(Press-News.org) RICHMOND, Va. (Dec. 5, 2012) – Approximately 68 percent of U.S. adults are overweight or obese, according to the National Cancer Institute, which puts them at greater risk for developing cancer, cardiovascular disease, diabetes and a host of other chronic illnesses. But an international team of scientists led by Virginia Commonwealth University Massey Cancer Center researcher Andrew Larner, M.D., Ph.D., has successfully reversed obesity in mice by manipulating the production of an enzyme known as tyrosine-protein kinase-2 (Tyk2). In their experiments, the scientists discovered that Tyk2 helps regulate obesity in mice and humans through the differentiation of a type of fat tissue known as brown adipose tissue (BAT).
Published today in the online edition of the journal Cell Metabolism, the study is the first to provide evidence of the relationship between Tyk2 and BAT. Previous studies by Larner and his team discovered that Tyk2 helps suppress the growth and metastasis of breast cancer, and now the current study suggests this same enzyme could help protect against and even reverse obesity.
The scientists were able to reverse obesity in mice that do not express Tyk2 by expressing a protein known as signal transducer and activator of transcription-3 (Stat3). Stat3 mediates the expression of a variety of genes that regulate a host of cellular processes. The researchers found that Stat3 formed a complex with a protein known as PR domain containing 16 (PRDM16) to restore the development of BAT and decrease obesity.
"We discovered that Tyk2 levels in mice are regulated by diet. We then tested tissue samples from humans and found that levels of Tyk2 were more than 50 percent lower in obese humans," said Larner, Martha Anne Hatcher Distinguished Professor in Oncology and co-leader of the Cancer Cell Signaling program at VCU Massey Cancer Center. "Our findings open new potential avenues for research and development of new pharmacological and nutritional treatments for obesity."
There are two different types of fat – white adipose tissue (WAT) and BAT. WAT is the primary site of energy storage. BAT is responsible for energy expenditure in order to maintain body temperature. BAT deposits are present in all mammals, but until recently, scientists thought BAT was only active in infants and not in adult humans. Only in the last four years have scientists realized that BAT is present in adults and helps to regulate energy expenditure. Additionally, research has shown that diminished BAT activity is associated with metabolic syndrome, a combination of medical disorders that increase the risk of developing cardiovascular disease and diabetes. Researchers estimate metabolic syndrome could affect as much as 25 percent of the U.S. population.
"We have made some very interesting observations in this study, but there are many questions left unanswered," said Larner. "We plan to further investigate the actions of Tyk2 and Stat3 in order to better understand the mechanisms involved in the development of brown adipose tissue. We're hopeful this research will help lead to new targets to treat a variety of obesity-related diseases such as cancer, cardiovascular disease and diabetes."
INFORMATION:
Larner collaborated on this study with Marta Derecka, Magdalena Morgan, Vidisha Raje, Jennifer Sisler and Quifang Zhang, all from the Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology at VCU School of Medicine; Tomasz Kordula, Ph.D., Cancer Cell Signaling program member at VCU Massey; Agnieszka Gornicka, from the Cleveland Clinic Foundation; Sergei B. Koralov, Ph.D., from New York University Medical School; Dennis Otero, Ph.D., from the University of California; Joanna Cichy, Ph.D., from Jagiellonian University in Krakow, Poland; Klaus Rajewsky, Ph.D., from Harvard Medical School; Kazuya Shimoda, M.D., Ph.D., from Miyazaki University in Japan; Valeria Poli, Ph.D., from the University of Turin in Torino, Italy; Brigit Strobl, Ph.D., from the University of Veterinary Medicine in Vienna, Austria; Sandra Pellegrini, Ph.D., from Institut Pasteur in Paris, France; Thurl E. Harris, Ph.D., and Susanna R. Keller, M.D., from University of Virginia School of Medicine; Patrick Seale, Ph.D., from the University of Pennsylvania School of Medicine; Aaron P. Russell, Ph.D., from Deakin University in Burwood, Australia; Andrew J. McAinch, Ph.D., from Victoria University in St. Albans, Australia; Paul E. O'Brien, M.D., from Monash University in Melbourne, Australia; and Colleen M. Croniger, Ph.D., from Case Western University School of Medicine.
This study was supported by National Institutes of Health grants R01 AI059710-01 and R21 AI088487, the Austrian Science Fund and, in part, by funding from VCU Massey Cancer Center's NIH-NCI Cancer Center Support Grant P30 CA016059.
News directors: Broadcast access to VCU Massey Cancer Center experts is available through VideoLink ReadyCam. ReadyCam transmits video and audio via fiber optics through a system that is routed to your newsroom. To schedule a live or taped interview, contact John Wallace, (804) 628-1550.
About VCU Massey Cancer Center
VCU Massey Cancer Center is one of only 67 National Cancer Institute-designated institutions in the country that leads and shapes America's cancer research efforts. Working with all kinds of cancers, the Center conducts basic, translational and clinical cancer research, provides state-of-the-art treatments and clinical trials, and promotes cancer prevention and education. Since 1974, Massey has served as an internationally recognized center of excellence. It has one of the largest offerings of clinical trials in Virginia and serves patients in Richmond and in four satellite locations. Its 1,000 researchers, clinicians and staff members are dedicated to improving the quality of human life by developing and delivering effective means to prevent, control and ultimately to cure cancer. Visit Massey online at www.massey.vcu.edu or call 877-4-MASSEY for more information.
About VCU and the VCU Medical Center
Virginia Commonwealth University is a major, urban public research university with national and international rankings in sponsored research. Located in downtown Richmond, VCU enrolls more than 31,000 students in 222 degree and certificate programs in the arts, sciences and humanities. Sixty-six of the programs are unique in Virginia, many of them crossing the disciplines of VCU's 13 schools and one college. MCV Hospitals and the health sciences schools of Virginia Commonwealth University compose the VCU Medical Center, one of the nation's leading academic medical centers. For more, see www.vcu.edu.
Scientists discover mechanism that could reduce obesity
2012-12-05
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Extraverted gorillas enjoy longer lives, research suggests
2012-12-05
An international team of researchers looked at the role of personality by studying
298 gorillas in North American zoos and sanctuaries for over 18 years.
The gorillas' personalities were assessed by keepers, volunteers, researchers and caretakers who knew the gorillas well. Their personality was scored with measures adapted from techniques for studying people and other primates.
Researchers found that out of four personality traits – dominance, extraversion, neuroticism and agreeableness – extraversion, which was associated with behaviours such as sociability, activity, ...
Mercury in coastal fog linked to upwelling of deep ocean water
2012-12-05
SANTA CRUZ, CA--An ongoing investigation of elevated mercury levels in coastal fog in California suggests that upwelling of deep ocean water along the coast brings mercury to the surface, where it enters the atmosphere and is absorbed by fog.
Peter Weiss-Penzias, an environmental toxicologist at the University of California, Santa Cruz, who leads the investigation, emphasized that the amount of mercury in fog is not a health concern. "These are parts-per-trillion levels, so when we say elevated, that's relative to what was expected in atmospheric water," he said. "The ...
Low percentage of medical residents plan to practice general internal medicine
2012-12-05
Colin P. West, M.D., Ph.D., and Denise M. Dupras, M.D., Ph.D., of Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn., conducted a study to evaluate career plans of internal medicine residents.
"General internists provide comprehensive and coordinated care for both acute and chronic diseases. General internists are expected to play an increasingly critical role in health care provision as the population ages, the burden of chronic disease grows, and health care reform targets coverage of tens of millions of currently uninsured patients," according to background information in the article. ...
Program of protected time for sleep improves morning alertness for medical interns
2012-12-05
Kevin G. Volpp, M.D., Ph.D., of the Philadelphia Veterans Affairs Medical Center and University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, and colleagues conducted a study to determine whether a protected sleep period of 5 hours is feasible and effective in increasing the time slept by interns on extended duty overnight shifts.
In 2009, the Institute of Medicine (IOM) published a report on resident work hours and work schedules to improve patient safety that recommended a protected sleep period of 5 hours during any work shift longer than 16 hours to reduce the risk of fatigue-related ...
Bias may exist in rating of medical trainees
2012-12-05
Peter Yeates, M.B.B.S., M.Clin.Ed., of the University of Manchester, United Kingdom, and colleagues conducted a study to examine whether observations of the performance of postgraduate year 1 physicians influence raters' scores of subsequent performances.
"The usefulness of performance assessments within medical education is limited by high interrater score variability, which neither rater training nor changes in scale format have successfully ameliorated. Several factors may explain raters' score variability, including a tendency of raters to make assessments by comparing ...
Shorter rotation for attending physicians does not appear to have adverse effects on patients
2012-12-05
Brian P. Lucas, M.D., M.S., of the Cook County Health and Hospitals System and Rush Medical College, Chicago, and colleagues conducted a study to compare the effects of 2- vs. 4-week inpatient attending physician rotations on unplanned patient revisits (a measure to assess the effect on patients), attending evaluations by trainees, and attending propensity for burnout.
"Trainees learn inpatient medicine on the job, providing clinical care to patients as members of ward teams led by attending physicians. Although the structures of these ward teams vary by local educational ...
Research evaluates possible benefit of mini-interviews as part of medical school admission process
2012-12-05
Kevin W. Eva, Ph.D., of the University of British Columbia, Vancouver, and colleagues conducted a study to determine whether students deemed acceptable through a revised admissions protocol using a 12-station multiple mini-interview (MMI) would outperform rejected medical students when they later took the Canadian national licensing examinations after completing medical school. The MMI process requires candidates to rotate through brief sequential interviews with structured tasks and independent assessment within each interview.
"Modern conceptions of medical practice ...
Children with heart devices and their parents struggle with quality of life
2012-12-05
Children with implanted heart-rhythm devices and their parents suffer from a lower quality of life compared with their healthy counterparts and may benefit from psychotherapy according to new research in Circulation: Arrhythmia & Electrophysiology, an American Heart Association journal.
Researchers at the Cincinnati Children's Hospital Medical Center studied 173 children with either a pacemaker (40 patients) or implanted defibrillator (133 patients) to assess their quality of life compared to other children with congenital heart disease and to healthy children. The children, ...
Crag keeps the light 'fantastic' for photoreceptors
2012-12-05
HOUSTON – (Dec. 4, 2012) –The ability of the eye of a fruit fly (Drosophila melanogaster) to respond to light depends on a delicate ballet that keeps the supply of light sensors called rhodopsin constant as photoreceptors turn on and off in response to light exposures, said researchers from Baylor College of Medicine (www.bcm.edu) and the Jan and Dan Duncan Neurological Research Institute (http://www.nri.texaschildrens.org/) at Texas Children's Hospital in an article that appears online in the journal PLOS Biology (http://www.plosbiology.org/home.action).
The gene Crag ...
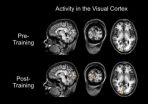
Learning to control brain activity improves visual sensitivity
2012-12-05
Training human volunteers to control their own brain activity in precise areas of the brain can enhance fundamental aspects of their visual sensitivity, according to a new study. This non-invasive 'neurofeedback' approach could one day be used to improve brain function in patients with abnormal patterns of activity, for example stroke patients.
Researchers at the Wellcome Trust Centre for Neuroimaging at UCL used non-invasive, real-time brain imaging that enabled participants to watch their own brain activity on a screen, a technique known as neurofeedback. During the ...