(Press-News.org) Six years of observations by ESA's Venus Express have shown large changes in the sulphur dioxide content of the planet's atmosphere, and one intriguing possible explanation is volcanic eruptions.
The thick atmosphere of Venus contains over a million times as much sulphur dioxide as Earth's, where almost all of the pungent, toxic gas is generated by volcanic activity.
Most of the sulphur dioxide on Venus is hidden below the planet's dense upper cloud deck, because the gas is readily destroyed by sunlight.
That means any sulphur dioxide detected in Venus' upper atmosphere above the cloud deck must have been recently supplied from below.
Venus is covered in hundreds of volcanoes, but whether they remain active today is much debated, providing an important scientific goal for Venus Express.
The mission has already found clues pointing to volcanism on geologically recent timescales, within the last few hundreds of thousands to millions of years.
A previous analysis of infrared radiation from the surface pointed to lava flows atop a volcano with a composition distinct from those of their surroundings, suggesting that the volcano had erupted in the planet's recent past.
Now, an analysis of sulphur dioxide concentration in the upper atmosphere over six years provides another clue.
Immediately after arriving at Venus in 2006, the spacecraft recorded a significant increase in the average density of sulphur dioxide in the upper atmosphere, followed by a sharp decrease to values roughly ten times lower by today.
A similar fall was also seen during NASA's Pioneer Venus mission, which orbited the planet from 1978 to 1992.
At that time, the preferred explanation was an earlier injection of sulphur dioxide from one or more volcanoes, with Pioneer Venus arriving in time for the decline.
"If you see a sulphur dioxide increase in the upper atmosphere, you know that something has brought it up recently, because individual molecules are destroyed there by sunlight after just a couple of days," says Dr Emmanuel Marcq of Laboratoire Atmosphères, Milieux, Observations Spatiales, France, and lead author of the paper published in Nature Geoscience.
"A volcanic eruption could act like a piston to blast sulphur dioxide up to these levels, but peculiarities in the circulation of the planet that we don't yet fully understand could also mix the gas to reproduce the same result," adds co-author Dr Jean-Loup Bertaux, Principal Investigator for the instrument on Venus Express that made the detections.
Venus has a 'super-rotating' atmosphere that whips around the planet in just four Earth-days, much faster than the 243 days the planet takes to complete one rotation about its axis.
Such rapid atmospheric circulation spreads the sulphur dioxide around, making it difficult to isolate any individual points of origin for the gas.
Dr Marcq's team speculate that if volcanism was responsible for the initial increase, then it could come from a relatively gentle increased output of several active volcanoes rather than one dramatic eruption.
"Alternatively, and taking into account the similar trend observed by Pioneer Venus, it's possible that we are seeing decadal-scale variability in the circulation of the atmosphere, which is turning out to be even more complex than we could ever have imagined," he notes.
"By following clues left by trace gases in the atmosphere, we are uncovering the way Venus works, which could point us to the smoking gun of active volcanism," adds Håkan Svedhem, ESA's Project Scientist for Venus Express.
INFORMATION:
Have Venusian volcanoes been caught in the act?
2012-12-03
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Malaria parasite's masquerade ball could be coming to an end
2012-12-03
More than a million people die each year of malaria caused by different strains of the Plasmodium parasite transmitted by the Anopheles mosquito. The medical world has yet to find an effective vaccine against the deadly parasite, which mainly affects pregnant women and children under the age of five. By figuring out how the most dangerous strain evades the watchful eye of the immune system, researchers from the Hebrew University of Jerusalem have now paved the way for the development of new approaches to cure this acute infection.
Upon entering the bloodstream, the Plasmodium ...
BU, VA study describes 68 CTE cases in veterans, high school, college and pro athletes
2012-12-03
(BOSTON) – A study done by investigators at the Boston University Center for the Study of Traumatic Encephalopathy (CSTE) and the Veterans Affairs Boston Healthcare System, in collaboration with the Sports Legacy Institute (SLI), describes 68 cases of chronic traumatic encephalopathy (CTE) among deceased athletes and military veterans whose brain and spinal cords were donated to the VA CSTE Brain Bank. Of the 68 cases, 34 were former professional football players, nine had played only college football, and six had played only high school football. The results, which will ...
New York's Medical Schools urge Congress to preserve NIH funding for scientific research
2012-12-03
The Associated Medical Schools of New York (AMSNY) today directed a letter to the New York State Congressional
Delegation calling on them to reject a nearly 10-percent cut to the National Institutes of Health (NIH), Medicare and
Title VII health professions programs, that will take effect January 2, 2013.
"In order to meet the health challenges of an aging and increasingly diverse population, continue to foster the types
of innovation that will drive our regional economy, and remain a vibrant force in the global economy, we need to
invest more in medical research ...
World's smallest wrench puts a new twist on microscopic manipulation
2012-12-03
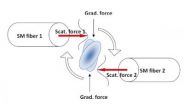
Harnessing laser light's ability to gently push and pull microscopic particles, researchers have created the fiber-optic equivalent of the world's smallest wrench. This virtual tool can precisely twist and turn the tiniest of particles, from living cells and DNA to microscopic motors and dynamos used in biological and physical research.
This new twist on controlling the incredibly small, developed by physicists at The University of Texas at Arlington, will give scientists the ability to skillfully manipulate single cells for cancer research, twist and untwist individual ...
Male chimpanzees choose their allies carefully
2012-12-03
The ability of male chimpanzees to form coalitions with one another in order to direct aggression at other male chimpanzees has certain benefits. A new study by Ian Gilby at Duke University in North Carolina and his colleagues has further revealed that it may not just be the coalition that is important, but who the coalition is with that determines future success. Their study finds that male chimpanzees with central positions in the coalitionary network were most likely to father offspring and increase in rank. Specifically, those who formed coalitions with males who did ...
Research explores markers of depression from childhood to adulthood
2012-12-03
Although several studies have followed the course of depression throughout the lifespan, the characteristics of depression at different developmental stages haven't been clearly identified. New research published in Clinical Psychological Science, a journal of the Association for Psychological Science, presents a unique longitudinal investigation of depression across four critical developmental periods from childhood to adulthood.
To better understand the developmental course of Major Depressive Disorder (MDD), Paul Rohde of the Oregon Research Institute and colleagues ...
Experts urge rapid evaluation for swallowing and voice problems after brain surgery
2012-12-03
Johns Hopkins experts are recommending early post-surgical assessment
-- preferably within 24 hours -- for trouble chewing and swallowing
food, or speaking normally, among patients who have had benign tumors
removed from the base of the brain.
Such early assessments, they say, may minimize complications
associated with the sometimes hazelnut-sized tumors, called
vestibular schwannomas. Damage can arise when the tumors themselves
press on the nearby cranial nerves -- key to controlling the tongue,
lips, mouth and throat -- or from the surgery itself.
Researchers ...
Leuven research opens new pathway for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease
2012-12-03
Scientists from VIB and KU Leuven have discovered a new target molecule for the development of a treatment against Alzheimer's disease. There is currently no cure for this disease. Many candidate drugs fail because they also target proteins essential to life. This discovery from Leuven could form a target for a treatment against Alzheimer's disease with fewer side effects and that suppresses the very first symptoms of the disease. This research will be published in the leading journal Nature Medicine.
Alzheimer's Disease
Alzheimer's Disease is the most common form of ...
Uncovering unique properties in a 2-dimensional crystal
2012-12-03
When the dry lubricant, molybdenum disulfide, is stripped down to a single layer of atoms, a tightly bound quasi-particle comprised of two electrons and a hole forms with unique spin and valley properties, researchers from Case Western Reserve University and colleagues discovered.
These charged quasi-particles, called negative trions, can be manipulated to change the light absorbed and emitted from this two-dimensional semi-conducting crystal, opening it to potential use in new solar cells and other electronic devices that are controlled by light or designed to control ...
Sharp spike in computer-related injuries predicted for medical workers, find studies
2012-12-03
ITHACA, N.Y. – As U.S. health care goes high tech, spurred by $20 billion in federal stimulus incentives, the widespread adoption of electronic medical records and related digital technologies is predicted to reduce errors and lower costs – but it is also likely to significantly boost musculoskeletal injuries among doctors and nurses, concludes a Cornell University ergonomics professor in two new papers.
The repetitive strain injuries, he said, will stem from poor office layouts and improper use of computer devices.
"Many hospitals are investing heavily in new technology ...