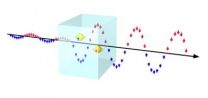
(Press-News.org) A fundamental cornerstone for spintronics that has been missing up until now has been constructed by a team of physicists at Linköping University in Sweden. It's the world's first spin amplifier that can be used at room temperature.
Great hopes have been placed on spintronics as the next big paradigm shift in the field of electronics. Spintronics combines microelectronics, which is built on the charge of electrons, with the magnetism that originates in the electrons' spin. This lays the foundation for entirely new applications that fire the imagination. The word "spin" aims at describing how electrons spin around, much like how the Earth spins on its own axis.
But turning theory into practice requires amplifying these very weak signals. Instead of transistors, rectifiers, and so on, the building blocks of spintronics will be formed by things like spin filters, spin amplifiers, and spin detectors. Through regulating and controlling electron spin, it will be possible to store data more densely and process it many times faster – and with greater energy efficiency – than today's technology.
In 2009, an LiU group from the Department of Functional Electronic Material, led by Professor Weimin Chen, presented a new type of spin filter that works at room temperature. The filter lets through electrons that have the desired spin direction, screening out the others. This function is crucial for constructing new types of components such as spin diodes and spin lasers.
Now the same group, in collaboration with colleagues from Germany and the United States, has published an article in the highly-ranked journal Advanced Materials, where they present an effective spin amplifier based on a non-magnetic semiconductor. The amplification occurs through deliberate defects in the form of extra gallium atoms introduced into an alloy of gallium, indium, nitrogen and arsenic.
A component of this kind can be set anywhere along a path of spin transport to amplify signals that have weakened along the way. By combining this with a spin detector, it may be possible to read even extremely weak spin signals.
"It's an advance that blazes a trail for a solution to the problem of controlling and detecting electron spin at room temperature, which is a prerequisite for the breakthrough of spintronics," says Weimin Chen.
INFORMATION:
Article: Room-temperature electron spin amplifier based on Ga(In)NAs alloys by Y. Puttisong, I.A. Buyanova, A.J. Ptak, C.W. Tu, L. Geelhaar, H. Richert and W.M. Chen. Advanced Materials online 26 October 2012. DOI 10.1002/adma.20120597
Important progress for spintronics
A spin amplifier to be used in room temperature
2012-11-16
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Melt water on Mars could sustain life
2012-11-16
Near surface water has shaped the landscape of Mars. Areas of the planet's northern and southern hemispheres have alternately thawed and frozen in recent geologic history and comprise striking similarities to the landscape of Svalbard. This suggests that water has played a more extensive role than previously envisioned, and that environments capable of sustaining life could exist, according to new research from the University of Gothenburg, Sweden.
Mars is a changing planet, and in recent geological time repeated freeze and thaw cycles has played a greater role than expected ...
Reconsidering cancer's bad guy
2012-11-16
Researchers at the University of Copenhagen have found that a protein, known for causing cancer cells to spread around the body, is also one of the molecules that trigger repair processes in the brain. These findings are the subject of a paper, published this week in Nature Communications. They point the way to new avenues of research into degenerative brain diseases like Alzheimer's.
How to repair brain injuries is a fundamental question facing brain researchers. Scientists have been familiar with the protein S100A4 for some time as a factor in metastasis, or how cancer ...
Dartmouth research: The clocks are ticking and the climate is changing
2012-11-16
Dartmouth plant biologist C. Robertson (Rob) McClung is not your typical clock-watcher. His clocks are internal, biological, and operate in circadian rhythms—cycles based on a 24-hour period. Living organisms depend upon these clocks to keep pace with the Earth's daily rotation and the recurring changes it imposes on the environment. These clocks allow the plant or animal to anticipate the changes and adapt to them by modifying its biology, behavior, and biochemistry.
"If you know that the sun is going to go down, and if you are a photosynthetic plant, you have to readjust ...
Dartmouth research pursues problematic polymers
2012-11-16
"You look at the material world and see objects and how you can use them. I look at the material world and see a fascinating hidden life which is within our control, if we can only understand how it works," says Jane Lipson, the Albert W. Smith Professor of Chemistry at Dartmouth. Lipson looks at things from the point of view of both a chemist and a physicist. "What I do lies between the two sciences, and there is some engineering thrown in there, too," she says.
Lipson is a polymer chemist who, by definition, deals with long chain molecules composed of repeating structural ...
Are we closer to understanding the cause of deadly sepsis?
2012-11-16
New Rochelle, NY, November 13, 2012—Following an infection, dysregulation of the immune system can result in a systemic inflammatory response and an often fatal condition called severe sepsis or septic shock. Sepsis is not uncommon, yet its cause and underlying immune dysfunction remain poorly understood. Regulatory T cells (Tregs), a component of the immune system, now appear to have an important role in suppressing the immune response in advance of sepsis, and understanding this role may lead to new therapeutic strategies for improving patient outcomes, as described in ...
Gene distinguishes early birds from night owls and helps predict time of death
2012-11-16
BOSTON – Many of the body's processes follow a natural daily rhythm or so-called circadian clock. There are certain times of the day when a person is most alert, when blood pressure is highest, and when the heart is most efficient. Several rare gene mutations have been found that can adjust this clock in humans, responsible for entire families in which people wake up at 3 a.m. or 4 a.m. and cannot stay up much after 8 at night. Now new research has, for the first time, identified a common gene variant that affects virtually the entire population, and which is responsible ...
ORNL recipe for oxide interface perfection opens path to novel materials
2012-11-16
By tweaking the formula for growing oxide thin films, researchers at the Department of Energy's Oak Ridge National Laboratory achieved virtual perfection at the interface of two insulator materials.
This finding, published in the journal Advanced Materials, could have significant ramifications for creation of novel materials with applications in energy and information technologies, leading to more efficient solar cells, batteries, solid oxide fuel cells, faster transistors and more powerful capacitors.
The research team, led by ORNL's Ho Nyung Lee, demonstrated that ...
Teenagers urged to exercise to ward off bone disease
2012-11-16
An international team, including an expert from the University of Exeter, has found evidence that adolescents who spend long periods engaged in certain sedentary activities are more likely to have low bone mineral content in parts of the body where it can be an indicator of the risk of developing osteoporosis.
In the research, published by PubMed on November 15, the team found that studying put girls at particular risk, while for boys leisure internet use posed the greatest threat. Scientists found that participating in at least three hours of certain sports could significantly ...
How does groundwater pumping affect streamflow?
2012-11-16
Groundwater provides drinking water for millions of Americans and is the primary source of water to irrigate cropland in many of the nations most productive agricultural settings. Although the benefits of groundwater development are many, groundwater pumping can reduce the flow of water in connected streams and rivers—a process called streamflow depletion by wells. The USGS has released a new report that summarizes the body of knowledge on streamflow depletion, highlights common misconceptions, and presents new concepts to help water managers and others understand the effects ...
USDA funded research leads to key discoveries in the pig genome
2012-11-16
WASHINGTON, Nov. 15, 2012 – Research conducted and supported by the U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA) has led to a new analysis of the pig genome, revealing new similarities between pigs and humans that could potentially advance biomedical research significantly. Additional findings from the study, reported today in the journal Nature, may also lead to better breeding strategies, improved pork production and improvements to human health. The research was conducted by a global team of scientists as part of the International Swine Genome Sequence Consortium (ISGSC).
"This ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Carsten Bönnemann, MD, joins St. Jude to expand research on pediatric catastrophic neurological disorders
Women use professional and social networks to push past the glass ceiling
Trial finds vitamin D supplements don’t reduce covid severity but could reduce long COVID risk
Personalized support program improves smoking cessation for cervical cancer survivors
Adverse childhood experiences and treatment-resistant depression
Psilocybin trends in states that decriminalized use
New data signals high demand in aesthetic surgery in southern, rural U.S. despite access issues
$3.4 million grant to improve weight-management programs
Higher burnout rates among physicians who treat sickle cell disease
Wetlands in Brazil’s Cerrado are carbon-storage powerhouses
Brain diseases: certain neurons are especially susceptible to ALS and FTD
Father’s tobacco use may raise children’s diabetes risk
Structured exercise programs may help combat “chemo brain” according to new study in JNCCN
The ‘croak’ conundrum: Parasites complicate love signals in frogs
Global trends in the integration of traditional and modern medicine: challenges and opportunities
Medicinal plants with anti-entamoeba histolytica activity: phytochemistry, efficacy, and clinical potential
What a releaf: Tomatoes, carrots and lettuce store pharmaceutical byproducts in their leaves
Evaluating the effects of hypnotics for insomnia in obstructive sleep apnea
A new reagent makes living brains transparent for deeper, non-invasive imaging
Smaller insects more likely to escape fish mouths
Failed experiment by Cambridge scientists leads to surprise drug development breakthrough
Salad packs a healthy punch to meet a growing Vitamin B12 need
Capsule technology opens new window into individual cells
We are not alone: Our Sun escaped together with stellar “twins” from galaxy center
Scientists find new way of measuring activity of cell editors that fuel cancer
Teens using AI meal plans could be eating too few calories — equivalent to skipping a meal
Inconsistent labeling and high doses found in delta-8 THC products: JSAD study
Bringing diabetes treatment into focus
Iowa-led research team names, describes new crocodile that hunted iconic Lucy’s species
One-third of Americans making financial trade-offs to pay for healthcare
[Press-News.org] Important progress for spintronicsA spin amplifier to be used in room temperature