(Press-News.org) A small molecule known to regulate white blood cells has a surprising second role in protecting brain cells from the deleterious effects of stroke, Johns Hopkins researchers report. The molecule, microRNA-223, affects how cells respond to the temporary loss of blood supply brought on by stroke — and thus the cells' likelihood of suffering permanent damage.
"We set out to find a small molecule with very specific effects in the brain, one that could be the target of a future stroke treatment," says Valina Dawson, Ph.D., a professor in the Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine's Institute for Cell Engineering. "What we found is this molecule involved in immune response, which also acts in complex ways on the brain. This opens up a suite of interesting questions about what microRNA-223 is doing and how, but it also presents a challenge to any therapeutic application." A report on the discovery is published in the Nov. 13 issue of the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
RNA is best known as a go-between that shuttles genetic information from DNA and then helps produce proteins based on that information. But, Dawson explains, a decade ago researchers unearthed a completely different class of RNA: small, nimble fragments that regulate protein production. In the case of microRNA, one member of this class, that control comes from the ability to bind to RNA messenger molecules carrying genetic information, and thus prevent them from delivering their messages. "Compared with most ways of shutting genes off, this one is very quick," Dawson notes.
Reasoning that this quick action, along with other properties, could make microRNAs a good target for therapy development, Dawson and her team searched for microRNAs that regulate brain cells' response to oxygen deprivation.
To do that, they looked for proteins that increased in number in cells subjected to stress, and then examined how production of these proteins was regulated. For many of them, microRNA-223 played a role, Dawson says.
In most cases, the proteins regulated by microRNA-223 turned out to be involved in detecting and responding to glutamate, a common chemical signal brain cells use to communicate with each other. A stroke or other injury can lead to a dangerous excess of glutamate in the brain, as can a range of diseases, including autism and Alzheimer's.
Because microRNA-223 is involved in regulating so many different proteins, and because it affects glutamate receptors, which themselves are involved in many different processes, the molecule's reach turned out to be much broader than expected, says Maged M. Harraz, Ph.D., a research associate at Hopkins who led the study. "Before this experiment, we didn't appreciate that a single microRNA could regulate so many proteins," he explains.
This finding suggests that microRNA-223 is unlikely to become a therapeutic target in the near future unless researchers figure out how to avoid unwanted side effects, Dawson says.
INFORMATION:
Other authors on the paper are Stephen M. Eacker, Ph.D., Xueqing Wang, Ph.D., and Ted M. Dawson, M.D., Ph.D., from the Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine.
This work was supported by a grant from the National Institute of Drug Abuse (grant DA000266) and by a Maryland Stem Cell Research Fund fellowship.
Related Stories:
Valina Dawson on preventing cell death in the brain: http://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/institute_cell_engineering/experts/meet_scientists/valina_dawson.html
Johns Hopkins Scientists Discover Brain's Guardian Protein: http://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/news/media/releases/johns_hopkins_scientists_discover_brains_guardian_protein
On the Web:
Link to article: http://www.pnas.org/content/early/2012/10/31/1217394109.abstract
END
WASHINGTON, November 28, 2012 – U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA) scientists working as part of an international team have completed a "shotgun sequencing" of the wheat genome, a paper published in the journal Nature reported today. The achievement is expected to increase wheat yields, help feed the world and speed up development of wheat varieties with enhanced nutritional value.
"By unlocking the genetic secrets of wheat, this study and others like it give us the molecular tools necessary to improve wheat traits and allow our farmers to produce yields sufficient ...
(SACRAMENTO, Calif.) — Amid increasing fear of overexposure to radiation from CT scans, a panel of experts has recommended more research on the health effects of medical imaging and ways to reduce unnecessary CT tests, as well as industry standardization of CT machines.
The recommendations, published in the November 2012 issue of Radiology, were developed at the Radiation Dose Summit, organized by the National Institute of Biomedical Imaging and Bioengineering (NIBIB). The summit included more than 100 medical physicists, radiologists, cardiologists, engineers, industry ...
MEDFORD/SOMERVILLE, Mass. (November 28, 2012) –Tufts University School of Engineering researchers have demonstrated silk-based implantable optics that offer significant improvement in tissue imaging while simultaneously enabling photo thermal therapy, administering drugs and monitoring drug delivery. The devices also lend themselves to a variety of other biomedical functions.
Biodegradable and biocompatible, these tiny mirror-like devices dissolve harmlessly at predetermined rates and require no surgery to remove them.
The technology is the brainchild of a research ...
A completely new method of manufacturing the smallest structures in electronics could make their manufacture thousands of times quicker, allowing for cheaper semiconductors. The findings have been published in the latest issue of Nature.
Instead of starting from a silicon wafer or other substrate, as is usual today, researchers have made it possible for the structures to grow from freely suspended nanoparticles of gold in a flowing gas.
Behind the discovery is Lars Samuelson, Professor of Semiconductor Physics at Lund University, Sweden, and head of the University's ...
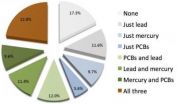
PROVIDENCE, R.I. [Brown University] — Nearly 23 percent of American women of childbearing age met or exceeded the median blood levels for all three environmental chemical pollutants — lead, mercury, and PCBs — tracked in an analysis of data on thousands of women by Brown University researchers. All but 17.3 percent of the women aged 16 to 49 were at or above the median blood level for one or more of these chemicals, which are passed to fetuses through the placenta and to babies through breast milk.
The study, published in advance online Nov. 15 in the journal Environmental ...
KINGSTON, R.I. – November 28, 2012 – A team of archaeologists from the University of Rhode Island, the Israel Antiquities Authority, and the University of Louisville have discovered the remains of a fleet of early-19th century ships and ancient harbor structures from the Hellenistic period (third to first century B.C.) at the city of Akko, one of the major ancient ports of the eastern Mediterranean. The findings shed light on a period of history that is little known and point to how and where additional remains may be found.
The discoveries were presented on November ...
The diagnostic system used by many mental health practitioners in the United States -- known as the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders -- assumes that symptoms of two disorders that occur at the same time are additive and that the order in which the disorders are presented doesn't matter. But new research suggests that order actually plays a significant role in determining how clinicians think about psychiatric disorders.
In an article published in Clinical Psychological Science, a journal of the Association for Psychological Science, researchers Jared ...
Boulder, Colo., USA – Geosphere articles posted online 16 November 2012 cover a variety of topics, such as the geophysics of the Hogri fault zone, 5 km offshore of the Diablo Canyon nuclear power plant; using web-based GIS technologies and readily available global remote sensing datasets for investigations of arid land; the structure and evolution of the U.S. Sierra Nevada; the ANDRILL McMurdo Ice Shelf and Southern McMurdo Sound Drilling Projects; and climate-tectonic interactions in the southern Alaskan orogen.
Abstracts for these and other Geosphere papers are available ...
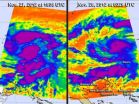
Tropical Storm Bopha continues to intensify in the western North Pacific Ocean as it heads toward Yap State, triggering more warnings and watches. Infrared imagery from NASA's Aqua satellite captured over two days revealed that the storm had consolidated, intensified and developed a large band of strong thunderstorms south of the center, that resemble a tail.
Infrared images of Tropical Storm Bopha were taken by the AIRS instrument on NASA's Aqua satellite on Nov. 27 at 1505 UTC when Bopha had maximum sustained winds near 45 mph, and on Nov. 28 at 0329 UTC when Bopha's ...
Data from NASA's Cassini spacecraft tie a shift in seasonal sunlight to a wholesale reversal, at unexpected altitudes, in the circulation of the atmosphere of Saturn's moon Titan. At the south pole, the data show definitive evidence for sinking air where it was upwelling earlier in the mission. So the key to circulation in the atmosphere of Saturn's moon Titan turned out to be a certain slant of light. The paper was published today in the journal Nature.
"Cassini's up-close observations are likely the only ones we'll have in our lifetime of a transition like this in action," ...