(Press-News.org) (Boston) – A new Boston University School of Medicine (BUSM) study has found that improving Human papillomavirus (HPV) vaccination rates in black women may require culturally sensitive approaches that address ethnic-specific barriers. The findings are published online in the November/December issue of the journal, Women's Health Issues.
According to the Centers for Disease Control, HPV is the most common sexually transmitted infection. There are more than 40 HPV types that can infect the genital areas of males and females and in advanced stages, can cause cervical cancer. Black women have higher rates of cervical cancer and lower rates of HPV vaccination than white women in the U.S., and Haitians may be an especially vulnerable subgroup of black women.
The study assessed similarities and differences in the knowledge, attitudes, beliefs and practices toward HPV vaccination compared to actual vaccination rates among African- American and Haitian immigrant women and their daughters.
Researchers led by Natalie Pierre-Joseph, MD and Rebecca Perkins, MD of the Women's Health Interdisciplinary Research Center at BUSM, surveyed African-American and Haitian women to measure HPV knowledge. The measures included perceived susceptibility of HPV, severity of cultural barriers and trust in physicians. The researchers then compared the survey responses to the women's medical records to determine vaccination rates.
Results of the study showed that both ethnic groups had high levels of trust in their physician and nearly 75 percent of all participants would vaccinate their daughters with a physician recommendation. However, fewer than half of participants' daughters were vaccinated in the following 12 month period.
"This study addresses an important public health issue given the lower uptake of HPV vaccination among racial/ethnic minorities as compared to white women in the U.S.," said Pierre-Joseph. "It also points out the importance of looking at the heterogeneity of the African- American population and tailoring preventive efforts to the specific sub-groups," she added.
###
Universal HPV vaccination has the potential to reduce racial disparities in cervical cancer mortality. These results highlight the need for a greater understanding of provider and patient communication in order to improve HPV vaccination rates among black women.
This research study was supported with funding by a Building Interdisciplinary Research
Careers in Women's Health (BIRCWH) grant (K12-HD43444) and an American Cancer
Society Career Development Award (CDDA-10-086-01).
BUSM study finds certain subgroups of black women have lower uptake of HPV vaccination
2012-11-13
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Autism treatment is more than skin deep
2012-11-13
Metal-binding agents rubbed into the skin, prescribed by some alternative practitioners for the treatment of autism, are not absorbed and therefore are unlikely to be effective at helping the body excrete excess mercury. The study by Jennifer Cohen and Michelle Ruha from Banner Good Samaritan Medical Center in the US, and their colleagues, provides evidence against the use of these treatments in children with autism. Their work is published online in Springer's Journal of Medical Toxicology.
Metal-binding agents such as DMPS* have received significant attention in recent ...
Childhood abuse leads to poor adult health
2012-11-13
Montreal, November 13, 2012 – The psychological scars of childhood abuse
can last well into adulthood. New research from Concordia University shows the harm can have longterm negative physical effects, as well as emotional ones.
Scientists hypothesize that stress in early childhood causes physiological changes that affect a victim's response to stress, which puts the individual at an increased risk of disease later in life. Jean-Philippe Gouin, who holds a Canada Research Chair in Chronic Stress and Health in Concordia's Department of Psychology, tested this link and ...
Effects of alcohol on lymphoma, leukemia, and other types of hematological cancers
2012-11-13
Many observational epidemiologic studies have found an inverse association between alcohol consumption and hematological cancers (such as lymphoma and leukemia). This study, based on the Million Women's Study in the UK, is large enough to permit an evaluation of associations with various types of such cancers. Further, it takes into account newer coding systems for morphology so that diseases associated with the lymphatic system can be separated from those of the myeloid system.
The key findings are that alcohol consumption appears to lower the risk of several types ...
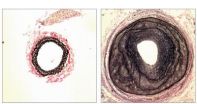
G proteins regulate remodelling of blood vessels
2012-11-13
This press release is available in German.
Blood vessels are extremely dynamic: depending on the external conditions, they can adapt their permeability for nutrients, their contractility, and even their shape. Unlike cardiac muscle cells, for example, the smooth muscle cells in blood vessels demonstrate a high degree of plasticity, so they can specialise or multiply as required, even repairing damage to the vessel wall. This vascular remodelling is evidently precisely regulated. Disruptions are extremely significant in conditions such as atherosclerosis or high blood ...
It pays to cooperate
2012-11-13
CAMBRIDGE, MA - Many species exhibit cooperative survival strategies — for example, sharing food or alerting other individuals when a predator is nearby. However, there are almost always freeloaders in the population who will take advantage of cooperators. This can be seen even among microbes such as yeast, where "cheaters" consume food produced by their neighbors without contributing any of their own.
In light of this, evolutionary biologists have long wondered why cooperation remains a viable survival strategy, since there will always be others who cheat. Now, MIT physicists ...
How online video stream quality affects viewer behavior
2012-11-13
AMHERST, Mass. – It may seem like common sense that the quality of online video streaming affects how willing viewers are to watch videos at a website. But until computer science researcher Ramesh Sitaraman at the University of Massachusetts Amherst and collaborators at Akamai developed a way to rigorously study the question, no one had been able to scientifically test the assumption.
They conducted the first large-scale study of its kind to quantitatively demonstrate how video stream quality causes changes in viewer behavior. "Video stream quality is a very big topic ...
Once the conflict is over, solidarity in alliances goes out of the window
2012-11-13
This press release is available in German.
It is not always wise to form an alliance while in a conflict or at war, especially when there is something to be shared afterward. Economists from the Max Planck Institute for Tax Law and Public Finance have now shown by game theory experiments that, as soon as the enemy is gone, in-group solidarity of alliances vanishes rapidly. Former brothers in arms fight even more vigorously over the spoils of a victory than strangers do. During the conflict, they expend together only half the effort of their enemy. Furthermore, when ...
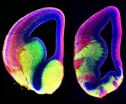
Watching the developing brain, scientists glean clues on neurological disorder
2012-11-13
CHAPEL HILL, N.C. – As the brain develops, each neuron must find its way to precisely the right spot to weave the intricate network of links the brain needs to function. Like the wiring in a computer, a few misplaced connections can throw off functioning for an entire segment of the brain.
A new study by researchers at the University of North Carolina School of Medicine reveals how some nerve cells, called interneurons, navigate during the development of the cerebral cortex. Mutations in a key gene behind this navigation system underlie a rare neurological disorder called ...
Glutamate neurotransmission system may be involved with depression risk
2012-11-13
Researchers using a new approach to identifying genes associated with depression have found that variants in a group of genes involved in transmission of signals by the neurotransmitter glutamate appear to increase the risk of depression. The report published in the journal Translational Psychiatry suggests that drugs targeting the glutamate system may help improve the limited success of treatment with current antidepressant drugs.
"Instead of looking at DNA variations one at a time, we looked at grouping of genes in the same biological pathways and found that a set ...
Baiting mosquitoes with knowledge and proven insecticides
2012-11-13
This press release is available in Spanish.
While one team of U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA) scientists is testing the effectiveness of pesticides against mosquitoes, another group is learning how repellents work.
At the Agricultural Research Service (ARS) Center for Medical, Agricultural and Veterinary Entomology (CMAVE) in Gainesville, Fla., entomologist Sandra Allan is using toxic sugar-based baits to lure and kill mosquitoes. Allan and her CMAVE cooperators are evaluating insecticides and designing innovative technology to fight biting insects and arthropods. ...