(Press-News.org) TORONTO, Dec. 5, 2012—Researchers at St. Michael's hospital have identified 29 proteins that are likely to be involved in the spread of kidney cancer. The discovery will help physicians recognize which tumours are going to behave more aggressively and provide those patients with more intensive treatment and closer followup.
"Metastatic renal cell carcinoma is one of the most treatment-resistant malignancies and patients have dismal prognosis," said Dr. George M Yousef, a laboratory pathologist. "Identification of markers that can predict the potential of metastases will have a great impact on improvement patient outcomes.
Dr. Yousef's research appears online in the journal Molecular & Cellular Proteomics.
Kidney cancer in general is very aggressive and has a high chance of metastasis, or spreading to other organs. The five-year survival rate for metastasized kidney cancer is less than 10 per cent. Although imaging technology has led to increased detection of kidney tumours, 25 to 30 per cent have already spread by the time they are found.
Using a mass spectrometer, Dr. Yousef identified 29 proteins that change when cancer cells spread from the original site of the kidney tumour. All 29 proteins have been previously been linked to other malignancies.
Dr. Yousef said if physicians can determine which kidney tumours have those proteins, and are likely to spread, they can monitor and treat those patients more aggressively. Patients who don't have those proteins and biomarkers might not have to undergo costly and intensive treatment or surgery.
The next steps would be to find ways to stop the proteins from turning on and triggering the metastasis.
###
This study was supported by grants from the Canadian Cancer Society, the Ontario Ministry of Research and Innovation, the Kidney Foundation of Canada and the Cancer Research Society.
About St. Michael's Hospital
St. Michael's Hospital provides compassionate care to all who enter its doors. The hospital also provides outstanding medical education to future health care professionals in more than 23 academic disciplines. Critical care and trauma, heart disease, neurosurgery, diabetes, cancer care, and care of the homeless are among the Hospital's recognized areas of expertise. Through the Keenan Research Centre and the Li Ka Shing International Healthcare Education Center, which make up the Li Ka Shing Knowledge Institute, research and education at St. Michael's Hospital are recognized and make an impact around the world. Founded in 1892, the hospital is fully affiliated with the University of Toronto.
For more information or to interview Dr.Yousef, please contact:
Leslie Shepherd
Manager, Media Strategy
St. Michael's Hospital
Phone: 416-864-6094 or 647-300-1753
shepherdl@smh.ca
Inspired Care. Inspiring Science. END
Researchers identify proteins that indicate which kidney tumors are most likely to spread
Discovery will help physicians recognize which tumours are going to behave more aggressively
2012-12-06
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Clinical trial tests rice bran to prevent cancer
2012-12-06
A recent University of Colorado Cancer Center review in the journal Advances in Nutrition shows that rice bran offers promising cancer prevention properties. Meanwhile, an ongoing clinical trial is testing the effectiveness of rice bran in preventing the recurrence of colon cancer.
"While I have been trained as a molecular toxicologist, I am excited about the opportunities to deliver bioactive, cancer fighting compounds with food, and this has led to my focus now primarily on the multiple drug-like characteristics of rice bran," says Elizabeth P. Ryan, PhD, CU Cancer ...
Adolescents under pressure to speak 'properly'
2012-12-06
EAST LANSING, Mich. — As adolescents transition to adulthood, the pressure to meet adult expectations – such as speaking properly – may be greater than expected, according to a new study by a Michigan State University researcher.
Suzanne Evans Wagner, assistant professor of linguistics, has proven for the first time that language changes with age in addition to community pressures. And, surprisingly, college and post-high school ambitions play a huge role.
"It seems as if in high school, students who want to go to a good college are the ones who early on begin to dial ...
Exercise affects reproductive ability in horses
2012-12-06
In the latest issue of the Journal of Animal Science, researchers at Clemson University and the University of Florida examine the impact of exercise on mare reproductive health and embryo transfer.
In the study, researchers divided light-horse mares into three research groups: no exercise (control), partial-exercise and full-exercise. Their goal was to measure reproductive blood flow and embryo number and quality. Partial-exercise mares were moderately exercised for 30 minutes daily during the periovulatory period and rested after ovulation for seven days. Full-exercise ...
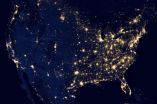
NASA-NOAA satellite reveals new views of earth at night
2012-12-06
VIDEO:
This new global view and animation of Earth’s city lights is a composite assembled from data acquired by the Suomi NPP satellite. The data was acquired over nine days in...
Click here for more information.
Scientists unveiled today an unprecedented new look at
our planet at night. A global composite image, constructed using
cloud-free night images from a new NASA and National Oceanic and
Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) satellite, shows the glow of
natural and ...
New report finds increase in media coverage of synthetic biology
2012-12-06
WASHINGTON – Press coverage of synthetic biology in the United States and Europe increased significantly between 2008 and 2011, according to a report released today by the Synthetic Biology Project at the Woodrow Wilson International Center for Scholars.
The report, Trends in American and European Press Coverage of Synthetic Biology: 2008 – 2011, builds on the project's earlier study of US-EU press coverage between 2003 and 2008. Synthetic biology, an area of research focused on the design and construction of new biological parts and devices, or re-design of existing ...
Synthetic fuel could eliminate US need for crude oil
2012-12-06
The United States could eliminate the need for crude oil by using a combination of coal, natural gas and non-food crops to make synthetic fuel, a team of Princeton researchers has found.
Besides economic and national security benefits, the plan has potential environmental advantages. Because plants absorb carbon dioxide to grow, the United States could cut vehicle greenhouse emissions by as much as 50 percent in the next several decades using non-food crops to create liquid fuels, the researchers said.
Synthetic fuels would be an easy fit for the transportation system ...
New '4-D' transistor is preview of future computers
2012-12-06
WEST LAFAYETTE, Ind. – A new type of transistor shaped like a Christmas tree has arrived just in time for the holidays, but the prototype won't be nestled under the tree along with the other gifts.
"It's a preview of things to come in the semiconductor industry," said Peide "Peter" Ye, a professor of electrical and computer engineering at Purdue University.
Researchers from Purdue and Harvard universities created the transistor, which is made from a material that could replace silicon within a decade. Each transistor contains three tiny nanowires made not of silicon, ...
NASA satellites analyze Typhoon Bopha inside and out
2012-12-06
Typhoon Bopha proved deadly to residents in the Mindanao region of the Philippines after ravaging islands in Micronesia. NASA's Aqua and TRMM satellites peered at the storm inside and out, providing forecasters with valuable data as the storm moved into the South China Sea.
On Dec. 5, 2012, Bopha crossed over Palawan and entered the South China Sea after crossing over the southern Philippines' Mindanao region, leaving death and destruction in its wake. According to Reuters news reports on Dec. 5, at least at total of 283 people were killed and hundreds remain missing ...
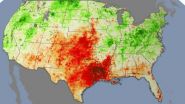
Plant stress paints early picture of drought
2012-12-06
In July 2012, farmers in the U.S. Midwest and Plains regions watched crops wilt and die after a stretch of unusually low precipitation and high temperatures. Before a lack of rain and record-breaking heat signaled a problem, however, scientists observed another indication of drought in data from NASA and NOAA satellites: plant stress.
Healthy vegetation requires a certain amount of water from the soil every day to stay alive, and when soil moisture falls below adequate levels, plants become stressed. Scientists with the U.S. Department of Agriculture's Agricultural Research ...
NASA investigates use of 'trailblazing' material for new sensors
2012-12-06
Tiny sensors -- made of a potentially trailblazing material just one atom thick and heralded as the "next best thing" since the invention of silicon -- are now being developed to detect trace elements in Earth's upper atmosphere and structural flaws in spacecraft.
Technologist Mahmooda Sultana, who joined NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Md., two years ago and has since emerged as Goddard's go-to expert in the development of graphene-based technology, has expanded her portfolio to include two new research and development efforts aimed at creating nano-sized ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Tundra tongue: The science behind a very cold mistake
Targeting a dangerous gut infection
Scientists successfully harvest chickpeas from “moon dirt”
Teen aggression a warning sign for faster aging later in life
Study confirms food fortification is highly cost-effective in fighting hidden hunger across 63 countries
Special issue elevates disease ecology in marine management
A kaleidoscope of cosmic collisions: the new catalogue of gravitational signals from LIGO, Virgo and KAGRA
New catalog more than doubles the number of gravitational-wave detections made by LIGO, Virgo, and KAGRA observatories
Antifibrotic drug shows promise for premature ovarian insufficiency
Altered copper metabolism is a crucial factor in inflammatory bone diseases
Real-time imaging of microplastics in the body improves understanding of health risks
Reconstructing the world’s ant diversity in 3D
UMD entomologist helps bring the world’s ant diversity to life in 3D imagery
ESA’s Mars orbiters watch solar superstorm hit the Red Planet
The secret lives of catalysts: How microscopic networks power reactions
Molecular ‘catapult’ fires electrons at the limits of physics
Researcher finds evidence supporting sucrose can help manage painful procedures in infants
New study identifies key factors supporting indigenous well-being
Bureaucracy Index 2026: Business sector hit hardest
ECMWF’s portable global forecasting model OpenIFS now available for all
Yale study challenges notion that aging means decline, finds many older adults improve over time
Korean researchers enable early detection of brain disorders with a single drop of saliva!
Swipe right, but safer
Duke-NUS scientists identify more effective way to detect poultry viruses in live markets
Low-intensity treadmill exercise preconditioning mitigates post-stroke injury in mouse models
How moss helped solve a grave-robbing mystery
How much sleep do teens get? Six-seven hours.
Patients regain weight rapidly after stopping weight loss drugs – but still keep off a quarter of weight lost
GLP-1 diabetes drugs linked to reduced risk of addiction and substance-related death
Councils face industry legal threats for campaigns warning against wood burning stoves
[Press-News.org] Researchers identify proteins that indicate which kidney tumors are most likely to spreadDiscovery will help physicians recognize which tumours are going to behave more aggressively