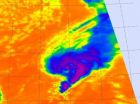
(Press-News.org) In a tropical cyclone, strong uplift of air pushes the tops of thunderstorms high into the troposphere. When that strength wanes, the cloud tops drop and become less cold. That's because the higher you go in the troposphere, the colder it gets. NASA satellite infrared data has revealed that Tropical Storm Tony's cloud top temperatures are warming and the storm is weakening.
The Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) instrument aboard NASA's Aqua satellite captured infrared imagery of Tropical Storm Tony on Oct. 24 at 12:17 p.m. EDT that showed the strongest thunderstorms east of the center of circulation, but cloud top temperatures are warming. Those thunderstorms are reaching high into the troposphere where cloud top temperatures are as cold as -63 Fahrenheit (-52 Celsius). The cloud pattern in Tony is also becoming less organized.
On Oct. 25, 2012 at 5 a.m. EDT Tropical Storm Tony had maximum sustained winds near 45 mph (75 kph). Tony was moving to the east-northeast near 23 mph (37 kph) and this general motion is expected to continue during the next couple of days. Tony's center is far from land, about 835 miles (1,345 km) southwest of the Azores Islands near 30.4 North latitude and 38.4 West longitude. Tropical storm force winds extend outward up to 105 miles (165 km) from the center.
According to the National Hurricane Center discussion of Tony, "the southwesterly winds have not substantially separated the surface circulation from the convective canopy, although a combination of the shear and cooler waters has weakened the deep convection."
The National Hurricane Center expects Tony to start losing tropical characteristics today and dissipate over the weekend of Oct. 27 and 28.
INFORMATION:
NASA sees warming cloud tops indicating Tropical Storm Tony weakening
2012-10-26
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
NASA sees power in Hurricane Sandy moving toward Bahamas
2012-10-26
NASA's Aqua satellite passed over Hurricane Sandy as it was moving over eastern Cuba early on Oct. 25. The AIRS instrument captured an infrared image of Sandy that showed a large area of very high, cold cloud tops indicating the power within the storm. Sandy is now headed toward the Bahamas and warnings and watches have already been posted for the mainland U.S.
The Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) instrument aboard NASA's Aqua satellite captured infrared imagery of Hurricane Sandy's eastern half on Oct. 25 at 0559 UTC (1:59 a.m. EDT) that showed some strong thunderstorms ...
NASA saw Tropical Storm Murjan making landfall on the Horn of Africa
2012-10-26
NASA's Aqua satellite watched from space as Somalia in the Horn of Africa experienced a landfalling tropical cyclone on Oct. 25.
On Oct. 25, NASA's Aqua satellite saw Tropical Storm Murjan begin to make landfall in eastern Somalia, just south of Cape Guardafui. Cape Guardafui is located in the northeastern Bari province and forms the geographical point of the Horn of Africa.
On Oct. 25, 2012 at 0720 UTC (3:20 a.m. EDT) the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) instrument that flies aboard NASA's Aqua satellite captured a visible image of Tropical Storm ...
USF researchers identify gene mutation linked to old age hearing loss
2012-10-26
TAMPA, Fla. (Oct. 25, 2012) - University of South Florida researchers have identified a genetic biomarker for age-related hearing loss, a major breakthrough in understanding and preventing a condition of aging that affects 30 million Americans and greatly diminishes their quality of life.
In a nine-year study that was a collaboration between USF's Global Center for Hearing & Speech Research and the National Technical Institute for the Deaf at the Rochester Institute of Technology, researchers were able to identify the first genetic biomarker for presbycusis. The genetic ...
NASA sees Tropical Storm Son-tinh moving into South China Sea
2012-10-26
Tropical Storm Son-tinh soaked the Philippines and is now moving into the South China Sea. NASA's Aqua satellite captured a visible image of the storm as the bulk western half of the storm had already moved over water.
On Oct. 25, 2012 at 0525 UTC (1:25 a.m. EDT) the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) instrument that flies aboard NASA's Aqua satellite captured a visible image of Tropical Storm Sin-Tingh. The image showed that the western half of the storm had already moved into the South China Sea, while powerful thunderstorms in the eastern half were ...
Study reveals impact of public DNS services; researchers develop tool to help
2012-10-26
A new study by Northwestern University researchers has revealed that public DNS services could actually slow down users' web-surfing experience. As a result, researchers have developed a solution to help avoid such an impact: a tool called namehelp that could speed web performance by 40 percent.
Through a large-scale study involving more than 10,000 hosts across nearly 100 countries, Fabián Bustamante, associate professor of electrical engineering and computer science at Northwestern's McCormick School of Engineering and Applied Science, and his team found that one cause ...
Triclosan needs to be monitored
2012-10-26
This press release is available in German.
Leipzig. Researchers from Germany and Slovakia have pointed out that the chemical triclosan is one of those particularly harmful substances for the ecological status of rivers that are still not sufficiently monitored. With extensive monitoring conducted in the Elbe river basin that was more comprehensive than standard monitoring procedures, concentrations of the chemical at numerous test sites exceeded the predicted no-effect concentration (PNEC) for algal communities up to a factor of twelve. From the 500 river basin-specific ...
Results of the AIDA STEMI MRI sub-study presented at TCT 2012
2012-10-26
MIAMI, FL – OCTOBER 25, 2012 – A study confirmed no differences in various measures of heart damage, according to cardiac magnetic resonance (MRI) imaging, in patients receiving the anti-clotting medication abxicimab directly into the heart (intracoronary) compared to those receiving it intravenously (IV). The results of the AIDA STEMI MRI sub-study were presented today the 24th annual Transcatheter Cardiovascular Therapeutics (TCT) scientific symposium. Sponsored by the Cardiovascular Research Foundation, TCT is the world's premier educational meeting specializing in interventional ...
Report: Bushmeat pushes Southern African species to the brink
2012-10-26
JOHANNESBURG, SOUTH AFRICA (October 25, 2012) – A recent report says illegal hunting of wildlife in South African Development Community (SADC) states can lead to the eradication of many species across extensive areas and even complete ecological collapse.
Africa's iconic large carnivores, such as cheetah, lion, leopard, and wild dog, are particularly vulnerable to this practice, either because they are caught in the bycatch from unselective methods such as snaring, or due to loss of prey. The report says that the scale and severity of the threat is such that, without ...
UC Davis researchers develop new drug delivery system for bladder cancer using nanoparticles
2012-10-26
(SACRAMENTO, Calif.) -- A team of UC Davis scientists has shown in experimental mouse models that a new drug delivery system allows for administration of three times the maximum tolerated dose of a standard drug therapy for advanced bladder cancer, leading to more effective cancer control without increasing toxicity.
The delivery system consists of specially designed nanoparticles that home in on tumor cells while carrying the anti-cancer drug paclitaxel. The same delivery system also was successfully used to carry a dye that lights up on imaging studies, making it potentially ...
New genomics study shows ancestry could help solve disease riddles
2012-10-26
LA JOLLA, CA – October 25, 2012 – Explosive advancement in human genome sequencing opens new possibilities for identifying the genetic roots of certain diseases and finding cures. However, so many variations among individual genomes exist that identifying mutations responsible for a specific disease has in many cases proven an insurmountable challenge. But now a new study by scientists at The Scripps Research Institute (TSRI), Scripps Health, and Scripps Translational Science Institute (STSI) reveals that by comparing the genomes of diseased patients with the genomes of ...