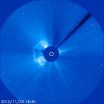
(Press-News.org) On Nov. 23, 2012, at 8:54 a.m. EST, the sun erupted with an Earth-directed coronal mass ejection or CME. Experimental NASA research models, based on observations from the Solar Terrestrial Relations Observatory (STEREO) and the ESA/NASA mission the Solar and Heliospheric Observatory, show that the Nov. 23 CME left the sun at speeds of 375 miles per second, which is a slow to average speed for CMEs. This is the third Earth-directed CME since Nov. 20.
Not to be confused with a solar flare, a CME is a solar phenomenon that can send solar particles into space and can reach Earth one to three days later. When Earth-directed, CMEs can cause a space weather phenomenon called a geomagnetic storm, which occurs when CMEs successfully connect up with the outside of the Earth's magnetic envelope, the magnetosphere, for an extended period of time. In the past, CMEs of this speed have not usually caused substantial geomagnetic storms. They have caused auroras near the poles but are unlikely to cause disruptions to electrical systems on Earth or interfere with GPS or satellite-based communications systems.
INFORMATION:
NOAA's Space Weather Prediction Center is the United States Government official source for space weather forecasts.
Continuing Thanksgiving eruptions on the sun
2012-11-26
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Personalities influence workforce planning
2012-11-26
Montreal, November 26, 2012 – What if factory foremen treated their workers less like the machines they operate, and more like people, with personality strengths and differences? Surely the workers would benefit, but might the employers also see positive results in the workplace, as well as being able to cut costs?
That's what Concordia researcher Mohammed Othman set out to prove in his paper "Integrating workers' differences into workforce planning," recently published in the journal Computers & Industrial Engineering.
Currently, explained Othman, two types of researchers ...
Bothered by negative, unwanted thoughts? Just throw them away
2012-11-26
COLUMBUS, Ohio -- If you want to get rid of unwanted, negative thoughts, try just ripping them up and tossing them in the trash.
In a new study, researchers found that when people wrote down their thoughts on a piece of paper and then threw the paper away, they mentally discarded the thoughts as well.
On the other hand, people were more likely to use their thoughts when making judgments if they first wrote them down on a piece of paper and tucked the paper in a pocket to protect it.
"However you tag your thoughts -- as trash or as worthy of protection -- seems to ...
Scientists analyze millions of news articles
2012-11-26
A study led by academics at the University of Bristol's Intelligent Systems Laboratory and the School of Journalism at Cardiff University have used Artificial Intelligence (AI) algorithms to analyse 2.5 million articles from 498 different English-language online news outlets over ten months.
The researchers found that:
• As expected, readability measures show that online tabloid newspapers are more readable than broadsheets and use more sentimental language. Among 15 US and UK newspapers, the Sun is the easiest to read, comparable to the BBC's children's news programme, ...
Scientists from Bangalore and Mainz develop new methods for cooling of ions
2012-11-26
Among the most important techniques developed in atomic physics over the past few years are methods that enable the storage and cooling of atoms and ions at temperatures just above absolute zero. Scientists from Bangalore and Mainz have now demonstrated in an experiment that captured ions can also be cooled through contact with cold atoms and may thus be stored in so-called ion traps in a stable condition for longer periods of time. This finding runs counter to predictions that ions would actually be heated through collisions with atoms. The results obtained by the joint ...
Geometries presented by Chinese scholars for all possible space-time kinematics and their relations
2012-11-26
The possible kinematics and their corresponding geometries were once regarded as an already-solved problem. The de Sitter relativity research group formed by researchers from Chinese Academy of Sciences, Tsinghua University, and Beijing Normal University, restudied the problem and showed that additional, previously unknown realizations exist of possible kinematical algebras, each of which has so(3) isotropy and a ten-generators symmetry group. They presented these geometries corresponding to all these realizations and provided a classification in an article, entitled "Geometries ...
Interannual variability in soil respiration from terrestrial ecosystems in China
2012-11-26
Soil respiration is a critical hydrological process that plays an important role in the terrestrial carbon cycle. Associate Professor CHEN ShuTao and his colleagues from the School of Environmental Science and Engineering at Nanjing University of Information Science and Technology set out to estimate annual soil respiration from terrestrial ecosystems in China. They have tabulated published estimates of annual soil respiration and developed an empirically based, semi-mechanistic model that includes climate and soil properties. They found that the highest and lowest annual ...
Yuzhou Flora -- a hidden gem of the Middle and Late Permian Cathaysian Flora
2012-11-26
About 250 million years ago, four major floral provinces existed on the Earth's surface, the Gondwana Floral Province in temperate Southern Hemisphere, the Angara Floral Province in temperate Northern Hemisphere, and the Euroamerican and the Cathaysian floral provinces in tropical equatorial regions. These floras evolved as the continents drifted. The Cathaysian Flora is mainly distributed in most areas of today's China, Japan, and Southeast Asia. North China lies at the center of the origin of the Cathaysian Flora. During the Permian, the southern part of the North China ...
Destruction of the North China Craton
2012-11-26
Archean cartons are commonly underlain by a cold, thick (>200 km), isotopically enriched, and compositionally refractory lithospheric keel, and represent some of the most stable regions on our planet. However, the North China Craton (NCC), an old continental geological structure dating back 4.0 Ga, is underlain by a thin lithosphere ( END ...
Putrescine water may be Fountain of Youth for eggs
2012-11-26
This press release is available in French.
Ottawa — An Ottawa scientist has discovered a critical reason why women experience fertility problems as they get older. The breakthrough by Dr. Johné Liu, a senior scientist at the Ottawa Hospital Research Institute and professor at the University of Ottawa, also points to a simple solution that could increase the viability of egg cells for women in their late 30s and older — putrescine water.
In an online editorial published by Aging based on his recently published findings, Liu outlines how a simple program of drinking water ...
Combination of two pharmaceuticals proves effective in the treatment of multiple sclerosis
2012-11-26
Bonn/Magdeburg/Halle, 26/11/2012. A new substance class for the treatment of multiple sclerosis and other neurodegenerative diseases now promises increased efficacy paired with fewer side effects. To achieve this, a team of scientists under the leadership of Prof. Gunter Fischer (Max Planck Research Unit for Enzymology of Protein Folding, Halle/Saale, Germany) and Dr. Frank Striggow (German Center for Neurodegenerative Diseases (DZNE)) have combined two already approved pharmaceutical substances with each other using a chemical linker structure. The objectives of this combination ...