(Press-News.org) Come rain or shine (or even snow), some glaciers of the Himalayas will continue shrinking for many years to come.
The forecast by Brigham Young University geology professor Summer Rupper comes after her research on Bhutan, a region in the bull's-eye of the monsoonal Himalayas. Published in Geophysical Research Letters, Rupper's most conservative findings indicate that even if climate remained steady, almost 10 percent of Bhutan's glaciers would vanish within the next few decades. What's more, the amount of melt water coming off these glaciers could drop by 30 percent.
Rupper says increasing temperatures are just one culprit behind glacier retreat. A number of climate factors such as wind, humidity, precipitation and evaporation of any given year can affect how glaciers behave. With some Bhutanese glaciers as long as 13 miles, an imbalance in any of these areas can take them decades to completely respond.
"These particular glaciers have seen so much warming in the past few decades that they're currently playing lots of catch up," Rupper explains.
In fact, snowfall rates in Bhutan would need to almost double to avoid glacier retreat, but it's not a likely scenario because warmer temperatures lead to rainfall instead of snow. If glaciers continue to lose more water than gained, the combination of more rain and more glacial melt increases the probability of flooding — which can be devastating to neighboring villages.
"Much of the world's population is just downstream of the Himalayas," Rupper points out. "A lot of culture and history could be lost, not just for Bhutan but for neighboring nations facing the same risks."
To illustrate the likelihood of such an outcome, Rupper took her research one moderate step further. Her results show if temperatures were to rise just 1 degree Celsius, the Bhutanese glaciers would shrink by 25 percent and the annual melt water would drop by as much as 65 percent. With climate continuing to warm, such a prediction is not altogether unlikely, especially given the years it can take for glaciers to react to change.
To make more precise predictions for Bhutan, Rupper and BYU graduate students Landon Burgener and Josh Maurer joined researchers from Columbia University, the Lamont-Doherty Earth Observatory, NASA and Bhutan's Department of Hydro-Meteorological Services. Together, they trekked through rainforests and barren cliffs to reach some of the world's most remote blocks of ice. There they placed a weather station and glacier monitoring equipment that can be used to gather real-time data in the months and years to follow.
"It took seven days just to get to the target glacier," Rupper recounts, having returned in October. "For our pack animals, horsemen and guides, that terrain and elevation are a way of life, but I'll admit the westerners in the group were a bit slower-moving."
Rupper's forecasts and fieldwork are among the first to look at glaciers in Bhutan, and the government hopes to use her research to make long-term decisions about the nation's water resources and flooding hazards.
"They could potentially have a better idea of where best to fortify homes or build new power plants," says Rupper. "Hopefully, good science can lead to good engineering solutions for the changes we're likely to witness in the coming decades."
### END
Himalayan glaciers will shrink even if temperatures hold steady
2012-11-16
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Fetus suffers when mother lacks vitamin C
2012-11-16
Maternal vitamin C deficiency during pregnancy can have serious consequences for the foetal brain. And once brain damage has occurred, it cannot be reversed by vitamin C supplements after birth. This is shown through new research at the University of Copenhagen just published in the scientific journal PLOS ONE.
Population studies show that between 10-20 per cent of all adults in the developed world suffer from vitamin C deficiency. Therefore, pregnant women should think twice about omitting the daily vitamin pill.
"Even marginal vitamin C deficiency in the mother stunts ...
Children who swim start smarter
2012-11-16
Children who learn how to swim at a young age are reaching many developmental milestones earlier than the norm.
Researchers from the Griffith Institute for Educational Research surveyed parents of 7000 under-fives from Australia, New Zealand and the US over three years.
A further 180 children aged 3, 4 and 5 years have been involved in intensive testing, making it the world's most comprehensive study into early-years swimming.
Lead researcher Professor Robyn Jorgensen says the study shows young children who participate in early-years swimming achieve a wide range ...
Into the magnetic resonance scanner with a cuddly toy
2012-11-16
For the first time, Bochum clinicians have been able to show on the basis of a large sample, that it is possible to examine children's heads in the MRI scanner without general anaesthesia or other medical sedation. In many cases it was sufficient to prepare the young patients for the examination in an age-appropriate manner in order to take away their fear of the tube. And the results speak for themselves: of the 2461 image sequences recorded with 326 patients, the participating radiologists classified 97 percent as "diagnostically relevant". At the same time, through his ...
Improving quality of life for the bedridden
2012-11-16
The skin is the most versatile of our organs: It protects the body from environmental effects, contributes to the body's immune system and supports metabolic functions such as breathing. The skin is always in action. Lack of movement is anathema to it. If a patient does not move, the ever higher moisture levels, pressure and effects of gravity lead to circulatory disorders. This increases the amount of toxic tissue, resulting in ulcers which can lead to life-threatening complications.
This affects two groups of patients in particular: the elderly and paraplegics. There ...
GOCE's second mission improving gravity map
2012-11-16
ESA's GOCE gravity satellite has already delivered the most accurate gravity map of Earth, but its orbit is now being lowered in order to obtain even better results.
The Gravity field and steady-state Ocean Circulation Explorer (GOCE) has been orbiting Earth since March 2009, reaching its ambitious objective to map our planet's gravity with unrivalled precision.
Although the planned mission has been completed, the fuel consumption was much lower than anticipated because of the low solar activity over the last two years. This has enabled ESA to extend GOCE's life, improving ...
Fear of the dentist is passed on to children by their parents
2012-11-16
Fear of visiting the dentist is a frequent problem in paediatric dentistry. A new study confirms the emotional transmission of dentist fear among family members and analyses the different roles that mothers and fathers might play.
A new study conducted by scientists at the Rey Juan Carlos University of Madrid highlights the important role that parents play in the transmission of dentist fear in their family.
Previous studies had already identified the association between the fear levels of parents and their children, but they never explored the different roles that ...
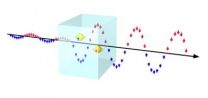
Important progress for spintronics
2012-11-16
A fundamental cornerstone for spintronics that has been missing up until now has been constructed by a team of physicists at Linköping University in Sweden. It's the world's first spin amplifier that can be used at room temperature.
Great hopes have been placed on spintronics as the next big paradigm shift in the field of electronics. Spintronics combines microelectronics, which is built on the charge of electrons, with the magnetism that originates in the electrons' spin. This lays the foundation for entirely new applications that fire the imagination. The word "spin" ...
Melt water on Mars could sustain life
2012-11-16
Near surface water has shaped the landscape of Mars. Areas of the planet's northern and southern hemispheres have alternately thawed and frozen in recent geologic history and comprise striking similarities to the landscape of Svalbard. This suggests that water has played a more extensive role than previously envisioned, and that environments capable of sustaining life could exist, according to new research from the University of Gothenburg, Sweden.
Mars is a changing planet, and in recent geological time repeated freeze and thaw cycles has played a greater role than expected ...
Reconsidering cancer's bad guy
2012-11-16
Researchers at the University of Copenhagen have found that a protein, known for causing cancer cells to spread around the body, is also one of the molecules that trigger repair processes in the brain. These findings are the subject of a paper, published this week in Nature Communications. They point the way to new avenues of research into degenerative brain diseases like Alzheimer's.
How to repair brain injuries is a fundamental question facing brain researchers. Scientists have been familiar with the protein S100A4 for some time as a factor in metastasis, or how cancer ...
Dartmouth research: The clocks are ticking and the climate is changing
2012-11-16
Dartmouth plant biologist C. Robertson (Rob) McClung is not your typical clock-watcher. His clocks are internal, biological, and operate in circadian rhythms—cycles based on a 24-hour period. Living organisms depend upon these clocks to keep pace with the Earth's daily rotation and the recurring changes it imposes on the environment. These clocks allow the plant or animal to anticipate the changes and adapt to them by modifying its biology, behavior, and biochemistry.
"If you know that the sun is going to go down, and if you are a photosynthetic plant, you have to readjust ...