(Press-News.org) KINGSTON, R.I. – November 28, 2012 – A team of archaeologists from the University of Rhode Island, the Israel Antiquities Authority, and the University of Louisville have discovered the remains of a fleet of early-19th century ships and ancient harbor structures from the Hellenistic period (third to first century B.C.) at the city of Akko, one of the major ancient ports of the eastern Mediterranean. The findings shed light on a period of history that is little known and point to how and where additional remains may be found.
The discoveries were presented on November 15 and 17 in Chicago at the annual meeting of the American Schools of Oriental Research by URI assistant professors Bridget Buxton and William Krieger on behalf of the Israel Coast Exploration project.
According to Buxton, three of the four well-preserved shipwrecks found off the coast south of Akko were first detected using a sub-bottom profiler in 2011. Later, storms stripped off several meters of inshore sediments and temporarily revealed the wrecks, as well as an additional large vessel. The wrecks are now reburied.
During the brief time the shipwrecks were exposed, the Israel Antiquities Authority investigated one of them: a 32 meter vessel which still preserved its brass gudgeon (rudder socket) and many small artifacts, such as plates, a candlestick, and even a cooking pot with bones in it. Laboratory analyses completed this summer by the IAA revealed that the ship's wood came from Turkey. The team believes these ships may have belonged to the Egyptian navy under Admiral Osman Nurredin Bey, whose ships were severely damaged in his attempt to capture Akko in the Egyptian-Ottoman War of 1831. The town eventually fell to Egyptian land forces under Ibrahim Pasha in 1832.
"These ships have occasionally been exposed and buried again by storms since we found them," Buxton said. "We're in a race against time to find other ships in the area and learn from them before storms totally dislodge or destroy them."
Although shipwrecks from the 1800s are not the highest priorities in a region where civilization goes back thousands of years, Buxton is excited by the discovery for what it tells her about where much older ships may be found.
"Like many underwater archaeologists I'm very interested in finding a well-preserved example of an ancient multi-decked warship from the Hellenistic age," said Buxton. "These ships were incredible pieces of technology, but we don't know much about their design because no hulls have been found. However, a combination of unusual environmental and historical factors leads us to believe we have a chance of finding the remains of one of these ships off the northern coast of Israel."
Buxton believes that the ships they are looking for are likely buried in the coastal sediment, which has built up over the centuries through natural processes. However, time is not on their side. "That protective silt is now being stripped away," she said. "And it's being stripped away a lot faster than it was originally dumped, by a combination of development, environmental changes, and the effects of the Aswan Dam." The Nile River has historically deposited large quantities of silt in the area, but the dam has significantly reduced the flow of silt.
The archaeologists found the ships and another early modern vessel within Akko's modern harbor while testing their equipment in preparation for an ongoing survey out in deeper water. The sub-bottom profiler detects anomalies below the sea floor. "It's the gift that keeps on giving," Buxton said. "We found so many targets to explore that we didn't have time to check all of them, but even just having information about where things are helps Koby (Jacob Sharvit, director of the IAA Maritime Antiquities Unit) know where to look after any big storms."
One line of buried targets detected off the southern seawall of old Akko is particularly suggestive. Continuing excavations in this area over the summer revealed an alignment between these targets and a newly-discovered slipway and shipshed structure, which continued out under the sea floor 25 meters from the Ottoman city wall. The feature resembles other naval shipsheds found in places such as Athens where they were used to haul up ancient warships. The excavation project was initially undertaken to strengthen the eroding sea wall, but it also revealed Hellenistic masonry, pottery vessels, an ancient mooring stone, and a stone quay 1.3 meters below the modern sea level. The possibility that much more of the Hellenistic port lies well-preserved under the sea floor is exciting for the archaeologists, because it means that shipwrecks from earlier centuries that have so far not been found at Akko may simply be buried deeper down in the sediment.
"We've got fragmentary historic records for this area in the Hellenistic period, and now we've found a very important feature from the ancient harbor. Ancient shipwrecks are another piece of the puzzle that will help us to rewrite the story of this region at a critical time in Mediterranean history," she said.
Located on the northern coast of Israel, the UNESCO World Heritage Site of Akko is one of the few cities in the Mediterranean with more than 5,000 years of maritime history. Also known as Acre, Ake and Ptolemais, its port was an important waypoint for the Phoenicians, Romans, Crusaders, Ottomans and other ancient maritime empires. In the Hellenistic period, it was bitterly fought over by the rival empires of Egypt and Syria.
"Understanding the history and archaeology of Akko's port is crucial to understanding the broader issues of maritime connectivity and the great power struggles that defined the history of the Eastern Mediterranean during the Hellenistic Age," Buxton said.
INFORMATION: END
The diagnostic system used by many mental health practitioners in the United States -- known as the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders -- assumes that symptoms of two disorders that occur at the same time are additive and that the order in which the disorders are presented doesn't matter. But new research suggests that order actually plays a significant role in determining how clinicians think about psychiatric disorders.
In an article published in Clinical Psychological Science, a journal of the Association for Psychological Science, researchers Jared ...
Boulder, Colo., USA – Geosphere articles posted online 16 November 2012 cover a variety of topics, such as the geophysics of the Hogri fault zone, 5 km offshore of the Diablo Canyon nuclear power plant; using web-based GIS technologies and readily available global remote sensing datasets for investigations of arid land; the structure and evolution of the U.S. Sierra Nevada; the ANDRILL McMurdo Ice Shelf and Southern McMurdo Sound Drilling Projects; and climate-tectonic interactions in the southern Alaskan orogen.
Abstracts for these and other Geosphere papers are available ...
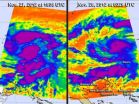
Tropical Storm Bopha continues to intensify in the western North Pacific Ocean as it heads toward Yap State, triggering more warnings and watches. Infrared imagery from NASA's Aqua satellite captured over two days revealed that the storm had consolidated, intensified and developed a large band of strong thunderstorms south of the center, that resemble a tail.
Infrared images of Tropical Storm Bopha were taken by the AIRS instrument on NASA's Aqua satellite on Nov. 27 at 1505 UTC when Bopha had maximum sustained winds near 45 mph, and on Nov. 28 at 0329 UTC when Bopha's ...
Data from NASA's Cassini spacecraft tie a shift in seasonal sunlight to a wholesale reversal, at unexpected altitudes, in the circulation of the atmosphere of Saturn's moon Titan. At the south pole, the data show definitive evidence for sinking air where it was upwelling earlier in the mission. So the key to circulation in the atmosphere of Saturn's moon Titan turned out to be a certain slant of light. The paper was published today in the journal Nature.
"Cassini's up-close observations are likely the only ones we'll have in our lifetime of a transition like this in action," ...
Berkeley — The primary source of light for more than a billion people in developing nations is also churning out black carbon at levels previously overlooked in greenhouse gas estimates, according to a new study led by researchers at the University of California, Berkeley, and the University of Illinois.
Results from field and lab tests found that 7 to 9 percent of the kerosene in wick lamps — used for light in 250-300 million households without electricity — is converted to black carbon when burned. In comparison, only half of 1 percent of the emissions from burning ...
Driven by the strong demand for high-definition video, digital health services, the Internet of Things, and virtual reality, broadband, ubiquitous and convergent information access has become the most important engine to drive the development of the modern information society. With increasing numbers of information-based interactions among humans, machines and objects, especially as new services, new terminals and new needs emerge, the networks are required to provide flexible, energy-efficient, safe and broadband access services anywhere at any time, and therefore wideband ...
Lanthanides comprise a unique and dominant resource of China. The increase in contact for populations through lanthanide mining and the wide applications for industry, agriculture, and medicine have raised great public concern regarding the metal toxicity of lanthanides, particularly on the issue of whether lanthanides are toxic to the human nervous system.
In the past decade, major progresses have been made toward elucidating the mechanisms of the biological actions of lanthanides. A recently published review by researchers at Peking University [Xia et al., Sci. China ...
The origin and dispersal of modern humans and modern human behavior are key interests in Paleolithic archaeology and anthropology. Engraved objects are usually seen as a hallmark of cognition and symbolism, which are viewed as important features of modern human behavior. In recent years, engraved ochre, bones and ostrich eggs unearthed from various Paleolithic sites in Africa, the Near East and Europe have attracted the attention of many scholars. However, such items are rarely encountered at Paleolithic sites in East Asia. Here, we report a very important discovery of ...
WASHINGTON, DC, November 26, 2012 — Organizations using fear and anger to spread negative messages about Muslims have moved from the fringes of public discourse into the mainstream media since the Sept. 11 attacks, according to new research by a University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill sociologist.
Titled, "The Fringe Effect: Civil Society Organizations and the Evolution of Media Discourse about Islam since the September 11th Attacks," the study appears in the December issue of the American Sociological Review.
Christopher Bail, an assistant professor of sociology ...
WASHINGTON, DC, November 26, 2012 — Behavior problems, not depression, are linked to lower grades for depressed adolescents, according to a study in the December issue of the Journal of Health and Social Behavior.
"Behavior problems including attention issues, delinquency, and substance use are associated with diminished achievement, but depression is not," said the study's lead author Jane D. McLeod, a sociology professor and an associate dean at Indiana University. "Certainly, there are depressed youths who have trouble in school, but it's likely because they are also ...