(Press-News.org) Physicists use hydrodynamics to understand the physical mechanism responsible for changes in the long-range order of groups of particles. Particularly, Aparna Baskaran of Brandeis University, Massachusetts, USA, and Cristina Marchetti of Syracuse University, New York, USA, focused on ordered groups of elongated self-propelled particles. They studied the breakdown of long-range order due to fluctuations that render them unstable and give rise to complex structures, in a study about to be published in EPJ E.
The authors coined the term self-propelled nematics to refer to internally driven elongated particles that spontaneously align head to tail, like tinned sardines. These are characterised by an ordered state that is stationary on average. This means that there is a long-range order, i.e., the long axes of the molecules tend to align along a preferred direction, whereas the locally preferred direction may vary throughout the medium due to local strains or disturbances.
In this study, Baskaran and Marchetti first found that a uniform nematic state can be disturbed by density fluctuations associated with an upward current of active particles. Since the density in turn controls the onset of nematic order, this phenomenon is self-regulating and universal.
They also found that an instability can be triggered by a local distortion of particles' orientation. Such a distortion results in local currents that in turn amplify the distortion, leading to an instability deep inside the nematic state.
Future research will involve solving numerically the hydrodynamic equations to test the theory presented in this study and characterise the emergent structures. Ultimately, this work may help us gain a deeper understanding of pattern formation and dynamics in a variety of internally driven systems, from epithelial cells and soil bacteria such as Myxococcus xanthus, to colloidal self-propelled nanorods.
###
Reference:
A. Baskaran, M. C. Marchetti (2012), Self-regulation in Self-Propelled Nematic Fluids, European Physical Journal E 35:95, DOI 10.1140/epje/i2012-12095-8
For more information, please visit www.epj.org
The full-text article is available for journalists on request.
Enigmatic nematics
The law of hydrodynamics governing the way internally driven systems behave could explain their complex structure
2012-10-30
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
New developments reveal a molecule with a promising function in terms of cancer treatment.
2012-10-30
Researchers from Inserm and CNRS from the Institute for genetics and molecular and cellular biology (IGBMC) and from the Research Institute at the Strasbourg school of biotechnology (Irebs) have focussed their efforts on PARG, currently thought to be a promising new therapeutic target in the treatment of cancer. Their work has revealed the role of this molecule in regulating gene expression. The results were published on 25 October 2012 in the on-line Molecular Cell review.
Cells are subjected to various stresses throughout their life. Some of this stress can damage DNA. ...
ORNL debuts Titan supercomputer
2012-10-30
OAK RIDGE, Tenn., Oct. 29, 2012 — The U.S. Department of Energy's (DOE) Oak Ridge National Laboratory launched a new era of scientific supercomputing today with Titan, a system capable of churning through more than 20,000 trillion calculations each second—or 20 petaflops—by employing a family of processors called graphic processing units first created for computer gaming. Titan will be 10 times more powerful than ORNL's last world-leading system, Jaguar, while overcoming power and space limitations inherent in the previous generation of high-performance computers.
Titan, ...
NASA's TRMM satellite analyzes Hurricane Sandy in 3-D
2012-10-30
NASA's Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission, or TRMM satellite can measure rainfall rates and cloud heights in tropical cyclones, and was used to create an image to look into Hurricane Sandy on Oct. 28, 2012. Owen Kelly of NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Md. created this image of Hurricane Sandy using TRMM data.
At 2:20 p.m. EDT on Sunday, Oct. 28, Hurricane Sandy was a marginal category 1 hurricane and its eyewall is modest, as TRMM reveals, which gives forecasters and scientists hints about its possible future strength.
The eyewall appeared somewhat ...
Prostate cancer prognosis hope
2012-10-30
Scientists have discovered a molecular 'tell' in laboratory experiments that could help doctors determine the severity of a patient's prostate cancer.
Cancer of the prostate – the most common male cancer in the UK – presents in two distinct ways: a low-risk type, which may never cause any symptoms, and a high-risk form that needs treatment to prevent it spreading to other parts of the body.
Knowing which type of prostate cancer each patient has – some 40,000 British men per year – is therefore essential to ensuring they receive the correct treatment.
Lead researcher ...
Radiation treatment after surgery improves survival for elderly women with early-stage breast cancer
2012-10-30
BOSTON, Mass. – Oct. 29, 2012. Elderly women with early-stage breast cancer live longer with radiation therapy and surgery compared with surgery alone, researchers at the University of Maryland School of Medicine have found. The researchers, who collected data on almost 30,000 women, ages 70 to 84, with early, highly treatable breast cancer enrolled in a nationwide cancer registry, are reporting their findings at the 54th annual meeting of the American Society for Radiation Oncology (ASTRO).
"Overall survival and breast cancer-specific survival were significantly better ...
Research: Pay satisfaction key driver of work-family conflict
2012-10-30
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. — Employees who are more satisfied with their pay report lower levels of work-family conflict, a study by a University of Illinois labor and employment relations professor shows.
A worker's actual salary is as important as pay satisfaction in determining a worker's happiness, according to the research by professor Amit Kramer.
"Pay, as you might expect, is a relative thing," Kramer said. "I think most people would agree that a certain level of pay that allows you to meet your needs is critical. However, beyond that level, relative pay becomes an issue ...
University of Texas at Austin study measures methane emissions released from natural gas production
2012-10-30
A research team led by The University of Texas at Austin, and including engineering and environmental testing firms URS and Aerodyne Research, is conducting a major field study to measure methane emissions from natural gas production, about which little empirical data exist. With a goal of obtaining scientifically rigorous, representative data from multiple producing basins, the study brings together Environmental Defense Fund (EDF), the university and nine of the nation's leading natural gas producers: Anadarko Petroleum Corporation, BG Group plc, Chevron, Encana Oil & ...
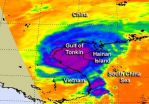
NASA sees Tropical Storm Son-Tinh fill the Gulf of Tonkin
2012-10-30
Tropical Storm Son-tinh made landfall in northern Vietnam is and is curving to the northeast to track over southern China. NASA's Aqua satellite revealed powerful thunderstorms around the storm's center before it made landfall and as it filled up the Gulf of Tonkin.
On Oct. 28 at 0553 UTC (2:53 a.m. EDT) the Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) instrument aboard NASA's Aqua satellite captured infrared imagery of Tropical Storm Son-tinh that showed a concentration of strong thunderstorms around the storm's center before it made landfall. Son-tinh was located over the Gulf ...
Early autism intervention improves brain responses to social cues
2012-10-30
An autism intervention program that emphasizes social interactions and is designed for children as young as 12 months has been found to improve cognitive skills and brain responses to faces, considered a building block for social skills. The researchers say that the study, which was completed at the University of Washington, is the first to demonstrate that an intensive behavioral intervention can change brain function in toddlers with autism spectrum disorders.
"So much of a toddler's learning involves social interaction, and early intervention that promotes attention ...
NASA examines Hurricane Sandy as it affects the eastern US
2012-10-30
On Monday, Oct. 29, Hurricane Sandy was ravaging the Mid-Atlantic with heavy rains and tropical storm force winds as it closed in for landfall. Earlier, NASA's CloudSat satellite passed over Hurricane Sandy and its radar dissected the storm get a profile or sideways look at the storm. NASA's Aqua satellite provided an infrared view of the cloud tops and NOAA's GOES-13 satellite showed the extent of the storm. The National Hurricane Center reported at 11 a.m. EDT on Oct. 29 that Hurricane Sandy is "expected to bring life-threatening storm surge and coastal hurricane winds ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Medicare patients get different stroke care depending on plan, analysis reveals
Polyploidy-induced senescence may drive aging, tissue repair, and cancer risk
Study shows that treating patients with lifestyle medicine may help reduce clinician burnout
Experimental and numerical framework for acoustic streaming prediction in mid-air phased arrays
Ancestral motif enables broad DNA binding by NIN, a master regulator of rhizobial symbiosis
Macrophage immune cells need constant reminders to retain memories of prior infections
Ultra-endurance running may accelerate aging and breakdown of red blood cells
Ancient mind-body practice proven to lower blood pressure in clinical trial
SwRI to create advanced Product Lifecycle Management system for the Air Force
Natural selection operates on multiple levels, comprehensive review of scientific studies shows
Developing a national research program on liquid metals for fusion
AI-powered ECG could help guide lifelong heart monitoring for patients with repaired tetralogy of fallot
Global shark bites return to average in 2025, with a smaller proportion in the United States
Millions are unaware of heart risks that don’t start in the heart
What freezing plants in blocks of ice can tell us about the future of Svalbard’s plant communities
A new vascularized tissueoid-on-a-chip model for liver regeneration and transplant rejection
Augmented reality menus may help restaurants attract more customers, improve brand perceptions
Power grids to epidemics: study shows small patterns trigger systemic failures
Computational insights into the interactions of andrographolide derivative SRJ09 with histone deacetylase for the management of beta thalassemia
A genetic brake that forms our muscles
CHEST announces first class of certified critical care advanced practice providers awarded CCAPP Designation
Jeonbuk National University researchers develop an innovative prussian-blue based electrode for effective and efficient cesium removal
Self-organization of cell-sized chiral rotating actin rings driven by a chiral myosin
Report: US history polarizes generations, but has potential to unite
Tiny bubbles, big breakthrough: Cracking cancer’s “fortress”
A biological material that becomes stronger when wet could replace plastics
Glacial feast: Seals caught closer to glaciers had fuller stomachs
Get the picture? High-tech, low-cost lens focuses on global consumer markets
Antimicrobial resistance in foodborne bacteria remains a public health concern in Europe
Safer batteries for storing energy at massive scale
[Press-News.org] Enigmatic nematicsThe law of hydrodynamics governing the way internally driven systems behave could explain their complex structure