(Press-News.org) PHILADELPHIA - The cancer-causing form of the gene Myc alters the metabolism of mitochondria, the cell's powerhouse, making it dependent on the amino acid glutamine for survival. In fact, 40 percent of all "hard-to-treat" cancers have a mutation in the Myc gene.
Accordingly, depriving cells of glutamine selectively induces programmed cell death in cells overexpressing mutant Myc.
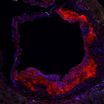
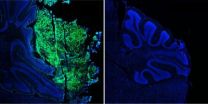
Using Myc-active neuroblastoma cancer cells, a team led by Howard Hughes Medical Institute (HHMI) investigator M. Celeste Simon, Ph.D., scientific director for the Abramson Family Cancer Research Institute (AFCRI), identified the proteins PUMA, NOXA, and TRB3 as executors of the glutamine-starved cells. These three proteins represent a downstream target in the Myc pathway at which to aim drugs. Roughly 25 percent of all neuroblastoma cases are associated with Myc-active cells.
The findings appear in this week's issue of Cancer Cell. Simon is also a professor of Cell and Developmental Biology at the Perelman School of Medicine, University of Pennsylvania. The Penn team collaborated with colleagues from The Children's Hospital of Philadelphia (CHOP) John Maris and Michael Hogarty.
"These findings come from studies of fundamental cellular pathways and would not have been discovered without ongoing support for basic research," notes Simon. "Translational research is very important, but equal emphasis on basic research of processes such as cellular metabolism is critical for the ultimate cure of cancer."
Glutamine depletion in Myc-mutant cells induces cell death through a complicated series of molecular switches involving the three protein executors and the DNA-binding protein ATF4. Knowing this, the team showed that either agonists of ATF4 or inhibitors of glutamine metabolism potently caused cell death in assays using neuroblastoma cells and inhibited tumor growth in transgenic mice. Drugs in these two classes have been approved by the Food and Drug Administration and are being tested in clinical trials for other disorders.
###
This study suggests that a combination of the two types of drugs might work for Myc-related neuroblastoma cancer patients.
Co-authors include Guoliang Qing, Bo Li, Nicolas Skuli, Zandra E. Walton, and David R. Wise, all from Penn, and Annette Vu, Xueyuan Liu, and Patrick A. Mayes, all from CHOP.
This research was supported by the Howard Hughes Medical Institute; National Cancer Institute grants CA104838, CA097323, CA97323; an NIH F32 Training Grant 1F32CA137988 and an National Natural Science Foundation grant 81171928 from China.
Penn Medicine is one of the world's leading academic medical centers, dedicated to the related missions of medical education, biomedical research, and excellence in patient care. Penn Medicine consists of the Raymond and Ruth Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania (founded in 1765 as the nation's first medical school) and the University of Pennsylvania Health System, which together form a $4.3 billion enterprise.
The Perelman School of Medicine is currently ranked #2 in U.S. News & World Report's survey of research-oriented medical schools. The School is consistently among the nation's top recipients of funding from the National Institutes of Health, with $479.3 million awarded in the 2011 fiscal year.
The University of Pennsylvania Health System's patient care facilities include: The Hospital of the University of Pennsylvania -- recognized as one of the nation's top "Honor Roll" hospitals by U.S. News & World Report; Penn Presbyterian Medical Center; and Pennsylvania Hospital — the nation's first hospital, founded in 1751. Penn Medicine also includes additional patient care facilities and services throughout the Philadelphia region.
Penn Medicine is committed to improving lives and health through a variety of community-based programs and activities. In fiscal year 2011, Penn Medicine provided $854 million to benefit our community.
Targeting downstream proteins in cancer-causing pathway shows promise in cell, animal model
2012-11-14
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Vitamin D may prevent clogged arteries in diabetics
2012-11-14
People with diabetes often develop clogged arteries that cause heart disease, and new research at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis suggests that low vitamin D levels are to blame.
In a study published Nov. 9 in the Journal of Biological Chemistry, the researchers report that blood vessels are less like to clog in people with diabetes who get adequate vitamin D. But in patients with insufficient vitamin D, immune cells bind to blood vessels near the heart, then trap cholesterol to block those blood vessels.
"About 26 million Americans now have type ...
Being neurotic, and conscientious, a good combo for health
2012-11-14
Under certain circumstances neuroticism can be good for your health, according to a University of Rochester Medical Center study showing that some self-described neurotics also tended to have the lowest levels of Interleukin 6 (IL-6), a biomarker for inflammation and chronic disease.
Researchers made the preliminary discovery while conducting research into how psychosocial factors such as personality traits influence underlying biology, to predict harmful conditions like inflammation.
Known as one of the "Big 5" traits, neuroticism is usually marked by being moody, nervous, ...
Research strengthens link between obesity and dental health in homeless children
2012-11-14
Obesity and dental cavities increase and become epidemic as children living below the poverty level age, according to nurse researchers from the Case Western Reserve University and the University of Akron.
"It's the leading cause of chronic infections in children," said Marguerite DiMarco, associate professor at the Frances Payne Bolton School of Nursing at Case Western Reserve University.
Researchers Sheau-Huey Chiu, assistant professor, and graduate assistant Jessica L. Prokp, from the University of Akron's College of Nursing, contributed to the study.
Researchers ...
For brain tumors, origins matter
2012-11-14
Cancers arise when a normal cell acquires a mutation in a gene that regulates cellular growth or survival. But the particular cell this mutation happens in—the cell of origin—can have an enormous impact on the behavior of the tumor, and on the strategies used to treat it.
Robert Wechsler-Reya, Ph.D., professor and program director at Sanford-Burnham Medical Research Institute, and his team study medulloblastoma, the most common malignant brain cancer in children. A few years ago, they made an important discovery: medulloblastoma can originate from one of two cell types: ...
Stem cell finding could advance immunotherapy for lung cancer
2012-11-14
CINCINNATI—A University of Cincinnati (UC) Cancer Institute lung cancer research team reports that lung cancer stem cells can be isolated—and then grown—in a preclinical model, offering a new avenue for investigating immunotherapy treatment options that specifically target stem cells.
John C. Morris, MD, and his colleagues report their findings in the Nov. 13, 2012, issue of PLOS One, a peer-reviewed online publication that features original research from all disciplines within science and medicine.
Stem cells are unique cells that can divide and differentiate into ...
New type of bacterial protection found within cells
2012-11-14
Irvine, Calif., Nov. 13, 2012 — UC Irvine biologists have discovered that fats within cells store a class of proteins with potent antibacterial activity, revealing a previously unknown type of immune system response that targets and kills bacterial infections.
Steven Gross, UCI professor of developmental & cell biology, and colleagues identified this novel intercellular role of histone proteins in fruit flies, and it could herald a new approach to fighting bacterial growth within cells. The study appears today in eLife, a new peer-reviewed, open-access journal supported ...
Uranium exposure linked to increased lupus rate
2012-11-14
CINCINNATI—People living near a former uranium ore processing facility in Ohio are experiencing a higher than average rate of lupus, according a new study conducted by scientists at the University of Cincinnati and Cincinnati Children's Hospital Medical Center.
Lupus is a chronic inflammatory disease that can affect the skin, joints, kidneys, lungs, nervous system and other organs of the body. The underlying causes of lupus are unknown, but it is usually more common in women of child-bearing age.
For this new study, a collaborative team of UC and Cincinnati Children's ...
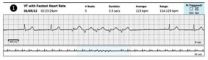
Less of a shock
2012-11-14
Implantable defibrillators currently on the market apply between 600 and 900 volts to the heart, almost 10 times the voltage from an electric outlet, says Ajit H. Janardhan, MD, PhD, a cardiac electrophysiology fellow at the Washington University's School of Medicine.
After being shocked, he says, some patients get post-traumatic stress disorder. Patients may even go so far as to ask their physicians to remove the defibrillator, even though they understand that the device has saved their lives.
The huge shocks are not only unbearably painful, they damage the heart muscle ...
The road to language learning is iconic
2012-11-14
Languages are highly complex systems and yet most children seem to acquire language easily, even in the absence of formal instruction. New research on young children's use of British Sign Language (BSL) sheds light on one of the mechanisms - iconicity - that may endow children with this amazing ability.
For spoken and written language, the arbitrary relationship between a word's form – how it sounds or how it looks on paper – and its meaning is a particularly challenging feature of language acquisition. But one of the first things people notice about sign languages is ...
State of Nuevo León first to benefit from improved nationwide air quality information system
2012-11-14
This press release is available in Spanish and French.
Monterrey, 13 November 2012—Today, the Nuevo León state ministry of sustainable development, with support from the Commission for Environmental Cooperation (CEC), launched a revamped air quality information management system in Monterrey, Mexico, using AirNow-International.
This CEC initiative, developed in coordination with Canadian, Mexican and US government agencies, is laying the foundation for improved ways to inform citizens around the country about air quality in their communities with real-time data that ...