(Press-News.org) The University of Granada researchers are pioneers in the application of thermography to the field Psychology. Thermography is a technique based on determining body temperature.
When a person lies they suffer a "Pinocchio effect", which is an increase in the temperature around the nose and in the orbital muscle in the inner corner of the eye. In addition, when we perform a considerable mental effort our face temperature drops and when we have an anxiety attack our face temperature raises. These are some of the conclusions drawn in this pioneer study conducted at the University of Granada Department of Experimental Psychology, which has introduced new applications of thermography.
Thermography is a technique based on body temperature that is applied in many fields such as general industry, the building industry and medicine. Thermographic cameras have a wide range of uses such as measuring energy loss in buildings, indicating respiratory diseases in bovine animals or rabies in raccoons. Thermography was developed in the USA during the II World War to detect the enemy (night vision).
Excitement is the Same in Men and Women
The University of Granada researchers Emilio Gómez Milán and Elvira Salazar López have been pioneers in applying thermography to the field of Psychology, and they have obtained very innovative and interesting results. Thus, sexual excitement and desire can be identified in men and women using thermography, since they induce an increase in chest and genital temperature. This study demonstrates that –in physiological terms– men and women get excited at the same time, even although women say they are not excited or only slightly excited.
Scientists have discovered that when a mental effort is made (performing difficult tasks, being interrogated on a specific event or lying) face temperature changes.
When we lie on our feelings, the temperature around our nose raises and a brain element called "insula" is activated. The insula is a component of the brain reward system, and it only activates when we experience real feelings (called "qualias"). The insula is involved in the detection and regulation of body temperature. Therefore, there is a strong negative correlation between insula activity and temperature increase: the more active the insule (the greater the feeling) the lower the temperature change, and viceversa, the researchers state.
The Thermal Footprint of Flamenco
Researchers also determined the thermal footprint of aerobic exercise and different dance modalities such as ballet. When a person is dancing flamenco the temperature in their buttocks drops and increases in their forearms. That is the thermal footprint of flamenco, and each dance modality has a specific thermal footprint, professor Salazar explains.
The researchers have demonstrated that temperature asymmetries in both sides of the body and local temperature changes are associated with the physical, mental and emotional status of the subject. The thermogram is a somatic marker of subjective or mental states and allows us see what a person is feeling or thinking, professor Salazar states.
Finally, thermography is useful for evaluating emotions (since the face thermal pattern is different) and identifying emotional contagion. For example, when a highly empathic person sees another person having an electric discharge in their forearm, they become infected by their suffering and temperature in their forearm increases. In patients with certain neurological disease such as multiple sclerosis, the body does not properly regulates temperature, which can be detected by a thermogram. Thermography can also be applied to determine body fat patterns, which is very useful in weight loss and training programs. It can also be applied to assess body temperature in celiac patients and in patients with anorexia, etc.
INFORMATION:
Researchers confirm the 'Pinocchio Effect': When you lie, your nose temperature raises
2012-12-03
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
BGI's ICG-7 and Bio-IT APAC provides updates on the latest genomics research to advance life science
2012-12-03
December 3, 2012, Hong Kong and Shenzhen, China – The 7th International Conference on Genomics and Bio-IT APAC 2012, organized by BGI, the world's largest genomics organization, successfully concluded with numerous updates on on-going research applying today's latest sequencing and bioinformatics technologies to a new paradigm of human diseases and to enhancing global agriculture development. The three-day conference, held in Hong Kong, also brought new insights into Bio-cloud and big data management. More than 300 participants attended this top-grade international conference.
The ...
Heart-warming memories: Nostalgia can make you feel warmer
2012-12-03
As the nights draw in and the temperature begins to drop, many of us will be thinking of ways to warm up on the dark winter nights. However, few would think that remembering days gone by would be an effective way of keeping warm.
But research from the University of Southampton has shown that feeling nostalgic can make us feel warmer.
The study, published in the journal Emotion, investigated the effects of nostalgic feelings on reaction to cold and the perception of warmth. The volunteers, from universities in China and the Netherlands, took part in one of five studies. ...
Genes link growth in the womb with adult metabolism and disease
2012-12-03
Researchers have identified four new genetic regions that influence birth weight, providing further evidence that genes as well as maternal nutrition are important for growth in the womb. Three of the regions are also linked to adult metabolism, helping to explain why smaller babies have higher rates of chronic diseases later in life.
It has been known for some time that babies born with a lower birth weight are at higher risk of chronic diseases such as type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular disease. Three genetic regions have already been identified that influence birth ...
An innovation will attach patients' electronic medical record to the foot of their hospital bed
2012-12-03
This press release is available in Spanish.
Information and Communication Technologies (ICT) present tremendous potential in the field of healthcare, according to the researchers. "ICTs are going to contribute to a change in focus in aid and health services," comments Jesús Espinosa, CEO of IonIDE Telematics. According to accreditation and standardization associations, Spain is a leader in the management of clinical processes, because it has the greatest number of hospitals that have adopted electronic medical record (EMR). This computerized registry of patients' social, ...
Corn: Many active genes - high yield
2012-12-03
Hybrid plants provide much higher yield than their homozygous parents. Plant breeders have known this for more than 100 years and used this effect called heterosis for richer harvests. Until now, science has puzzled over the molecular processes underlying this phenomenon. Researchers at the University of Bonn and partners from Tübingen and the USA have now decoded one possible mechanism in corn roots. More genes are active in hybrid plants than in their homozygous parents. This might increase growth and yield of the corn plants. The results are published in the renowned ...
Have Venusian volcanoes been caught in the act?
2012-12-03
Six years of observations by ESA's Venus Express have shown large changes in the sulphur dioxide content of the planet's atmosphere, and one intriguing possible explanation is volcanic eruptions.
The thick atmosphere of Venus contains over a million times as much sulphur dioxide as Earth's, where almost all of the pungent, toxic gas is generated by volcanic activity.
Most of the sulphur dioxide on Venus is hidden below the planet's dense upper cloud deck, because the gas is readily destroyed by sunlight.
That means any sulphur dioxide detected in Venus' upper atmosphere ...
Malaria parasite's masquerade ball could be coming to an end
2012-12-03
More than a million people die each year of malaria caused by different strains of the Plasmodium parasite transmitted by the Anopheles mosquito. The medical world has yet to find an effective vaccine against the deadly parasite, which mainly affects pregnant women and children under the age of five. By figuring out how the most dangerous strain evades the watchful eye of the immune system, researchers from the Hebrew University of Jerusalem have now paved the way for the development of new approaches to cure this acute infection.
Upon entering the bloodstream, the Plasmodium ...
BU, VA study describes 68 CTE cases in veterans, high school, college and pro athletes
2012-12-03
(BOSTON) – A study done by investigators at the Boston University Center for the Study of Traumatic Encephalopathy (CSTE) and the Veterans Affairs Boston Healthcare System, in collaboration with the Sports Legacy Institute (SLI), describes 68 cases of chronic traumatic encephalopathy (CTE) among deceased athletes and military veterans whose brain and spinal cords were donated to the VA CSTE Brain Bank. Of the 68 cases, 34 were former professional football players, nine had played only college football, and six had played only high school football. The results, which will ...
New York's Medical Schools urge Congress to preserve NIH funding for scientific research
2012-12-03
The Associated Medical Schools of New York (AMSNY) today directed a letter to the New York State Congressional
Delegation calling on them to reject a nearly 10-percent cut to the National Institutes of Health (NIH), Medicare and
Title VII health professions programs, that will take effect January 2, 2013.
"In order to meet the health challenges of an aging and increasingly diverse population, continue to foster the types
of innovation that will drive our regional economy, and remain a vibrant force in the global economy, we need to
invest more in medical research ...
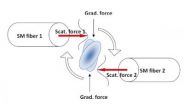
World's smallest wrench puts a new twist on microscopic manipulation
2012-12-03
Harnessing laser light's ability to gently push and pull microscopic particles, researchers have created the fiber-optic equivalent of the world's smallest wrench. This virtual tool can precisely twist and turn the tiniest of particles, from living cells and DNA to microscopic motors and dynamos used in biological and physical research.
This new twist on controlling the incredibly small, developed by physicists at The University of Texas at Arlington, will give scientists the ability to skillfully manipulate single cells for cancer research, twist and untwist individual ...