(Press-News.org) Copenhagen, Denmark – Data publishers should have the option of submitting their biodiversity datasets for peer review, according to a discussion paper commissioned by the Global Biodiversity Information Facility (GBIF).
The proposal is among a set of recommendations made by Mark Costello and co-authors in the paper Quality assurance and Intellectual Property Rights in advancing biodiversity data publication, freely available for download through the GBIF Online Resource Centre.
The paper argues that concerns over data quality impede the use of large biodiversity databases by researchers, and subsequent benefits to society. Peer review is proposed as the highest standard of a scale of quality assurance that could be attached to datasets published through online networks such as GBIF.
"Peer review is the standard mechanism used to distinguish the quality of scientific publications. Here, we argue that the next step in data publication is to include the option of peer review," the authors write.
"Data publication can be similar to the conventional publication of articles in journals that includes online submission, quality checks, peer-review, and editorial decisions.
"This quality-assurance process will at least assess, and potentially could improve the accuracy of the data, which in turn reduces the need for users to 'clean' the data, and thus increases data use while the authors and/or editors get due credit for a peer-reviewed (data) publication."
The proposal complements existing procedures, which enable authors of metadata documents describing datasets published through GBIF, to submit 'data papers' to online journals). Experience has found that referees of these papers in practice review the data as well as the metadata, thus adding a layer of quality control.
The paper also recommends adoption of community-wide standards related to data citation, accessibility, metadata, and quality control to enable easier integration of data across datasets.
### For further information, contact:
Vishwas Chavan
GBIF Secretariat
vchavan@gbif.org
Notes to editors:
The Global Biodiversity Information Facility (GBIF) was established by governments in 2001 to encourage free and open access to biodiversity data, via the Internet. Through a global network of 57 countries and 47 organizations, GBIF promotes and facilitates the mobilization, access, discovery and use of information about the occurrence of organisms over time and across the planet.
Peer review option proposed for biodiversity data
Discussion paper suggests new quality control procedures to promote data publishing and use
2012-10-25
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Lonely older adults face more health risks
2012-10-25
Montreal, October 25, 2012 – Always look on the bright side of life. Thanks to a new study from Concordia University, this catchy refrain offers a prescription for staying healthy during one's golden years.
Research has shown that lonely older adults are at greater risk of developing health problems but a new study by Carsten Wrosch, a professor in Concordia's Department of Psychology and member of the Centre for Research in Human Development, offers hope. In a forthcoming article in Psychosomatic Medicine, Wrosch proves that older adults who approach life with a positive ...
After-effects of Saturn's super storm shine on
2012-10-25
VIDEO:
This animation shows the evolution of Saturn's 'Great Springtime Storm' in the planet's stratosphere. It is based on observations performed at mid-infrared wavelengths.
As clouds broke out in Saturn's stormy troposphere,...
Click here for more information.
The heat-seeking capabilities of the international Cassini spacecraft and two ground-based telescopes have provided the first look at the aftermath of Saturn's 'Great Springtime Storm'. Concealed from the naked ...
Gene that's usually bad news loses its punch if you live to your 90s, Mayo study finds
2012-10-25
ROCHESTER, Minn. -- A gene linked to the risk of developing Alzheimer's, heart disease and diabetes becomes less important to quality of life once people hit their 90s, a Mayo Clinic study shows. At that point, good friends and a positive attitude have a bigger impact, the researchers say. The findings are published this month in the Journal of American Medical Directors Association.
Researchers used the National Institutes of Health-supported Rochester Epidemiology Project, a database of patient records in Olmsted County, Minn., to find people ages 90 to 99 living on ...
Highlights of the 25th Congress of the European College of Neuropsychopharmacology 2012
2012-10-25
In the course of the 25th ECNP Congress leading experts and five and a half thousand psychiatrists, neurologists, neuroscience researchers and public health professionals from over 90 different countries met from 13 to 17 October 2012 in Vienna, Austria, to celebrate ECNP´s 25-year anniversary and engage in groundbreaking debate.
Against the background of the increasing burden of disorders of the brain and restrained drug development in this area, the ECNP Congress once again highlighted the key importance of neuroscience for better treatment and prevention. "Crucially, ...
US NAS and Royal Society Issue Statement on Earthquake Case in Italy
2012-10-25
The case of six Italian scientists sentenced to be jailed for failing to warn of the L'Aquila earthquake in Italy in 2009 highlights the difficult task facing scientists in dealing with risk communication and uncertainty.
We deal with risks and uncertainty all the time in our daily lives. Weather forecasts do not come with guarantees and despite the death tolls on our roads we continue to use bikes, cars, and buses. We have also long built our homes and workplaces in areas known to have a history of earthquakes, floods, or volcanic activity.
Much as society and governments ...
New bio-adhesive polymer demonstrated in JoVE
2012-10-25
A new video-article in JoVE, Journal of Visualized Experiments, details the use of a new laser-activated bio-adhesive polymer. The chitosan-based polymer, SurgiLux, was developed by scientists at the University of New South Wales. Chitosan is a polymer derived from chitin, which is found in fungal cell walls or in exoskeletons of crustaceans and insects.This molecular component allows SurgiLux to form low energy bonds between the polymer and the desired tissue when it absorbs light. The technology may soon replace traditional sutures in the clinic.
For thousands of years, ...
Omega-3 intake heightens working memory in healthy young adults
2012-10-25
PITTSBURGH—While Omega-3 essential fatty acids—found in foods like wild fish and grass-fed livestock—are necessary for human body functioning, their effects on the working memory of healthy young adults have not been studied until now.
In the first study of its kind, researchers at the University of Pittsburgh have determined that healthy young adults ages 18-25 can improve their working memory even further by increasing their Omega-3 fatty acid intake. Their findings have been published online in PLOS One.
"Before seeing this data, I would have said it was impossible ...
Study shows PFO closure may be superior to medical therapy in preventing stroke
2012-10-25
HOUSTON – (Oct. 25, 2012) – Results of a large-scale, randomized clinical trial called RESPECT revealed that patent foramen ovale (PFO) closure may be superior to medical therapy in preventing recurrent stroke, according to a presentation of findings today at the Transcatheter Cardiovascular Therapeutics (TCT) conference in Miami.
"In contrast to a previously reported randomized trial for the treatment of cryptogenic stroke, the RESPECT trial enrolled only patients with documented cryptogenic embolic strokes and excluded patients with other potential causes of stroke ...
New anti-tumor cell therapy strategies are more effective
2012-10-25
New Rochelle, NY, October 25, 2012—Targeted T-cells can seek out and destroy tumor cells that carry specific antigen markers. Two novel anti-tumor therapies that take advantage of this T-cell response are described in articles published in Human Gene Therapy, a peer-reviewed journal from Mary Ann Liebert, Inc., publishers. The articles are available free on the Human Gene Therapy website at http://www.liebertpub.com/hum.
Richard Morgan and colleagues from the National Cancer Institute (NCI), National Institutes of Health (NIH), Bethesda, MD, and Duke University Medical ...
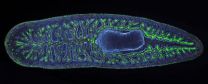
Using planarian flatworms to understand organ regeneration
2012-10-25
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. — Researchers report in the journal Developmental Cell that they have identified genes that control growth and regeneration of the intestine in the freshwater planarian Schmidtea mediterranea.
"How animals repair their internal organs after injury is not well understood," said University of Illinois cell and developmental biology professor Phillip Newmark, who led the study. "Planarian flatworms are useful models for studying this question."
After injury, planaria are able to re-grow missing body parts, including any organs that are damaged or lost, ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Governing with AI: a new AI implementation blueprint for policymakers
Recent pandemic viruses jumped to humans without prior adaptation, UC San Diego study finds
Exercise triggers memory-related brain 'ripples' in humans, researchers report
Increased risk of bullying in open-plan offices
Frequent scrolling affects perceptions of the work environment
Brain activity reveals how well we mentally size up others
Taiwanese and UK scientists identify FOXJ3 gene linked to drug-resistant focal epilepsy
Pregnancy complications impact women’s stress levels and cardiovascular risk long after delivery
Spring fatigue cannot be empirically proven
Do prostate cancer drugs interact with certain anticoagulants to increase bleeding and clotting risks?
Many patients want to talk about their faith. Neurologists often don't know how.
AI disclosure labels may do more harm than good
The ultra-high-energy neutrino may have begun its journey in blazars
Doubling of new prescriptions for ADHD medications among adults since start of COVID-19 pandemic
“Peculiar” ancient ancestor of the crocodile started life on four legs in adolescence before it began walking on two
AI can predict risk of serious heart disease from mammograms
New ultra-low-cost technique could slash the price of soft robotics
Increased connectivity in early Alzheimer’s is lowered by cancer drug in the lab
Study highlights stroke risk linked to recreational drugs, including among young users
Modeling brain aging and resilience over the lifespan reveals new individual factors
ESC launches guidelines for patients to empower women with cardiovascular disease to make informed pregnancy health decisions
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
[Press-News.org] Peer review option proposed for biodiversity dataDiscussion paper suggests new quality control procedures to promote data publishing and use