provides initial evidence that New Jersey's Graduated Driver Licensing (GDL) decal requirement lowers crash rates among intermediate (i.e., probationary) teen drivers and supports the ability of police to enforce GDL provisions. The study, which linked New Jersey's licensing and crash record databases to measure effects of the requirement, was published today in the American Journal of Preventive Medicine. Crash involvement of an estimated 1,624 intermediate drivers was prevented in the first year after the ...
Leaner Navy looking at future technology, fleet size and sequestration
2012-10-24
ARLINGTON, Va.—Adm. Mark Ferguson, vice chief of naval operations, headlined the opening of the ONR (Office of Naval Research) Naval S&T (science and technology) Partnership Conference and ASNE Expo Oct. 22, 2012, and highlighted the importance of innovative S&T programs being developed by the Navy. He also offered a revealing look at the potential future for the Navy if sequestration, or automatic defense cuts, goes into effect in January.
Speaking to a capacity crowd as keynote speaker, Ferguson said the Navy is already working hard to do more across the globe—with ...