(Press-News.org) Scientists from the Niels Bohr Institute have been studying distant galaxies, which are among the most active star-forming galaxies in the Universe. They form around 1,000 new stars a year – a 1,000 times more than our own galaxy, the Milky Way. The findings have been published in Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society.
"The galaxies are located in the far distant Universe – when the universe was 3 billion years old (equivalent to only 20 percent of its current age). It is a period of the Universe when the galaxies were very active, almost teenager-like and out of control", describes Thomas R. Greve, Associate professor in astrophysics at Dark Cosmology Centre, Niels Bohr Institute at the University of Copenhagen.
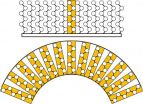
Together with researchers from the Royal Observatory, Edinburgh and Durham University in England, he has studied the distant galaxies using the Expanded Very Large Array, which is an astronomical observatory in New Mexico, USA. The observatory consists of 27 parabolic antennas, each of which have a diameter of 25 meters and can measure radio waves from distant objects. Data from each antenna is combined electronically so that the final measurements have an angular resolution equivalent to a single antenna with a diameter of 36 km and a sensitivity equal to that of a single antenna with a diameter of 130 meters.
"We have measured the CO levels, that is to say carbon monoxide, which is one of the most common molecules in the universe, after the hydrogen molecule, H2. Using the measurements we have calculated how much gas there is in the galaxy and it turns out there are extremely large amounts of gas in these galaxies ", explains Thomas R. Greve.
Raw material for new stars
Gas is the raw material used in the Universe to form stars. In the galaxies the gas collects in large clouds, which become denser and denser as a result of their own gravitational pull. Eventually, the gas becomes so dense that it collapses into a ball of glowing gas, which forms a new star – the cloud almost 'explodes' in a cosmic firework display of new stars.
"What is new about our observations is that we have looked at the amount of cold, diffuse gas that is not yet actively star-forming, and what we can determine is that there is more than twice as much gas than previously thought. This means that there is an enormous amount of raw material, which can condense and form new stars ", explains Thomas R. Greve.
The measurements of the morphology of the gas also suggest that these galaxies are not only bigger than we thought, but also very irregular in their shape. It is only much later (several hundred billion years) in their development, after they have undergone their intense star formation that they become the mature, regular, elliptical shaped galaxies that we see in our Universe today.
INFORMATION:
Contact:
Thomas Greve, Associate professor, Dark Cosmology Centre, Niels Bohr Institute, University of Copenhagen, + 45 3532-5939, tgreve@dark-cosmology.dk
Article in arXiv: http://arxiv.org/abs/1009.0749
Wild 'teenage' galaxies booming with star births
2010-10-13
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Scientist develops new, innovative methods for characterizing proteins
2010-10-13
Using a combination of high-powered computers and advanced experimental magnetic resonance data, a Florida State University biophysical chemist has developed techniques that improve the way scientists can study and predict the structure and dynamics of proteins found in the human body. His innovations could ultimately shorten the time it takes researchers to develop new, more effective drugs and better understand biomedical processes that underlie a variety of health conditions.
The new techniques "allow us to more accurately understand protein behavior and function at ...
Hormone therapy after menopause might increase risk of kidney stones
2010-10-13
DALLAS – Oct. 11, 2010 – The use of estrogen therapy by postmenopausal women might increase the risk of developing kidney stones, according to findings by UT Southwestern Medical Center researchers.
In a study available online and in today's issue of the Archives of Internal Medicine, investigators found that estrogen therapy after menopause increased a woman's chances of developing kidney stones by approximately 20 percent. This discovery calls into question the long-held belief that estrogen might actually protect women from the disease, and clinicians need to keep ...
Diabetes hospitalizations rise dramatically for young women
2010-10-13
ANN ARBOR, Mich. – A study published in Journal of Women's Health shows a rapid increase in the number of hospitalizations due to diabetes for young adults – particularly young women.
Diabetes hospitalizations were up by 66 percent for all ages and sexes, but the number of diabetes hospitalizations among younger adults, ages 30-39, more than doubled from 1993 to 2006.
This pattern of hospitalizations echoes the dramatic increase in rates of obesity across the United States in the last 30 years, according to the study by the University of Michigan Health System.
Young ...
Listen up: Ocean acidification poses little threat to whales' hearing
2010-10-13
Contrary to some previous, highly publicized, reports, ocean acidification is not likely to worsen the hearing of whales and other animals, according to a Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) scientist who studies sound propagation in the ocean.
Tim Duda, of WHOI's Applied Ocean Physics & Engineering Department, undertook a study in response to warnings that as the ocean becomes more acidic—due to elevated levels of atmospheric carbon dioxide (CO2)--noise from ships will be able to travel farther and possibly interfere with whales and other animals that rely on ...
Scientists pinpoint gene linked to drug resistance in malaria
2010-10-13
Scientists have shed light on how malaria is able to resist treatment with a leading drug.
Researchers have identified a gene that enables the parasite that causes the infection to resist treatment with the plant-based remedy artemisinin.
In many countries where the parasite has developed resistance to previously effective common treatments such as chloroquine, artemisinin remains the only effective treatment against the infection. However, malarial resistance to artemisinin appears to be developing, potentially creating problems in controlling malaria.
Identification ...
Lack of antiepileptic drugs hurts awareness, treatment efforts in Zambia
2010-10-13
EAST LANSING, Mich. — Despite an international effort to raise awareness about epilepsy in resource-poor nations, a recently published study found nearly 50 percent of pharmacies in Zambia do not carry antiepileptic drugs, seriously hampering efforts to tackle one of the most cost-effective chronic conditions to treat.
The study, recently published in the American Journal of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene, was led by Gretchen Birbeck, an associate professor of neurology and ophthalmology and director for the International Neurologic & Psychiatric Epidemiology Program in ...
Nanoscopic particles resist full encapsulation, Sandia simulations show
2010-10-13
ALBUQUERQUE, N.M.— It may seem obvious that dunking relatively spherical objects in a sauce — blueberries in melted chocolate, say — will result in an array of completely encapsulated berries.
Relying on that concept, fabricators of spherical nanoparticles have similarly dunked their wares in protective coatings in the belief such encapsulations would prevent clumping and unwanted chemical interactions with solvents.
Unfortunately, reactions in the nanoworld are not logical extensions of the macroworld, Sandia National Laboratories researchers Matthew Lane and Gary ...
Young people with mental health problems at risk of falling through 'gap' in care services
2010-10-13
Many young people with mental health problems are at risk of falling through a huge gap in provision when they move from adolescent to adult care services, according to new research from the University of Warwick.
A team led by Professor Swaran Singh at Warwick Medical School looked at the transition from child mental health services to adult mental health services and found for the vast majority of users the move was "poorly planned, poorly executed and poorly experienced".
In a study published in The British Journal of Psychiatry, the research team looked at 154 service ...
Successful kidney transplantation despite tissue incompatibility
2010-10-13
Donor kidneys can be successfully transplanted even if there is strong tissue incompatibility between donor and recipient. An interdisciplinary working group headed by Dr. Christian Morath, senior consultant at the Department of Nephrology at Heidelberg University Hospital (Medical Director: Professor Dr. Martin Zeier) and Professor Dr. Caner Süsal, head of antibody laboratory in the Department of Transplantation Immunology, showed in a study of 34 sensitized high-risk patients that the success rate in these patients was not different from the success rate of patients with ...
Large study shows females are equal to males in math skills
2010-10-13
MADISON — The mathematical skills of boys and girls, as well as men and women, are substantially equal, according to a new examination of existing studies in the current online edition of journal Psychological Bulletin.
One portion of the new study looked systematically at 242 articles that assessed the math skills of 1,286,350 people, says chief author Janet Hyde, a professor of psychology and women's studies at the University of Wisconsin-Madison.
These studies, all published in English between 1990 and 2007, looked at people from grade school to college and beyond. ...