(Press-News.org) The twenty-sixth tropical cyclone of the western North Pacific Ocean season formed and has some areas of heavy rain, according to data from NASA's TRMM satellite. Tropical Depression 26W is threatening islands within Micronesia and warnings and watches are currently in effect.
Micronesia is a region in the western North Pacific Ocean made up of thousands of small islands. West of the region is the Philippines, while Indonesia is located to the southwest.
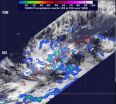
NASA's Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission (TRMM) satellite passed over Tropical Depression 26W on Nov. 26 at 0526 UTC (12:26 a.m. EST). The imagery showed that the depression's low-level center was large, and it had some fragmented convective bands of thunderstorms wrapping around it that contained heavy rain, falling at 2 inches/50 mm per hour. TRMM data also revealed tall convective towering thunderstorms about 15 kilometers (9.3 miles) high. According to previous NASA research, those "hot towers" usually signify that a tropical cyclone will intensify.
According to NOAA's National Weather Service in Tiyan, Guam, a tropical storm warning remains in effect for Nukuoro in Pohnpei State and Lukunor in Chuuk State. A tropical storm watch remains in effect for Losap and for Chuuk Lagoon Islands in Chuuk State.
A tropical storm warning means tropical storm conditions, including damaging winds of 39 to 73 mph are expected within 24 hours while a tropical storm watch means that tropical storm conditions are possible within 48 hours.
At 1500 UTC (10 a.m. EST) on Nov. 26, 2012, Tropical Depression 26W (TD26W) was centered near 4.8 degrees north latitude and 155.1 degrees east longitude. That put TD26W's center about 65 miles north of Nukuoro, 95 miles southeast of Lukunor, and 215 miles southeast of Losap. The National Weather Service noted that TD26W is moving west-northwest at 7 mph and is expected to move in a more westerly direction and slightly speed up over the next day. Maximum sustained winds are near 35 mph, and could become a tropical storm later today, Nov. 26.
Forecasters at the Joint Typhoon Warning Center expect Tropical Depression 26W to track to the west-northwest over the next several days and strengthen to typhoon status as it tracks through the warm waters of the Philippine Sea. TD26W is forecast to pass just south of Chuuk and affect Yap and Palau by the weekend of Dec. 1 and Dec. 2.
INFORMATION:
NASA spots heavy rainfall in Tropical Depression 26W threatening Micronesia
2012-11-27
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Scatter radiation from mammography presents no cancer risk
2012-11-27
CHICAGO – The radiation dose to areas of the body near the breast during mammography is negligible, or very low, and does not result in an increased risk of cancer, according to a study presented today at the annual meeting of the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA). The results suggest that the use of thyroid shields during mammography is unnecessary.
"Thyroid shields can impede good mammographic quality and, therefore, are not recommended during mammography," said Alison L. Chetlen, D.O., assistant professor of radiology at Penn State Hershey Medical Center.
During ...
Radiologic and physical findings identify elder abuse
2012-11-27
CHICAGO – Radiologists in Toronto have begun to identify a pattern of injuries that may be indicative of elder abuse, according to a study presented today at the annual meeting of the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA).
According to lead researcher Kieran J. Murphy, M.D., F.R.C.P.C., F.S.I.R., interim radiologist-in-chief at University Health Network in Toronto, Canada, only 2 percent of physical elder abuse is reported by clinicians.
"Unlike cases of child abuse, there is very little information available on this subject," Dr. Murphy said. "It's a much ...
Breast cancer risk estimates increased with repeated prior ct and nuclear imaging
2012-11-27
CHICAGO – Researchers reviewing the records of approximately 250,000 women enrolled in an integrated healthcare delivery system found that increased CT utilization between 2000 and 2010 could result in an increase in the risk of breast cancer for certain women, including younger patients and those who received repeat exams. According to the study, which was presented today at the annual meeting of the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA), nuclear medicine examinations may also contribute to increased breast cancer risk.
CT uses ionizing radiation in the form ...
Women with dense breasts welcome additional screening
2012-11-27
CHICAGO – A survey of women undergoing routine screening mammography found that many of them would be interested in pursuing additional screening tests if notified they had dense breast tissue, despite the possibility of false positives, invasive procedures, and out-of-pocket costs, according to a study presented today at the annual meeting of the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA).
"Our study highlights the need for patient education regarding breast density," said Jafi Lipson, M.D., assistant professor of radiology at Stanford University School of Medicine ...
New studies show effects of mammography guideline changes
2012-11-27
CHICAGO – Researchers assessing the impact of revised guidelines for screening mammography issued by the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) found evidence that the new recommendations may lead to missed cancers and a decline in screening, according to two studies presented today at the annual meeting of the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA).
Routine screening mammography has traditionally been recommended by both the USPSTF and the American Cancer Society for all women over the age of 40. In 2009, the USPSTF issued controversial new guidelines recommending ...
Researchers identify physiological evidence of 'chemo brain'
2012-11-27
CHICAGO – Chemotherapy can induce changes in the brain that may affect concentration and memory, according to a study presented today at the annual meeting of the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA). Using positron emission tomography combined with computed tomography (PET/CT), researchers were able to detect physiological evidence of chemo brain, a common side effect in patients undergoing chemotherapy for cancer treatment.
"The chemo brain phenomenon is described as 'mental fog' and 'loss of coping skills' by patients who receive chemotherapy," said Rachel ...
A new look at wetting models: Continuum analysis
2012-11-27
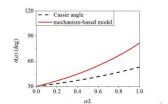
The wetting model is a classical problem in surface science and biomimetic science. Professor LIU Jianlin and his collaborators from China University of Petroleum, Wuhan University and Fourth Military Medical University approached this old and classical problem from a new direction. They stressed that it is the triple contact line and not the contact area of the droplet/solid interface that determines the macroscopic contact angle. The proposed continuum model, termed the mechanism-based model, can illustrate the contact line pinning effect at some wedges or phase interfaces ...
Gene that causes tumor disorder linked to increased breast cancer risk
2012-11-27
New Johns Hopkins research showing a more than four-fold increase in the incidence of breast cancer in women with neurofibromatosis-1 (NF1) adds to growing evidence that women with this rare genetic disorder may benefit from early breast cancer screening with mammograms beginning at age 40, and manual breast exams as early as adolescence.
In a small study of 126 women with NF1 at the Johns Hopkins Comprehensive Neurofibromatosis Center, the Johns Hopkins scientists identified four cases of breast cancer. The study showed a four-fold increased risk for breast cancer in ...
Researchers find chemical 'switches' for neurodegenerative diseases
2012-11-27
By using a model, researchers at the University of Montreal have identified and "switched off" a chemical chain that causes neurodegenerative diseases such as Huntington's disease, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and dementia. The findings could one day be of particular therapeutic benefit to Huntington's disease patients. "We've identified a new way to protect neurons that express mutant huntingtin proteins," explained Dr. Alex Parker of the University of Montreal's Department of Pathology and Cell Biology and its affiliated CRCHUM Research Centre. A cardinal feature of ...
Four Steps to Protect Your Finances During a Divorce
2012-11-27
Four Steps to Protect Your Finances During a Divorce
Divorce is not only emotionally draining, but it also can be financially draining if you do not carefully plan your finances. With the current divorce rate in America sitting at 40 to 50 percent, divorce is a prevalent issue for many people. When going through a divorce, you can avoid financial turmoil by following a few simple planning tips.
Assess the Impact of Divorce on Your Financial Goals
Project future expenses that the divorce will create as well as any future expenses to which you will now contribute ...