(Press-News.org) Using an enhanced form of "chemical microscopy" developed at the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), researchers there have shown that they can peer into the structure of blended polymers, resolving details of the molecular arrangement at sub-micrometer levels.* The capability has important implications for the design of industrially important polymers like the polyethylene blends used to repair aging waterlines.
Polyethylene is one of the most widely produced and used polymers in the world. It's used in many familiar applications—milk bottles, for instance—but the NIST research is motivated by a more critical application: water pipes. Aging water infrastructure is a significant national issue. The Environmental Protection Agency has reported that in the United States there are over 240,000 water main breaks per year, leaks wasting 1.7 trillion gallons of water per year, and costs to taxpayers of $2.6 billion per year.
Polyethylene pipes are one potential solution. They're relatively inexpensive to make and install, and they have negligible corrosion issues and a predicted service life of up to a century under ideal conditions. Unfortunately, current test standards do not address service life under field conditions, especially for fusion joints in the pipes. This uncertainty has slowed the use of large diameter polyethylene pipe.
The industry standard for polyethylene pipes is a blend of two different forms of the polymer, a medium-weight, high-density polyethylene (HDPE) and a high molecular weight "linear low-density polyethylene" (LLDPE). Combining the two, says NIST materials scientist Young Jong Lee, dramatically improves the toughness, strength and resistance to fracture of the polymer.
The problem for quantitative service-life prediction is understanding exactly why that is. Developing the necessary predictive models has been hindered by knowing just how the HDPE and LLDPE molecules blend together. They are so close chemically that X-ray or electron imaging—the usual go-to techniques for molecular structure—can't readily distinguish them.
The NIST team is using a variation of Raman spectroscopy, which can distinguish different chemical species—and measure how much of each—by analyzing the frequencies associated with the different vibrational modes of each molecule. The exact mix of these frequencies is an extremely discriminating "fingerprint" for any particular molecule without help of fluorescence labeling. Raman spectroscopy using focused laser beams has been used as a chemical microscope, able to detail the structure of complex objects by mapping the chemical composition at each point in a three-dimensional space.
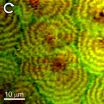
The NIST instrument, called "BCARS" (broadband coherent anti-Stokes Raman scattering) microscopy, uses a pair of lasers to gather Raman data at least 10 times faster than other Raman imaging methods, a critical feature because of the vast amount of data that must be gathered to understand such highly structured blend systems.** The extra trick is to substitute deuterium ("heavy hydrogen") for hydrogen atoms in the HDPE component. The deuterium strongly shifts the Raman spectrum, making it easy to distinguish the two components. By controlling the polarization of the light, the technique provides additional details on the local crystal orientation of molecules in the polymer. The images show, for example, the formation of microscopic spherical regions of partial crystallization with the LLDPE more concentrated towards the center.
"This is a fast, three-dimensional chemical imaging technique that's particularly useful for studying microstructures of polymeric materials," says Lee.
INFORMATION:
The group currently is using BCARS to find the correlation between microscopic structures with characteristics of deformation and thermal fusion on polyethylene pipes. For more on Broadband CARS microscopy, see www.nist.gov/mml/bbd/biomaterials/bcars.cfm.
* Y.J. Lee, C.R. Snyder, A.M. Forster, M.T. Cicerone and W. Wu. Imaging the molecular structure of polyethylene blends with broadband coherent Raman microscopy. ACS Macro Lett. 2012, 1, 1347-1351.DOI: dx.doi.org/10.1021/mz300546e.
** See, for example, the Oct. 2010 story, "Faster CARS, Less Damage: NIST Chemical Microscopy Shows Potential for Cell Diagnostics" at www.nist.gov/public_affairs/tech-beat/tb20101013.cfm#cars.
Mix masters: NIST scientists image the molecular structure of polymer blends
2012-11-28
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
USDA study shows trends in public and private agricultural R&D
2012-11-28
WASHINGTON, Nov. 26, 2012—Analysis published by the U.S. Department of Agriculture's (USDA) Economic Research Service (ERS) in the most recent issue of the journal Science examine the relationship between public and private investments in research and development (R&D) and their importance in agricultural input industries. The Science article is drawn from a recent ERS study that provides new details on the rapid growth and changing composition of private investments in global agricultural R&D and traces the implications for agriculture.
"Agriculture is more dependent ...
Hagfish slime as a model for tomorrow's natural fabrics
2012-11-28
Nylon, Kevlar and other synthetic fabrics: Step aside. If new scientific research pans out, people may be sporting shirts, blouses and other garments made from fibers modeled after those in the icky, super-strong slime from a creature called the hagfish. The study appears in ACS' journal Biomacromolecules.
Lead author Atsuko Negishi, her supervisor Douglas S. Fudge and colleagues explain that petroleum is the raw material for making modern synthetics. Rising prices and the quest for more sustainable alternatives have led scientists to consider the possibilities of using ...
Many home couches contain potentially toxic flame retardants
2012-11-28
Scientists are reporting an increasing use of flame retardants in the main gathering spot for adults, children and family pets in the home — the couch. In a study published in ACS' journal Environmental Science & Technology, they describe the first efforts to detect and identify the flame retardants applied to the foam inside couches found in millions of family rooms and living rooms across the U.S.
Heather Stapleton and colleagues explain that many U.S. manufacturers adhere to California's flammability standard — termed "Technical Bulletin 117" (TB117) — and use flame ...
Scientists sniff out the substances behind the aroma in the 'king of fruits'
2012-11-28
The latest effort to decipher the unique aroma signature of the durian — revered as the "king of fruits" in southeast Asia but reviled elsewhere as the world's foulest smelling food — has uncovered several new substances that contribute to the fragrance. The research appears in ACS' Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry.
Martin Steinhaus and colleagues explain that durian, available in Asian food shops in the United States and elsewhere, has a creamy yellowish flesh that can be eaten fresh or used in cakes, ice cream and other foods. Some people relish the durian's ...
Research criticizes young offenders' institution for gang-related violence
2012-11-28
A youth offending facility in the East Midlands has been criticised in a new report for taking criminals from rival gangs in Leicester and Nottingham.
The research, led by an academic at Nottingham University Business School, said that the policy by Glen Parva Young Offenders Institution to take criminals from both cities was a recipe for trouble and has led to an increase in violence and gang warfare.
In the report Dr Richard Simper, an associate professor in financial economics, says that rival young offenders should be separated in a bid to decrease the incidence ...
Tight times may influence how we perceive others
2012-11-28
From the playground to the office, a key aspect of our social lives involves figuring out who "belongs" and who doesn't. Our biases lead us -- whether we're aware of it or not -- to favor people who belong to our own social group. Scientists theorize that these prevalent in-group biases may give us a competitive advantage against others, especially when important resources are limited.
Psychological scientist Christopher Rodeheffer and his colleagues at Texas Christian University wanted to examine whether resource scarcity might actually lead us to change our definition ...
Changes in nerve cells may contribute to the development of mental illness
2012-11-28
Reduced production of myelin, a type of protective nerve fiber that is lost in diseases like multiple sclerosis, may also play a role in the development of mental illness, according to researchers at the Graduate School of Biomedical Sciences at Mount Sinai School of Medicine. The study is published in the journal Nature Neuroscience.
Myelin is an insulating material that wraps around the axon, the threadlike part of a nerve cell through which the cell sends impulses to other nerve cells. New myelin is produced by nerve cells called oligodendrocytes both during development ...
University of Cincinnati leads first trial on steroid and CNI withdrawal post-transplant
2012-11-28
CINCINNATI—The University of Cincinnati will lead a $5.2 million national trial studying removal of both corticosteroids and common immunosuppression treatments from the post-transplant drug regimen for kidney transplant patients.
The Belatacept Early Steroid withdrawal Trial (BEST) seeks to determine if a belatacept-based regimen for post-transplant patients can prevent organ rejection without the harmful side effects posed by corticosteroids and calcineurin inhibitor (CNI) immunosuppressants. Belatacept is a modified version of the drug abatacept, which is used to treat ...
NIST releases annual report on federal technology transfer
2012-11-28
With new treatments for disease, test suites that safeguard computers, and even expertise to rescue miners trapped thousands of feet underground, federal laboratories have a wealth of technologies and know-how that can give U.S. companies a competitive edge and improve quality of life.
These science and technology resources were developed in response to national challenges, but they also can be valuable assets for private industry and academia as well as other government agencies.
Each year—as required by federal regulation—the National Institute of Standards and Technology ...
Babies born to mothers from the Philippines significantly smaller than those of Canadian-born women
2012-11-28
TORONTO, Nov. 28, 2012—Babies born in Ontario to mothers from the Philippines have significantly lower birth weights than those whose mothers were born in Canada or elsewhere in East Asia and are twice as likely to be classified as small for their gestational age, a new study has found.
The classification is often incorrect, researchers say, because the babies are being compared to those of other ethnic backgrounds. When compared to other Filipino babies, they are well within appropriate heights and weights.
The lead author of the study, published online in the Journal ...