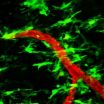
(Press-News.org) High-resolution real-time images show in mice how nerves may be damaged during the earliest stages of multiple sclerosis. The results suggest that the critical step happens when fibrinogen, a blood-clotting protein, leaks into the central nervous system and activates immune cells called microglia.
"We have shown that fibrinogen is the trigger," said Katerina Akassoglou, Ph.D., an associate investigator at the Gladstone Institute for Neurological Disease and professor of neurology at the University of California, San Francisco, and senior author of the paper published online in Nature Communications.
Multiple sclerosis, or MS, is thought to be an autoimmune disease in which cells that normally protect the body against infections attack nerve cells in the brain and spinal cord, often leading to problems with vision, muscle strength, balance and coordination, thinking and memory. Typically during MS, the immune cells destroy myelin, a protective sheath surrounding nerves, and eventually leading to nerve damage. The immune attack also causes leaks in the blood-brain barrier, which normally separates the brain from potentially harmful substances in the blood.
"Dr. Akassoglou has focused on the role of the blood-brain barrier leak in MS and has discovered that leakage of the blood clotting protein fibrinogen can trigger brain inflammation," said Ursula Utz, Ph.D., M.B.A., a program director at NIH's National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NINDS).
Microglia are cells traditionally thought to control immunity in the nervous system. Previous studies suggested that leakage of fibrinogen activates microglia. In this study, Dr. Akassoglou and her colleagues used a cutting-edge imaging technique called two-photon laser scanning microscopy to watch what happens in an animal model of MS.
"Our results provide the first evidence linking leakage of fibrinogen to neuronal damage," said Dr. Akassoglou, "Vascular changes are the instigator of neurotoxicity."
Using a mouse model of MS, the researchers found that leakage of fibrinogen and microglial activation occurred days before nerve damage began, suggesting they occur in an early, pre-clinical stage of the disease.
During this period, microglia changed shapes and clustered around blood vessels along with other immune cells. Further experiments suggested that fibrinogen activated microglia by binding to a receptor, called CD11b/CD18, which caused the microglia to release reactive oxygen molecules that, in turn, damaged neurons. Inhibiting the binding of fibrinogen to the receptor prevented microglial activation and nerve damage.
Current treatments for MS are designed to suppress autoimmunity. The results from this study suggest that targeting the interaction between fibrinogen and microglia may be an effective alternative. In the mice, blocking fibrinogen's blood clotting activity prevented microglial activation and nerve damage.
"Current drugs target primarily downstream events. This interaction could be an upstream target that suppresses immunity and neurodegeneration," said Dr. Akassoglou.
In 2006, Dr. Akassoglou received a Presidential Early Career Award for Scientists and Engineers, which honors and supports the finest and most promising researchers early in their careers.
INFORMATION:
This study was supported by NINDS (NS051470, NS052189, NS066361); the National Cancer Institute (CA082103); the National Center for Research Resources (RR004050), the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (HL096126), the American Heart Association, the Bechtel Foundation, the Dana Program in Brain and Immuno-imaging, the H. Lundbeck A/S, the Howard Hughes Medical Institute, the National Multiple Sclerosis Society, the Nancy Davis Foundation for Multiple Sclerosis, and the March of Dimes.
Reference: Davalos et al., "Fibrinogen-induced perivascular microglial clustering is required for the development of axonal damage in neuroinflammation." Nature Communications, published online November 27, 2012. DOI: 10.1038/ncomms2230
NINDS is the nation's leading funder of research on the brain and nervous system. The NINDS mission is to reduce the burden of neurological disease – a burden borne by every age group, by every segment of society, by people all over the world.
About the National Institutes of Health (NIH): NIH, the nation's medical research agency, includes 27 Institutes and Centers and is a component of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. NIH is the primary federal agency conducting and supporting basic, clinical, and translational medical research, and is investigating the causes, treatments, and cures for both common and rare diseases. For more information about NIH and its programs, visit http://www.nih.gov.
NIH-funded researchers show possible trigger for MS nerve damage
Results of study in mice may lead to new treatments
2012-11-28
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Rocks, water, air, space ... and humans: An NSF recipe for AGU success
2012-11-28
The National Science Foundation is suggesting adding a bit of spice to a geophysical scientist's research recipe of rocks, water, air, space and life:
Humans.
At next month's Fall Meeting of the American Geophysical Union (AGU) a behemoth of a conference of nearly 20,000 Earth and space scientists, educators, students and policy makers, an international group of scientists will make the case for adding the human element to their research.
The International Network of Research in Coupled Human and Natural Systems – CHANS-Net – is supported by the National Science ...
Kentucky study finds common drug increases deaths in atrial fibrillation patients
2012-11-28
LEXINGTON, Ky. (Nov. 27, 2012) -- Digoxin, a drug widely used to treat heart disease, increases the possibility of death when used by patients with a common heart rhythm problem − atrial fibrillation (AF), according to new study findings by University of Kentucky researchers. The results have been published in the prestigious European Heart Journal, and raises serious concerns about the expansive use of this long-standing heart medication in patients with AF.
UK researchers led by Dr. Samy Claude Elayi, associate professor of medicine at UK HealthCare's Gill Heart ...
Scripps Research Institute study points to potential new therapies for cancer and other diseases
2012-11-28
LA JOLLA, CA – November 27, 2012 – Researchers at The Scripps Research Institute (TRSI) are fueling the future of cancer treatment by improving a powerful tool in disease defense: the body's immune system. By revealing a novel but widespread cell signaling process, the scientists may have found a way to manipulate an important component of the immune system into more effectively fighting disease.
The study, recently published online ahead of print by the journal Blood, shows that disabling a particular enzyme, called ItpkB, in mice improves the function of a type of immune ...
New thermoelectric material could be an energy saver
2012-11-28
By using common materials found pretty much anywhere there is dirt, a team of Michigan State University researchers have developed a new thermoelectric material.
This is important, they said, because the vast majority of heat that is generated from, for example, a car engine, is lost through the tail pipe. It's the thermoelectric material's job to take that heat and turn it into something useful, like electricity.
The researchers, led by Donald Morelli, a professor of chemical engineering and materials science, developed the material based on natural minerals known ...
Princeton research: Embracing data 'noise' brings Greenland's complex ice melt into focus
2012-11-28
VIDEO:
Princeton University researchers developed an enhanced approach to capturing changes on the Earth's surface via satellite that could provide a more accurate account of how geographic areas change as a...
Click here for more information.
An enhanced approach to capturing changes on the Earth's surface via satellite could provide a more accurate account of how ice sheets, river basins and other geographic areas are changing as a result of natural and human factors. ...
'Fountain of youth' technique rejuvenates aging stem cells
2012-11-28
Toronto, ON (27 November, 2012) -- A new method of growing cardiac tissue is teaching old stem cells new tricks. The discovery, which transforms aged stem cells into cells that function like much younger ones, may one day enable scientists to grow cardiac patches for damaged or diseased hearts from a patient's own stem cells—no matter what age the patient—while avoiding the threat of rejection.
Stem cell therapies involving donated bone marrow stem cells run the risk of patient rejection in a portion of the population, argues Milica Radisic, Canada Research Chair in ...
How vegetables make the meal
2012-11-28
Parents may have some new motivations to serve their kids vegetables. A new Cornell University study, published in Public Health Nutrition, found that by simply serving vegetables with dinner, the main course would taste better and the preparer was perceived to be more thoughtful and attentive.
"Most parents know that vegetables are healthy, yet vegetables are served at only 23% of American dinners," said lead author Brian Wansink, PhD, the John Dyson Professor of Marketing and Consumer Behavior at Cornell University. "If parents knew that adding vegetables to the plate ...
GSA Bulletin: From Titan to Tibet
2012-11-28
Boulder, Colo., USA – GSA Bulletin articles posted online between 2 October and 21 November span locations such as the San Andreas fault, California; Tibet; Mongolia; Maine; the Owyhee River, Oregon; the Afar Rift, Ethiopia; Wyoming; Argentina; the Sinai Peninsula, Egypt; British Columbia; the southern Rocky Mountains; Scandinavia; and Saturn's largest moon, Titan. Topics include the "big crisis" in the history of life on Earth; the structural geology of Mount St. Helens; and the evolution of a piggyback basin.
GSA Bulletin articles published ahead of print are online ...
NASA's TRMM satellite confirms 2010 landslides
2012-11-28
A NASA study using TRMM satellite data revealed that the year 2010 was a particularly bad year for landslides around the world.
A recent NASA study published in the October issue of the Journal of Hydrometeorology compared satellite rain data from NASA's Tropical Rainfall Measurement Mission (TRMM) to landslides in central eastern China, Central America and the Himalayan Arc, three regions with diverse climates and topography where rainfall-triggered landslides are frequent and destructive hazards to the local populations.
The work, led by Dalia Kirschbaum, a research ...
Fast forward to the past: NASA technologists test 'game-changing' data-processing technology
2012-11-28
It's a digital world. Or is it?
NASA technologist Jonathan Pellish isn't convinced. In fact, he believes a computing technology of yesteryear could potentially revolutionize everything from autonomous rendezvous and docking to remotely correcting wavefront errors on large, deployable space telescope mirrors like those to fly on the James Webb Space Telescope.
"It's fast forward to the past," Pellish said, referring to an emerging processing technology developed by a Cambridge, Mass.-based company, Analog Devices Lyric Labs.
So convinced is he of its potential, Pellish ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Increased risk of bullying in open-plan offices
Frequent scrolling affects perceptions of the work environment
Brain activity reveals how well we mentally size up others
Taiwanese and UK scientists identify FOXJ3 gene linked to drug-resistant focal epilepsy
Pregnancy complications impact women’s stress levels and cardiovascular risk long after delivery
Spring fatigue cannot be empirically proven
Do prostate cancer drugs interact with certain anticoagulants to increase bleeding and clotting risks?
Many patients want to talk about their faith. Neurologists often don't know how.
AI disclosure labels may do more harm than good
The ultra-high-energy neutrino may have begun its journey in blazars
Doubling of new prescriptions for ADHD medications among adults since start of COVID-19 pandemic
“Peculiar” ancient ancestor of the crocodile started life on four legs in adolescence before it began walking on two
AI can predict risk of serious heart disease from mammograms
New ultra-low-cost technique could slash the price of soft robotics
Increased connectivity in early Alzheimer’s is lowered by cancer drug in the lab
Study highlights stroke risk linked to recreational drugs, including among young users
Modeling brain aging and resilience over the lifespan reveals new individual factors
ESC launches guidelines for patients to empower women with cardiovascular disease to make informed pregnancy health decisions
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
[Press-News.org] NIH-funded researchers show possible trigger for MS nerve damageResults of study in mice may lead to new treatments