(Press-News.org) A recent University of Colorado Cancer Center review in the journal Advances in Nutrition shows that rice bran offers promising cancer prevention properties. Meanwhile, an ongoing clinical trial is testing the effectiveness of rice bran in preventing the recurrence of colon cancer.
"While I have been trained as a molecular toxicologist, I am excited about the opportunities to deliver bioactive, cancer fighting compounds with food, and this has led to my focus now primarily on the multiple drug-like characteristics of rice bran," says Elizabeth P. Ryan, PhD, CU Cancer Center investigator, assistant professor in the Department of Environmental and Radiological Health Sciences at the CSU Animal Cancer Center, and the review's senior author. "There's a delicate balance of bioactive components in rice bran that together show anti-cancer activity including the ability to inhibit cell proliferation, alter cell cycle progression and initiate the programmed cell death known as apoptosis in malignant cells," Ryan says.
Ryan and colleagues show that bioactive rice bran derived small molecules include, but are not limited to polyphenolics, ferulic acid, tricin, β-sitosterol, γ-oryzanol, tocotrienols/tocopherols, and phytic acid.
"We're working now to tease apart the ratios of these active molecules required for bioactivity and mechanisms. Previous attempts to isolate one or another compound have been largely unsuccessful and so it looks now as if rather than any one compound giving rice bran its chemopreventive powers, it's the synergistic activity of multiple components in the whole food that should be studied."
Work with cancer cell lines and animal models shows that the bioactive components of rice bran act not only within cancer cells but around the cells to create conditions in the surrounding tissues that promote the function of healthy cells while inhibiting the function of cancer cells. This tissue microenvironment activity includes mediating chronic inflammation that provides a ripe landscape for cancer. Ryan and colleagues including Tiffany Weir, PhD, and Rajesh Agarwal, PhD, are collaborating to evaluate how rice bran may also help to promote an anti-cancer immune response and modulate gut microbiota metabolism for protection against cancer.
"There are well over 100,000 varieties of rice in the world, many with their own unique mix of bioactive components and so one major challenge is to discover the optimal composition for chemoprevention. Another challenge is ensuring that people consistently receive the required daily intake amount or 'dose' needed to demonstrate these chemo-protective effects. That said, rice is an accessible, low-cost food in most places of the world, and so work with rice bran as a dietary chemopreventive agent has the potential to impact a significant portion of the world's population," Ryan says.
Ryan has taken the next step in the evolution of rice bran from diet to prescription, in the form of an ongoing clinical trial testing its chemopreventive effectiveness in a population of colon cancer survivors.
### END
Clinical trial tests rice bran to prevent cancer
Bioactive small molecules work synergistically, like a drug
2012-12-06
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Adolescents under pressure to speak 'properly'
2012-12-06
EAST LANSING, Mich. — As adolescents transition to adulthood, the pressure to meet adult expectations – such as speaking properly – may be greater than expected, according to a new study by a Michigan State University researcher.
Suzanne Evans Wagner, assistant professor of linguistics, has proven for the first time that language changes with age in addition to community pressures. And, surprisingly, college and post-high school ambitions play a huge role.
"It seems as if in high school, students who want to go to a good college are the ones who early on begin to dial ...
Exercise affects reproductive ability in horses
2012-12-06
In the latest issue of the Journal of Animal Science, researchers at Clemson University and the University of Florida examine the impact of exercise on mare reproductive health and embryo transfer.
In the study, researchers divided light-horse mares into three research groups: no exercise (control), partial-exercise and full-exercise. Their goal was to measure reproductive blood flow and embryo number and quality. Partial-exercise mares were moderately exercised for 30 minutes daily during the periovulatory period and rested after ovulation for seven days. Full-exercise ...
NASA-NOAA satellite reveals new views of earth at night
2012-12-06
VIDEO:
This new global view and animation of Earth’s city lights is a composite assembled from data acquired by the Suomi NPP satellite. The data was acquired over nine days in...
Click here for more information.
Scientists unveiled today an unprecedented new look at
our planet at night. A global composite image, constructed using
cloud-free night images from a new NASA and National Oceanic and
Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) satellite, shows the glow of
natural and ...
New report finds increase in media coverage of synthetic biology
2012-12-06
WASHINGTON – Press coverage of synthetic biology in the United States and Europe increased significantly between 2008 and 2011, according to a report released today by the Synthetic Biology Project at the Woodrow Wilson International Center for Scholars.
The report, Trends in American and European Press Coverage of Synthetic Biology: 2008 – 2011, builds on the project's earlier study of US-EU press coverage between 2003 and 2008. Synthetic biology, an area of research focused on the design and construction of new biological parts and devices, or re-design of existing ...
Synthetic fuel could eliminate US need for crude oil
2012-12-06
The United States could eliminate the need for crude oil by using a combination of coal, natural gas and non-food crops to make synthetic fuel, a team of Princeton researchers has found.
Besides economic and national security benefits, the plan has potential environmental advantages. Because plants absorb carbon dioxide to grow, the United States could cut vehicle greenhouse emissions by as much as 50 percent in the next several decades using non-food crops to create liquid fuels, the researchers said.
Synthetic fuels would be an easy fit for the transportation system ...
New '4-D' transistor is preview of future computers
2012-12-06
WEST LAFAYETTE, Ind. – A new type of transistor shaped like a Christmas tree has arrived just in time for the holidays, but the prototype won't be nestled under the tree along with the other gifts.
"It's a preview of things to come in the semiconductor industry," said Peide "Peter" Ye, a professor of electrical and computer engineering at Purdue University.
Researchers from Purdue and Harvard universities created the transistor, which is made from a material that could replace silicon within a decade. Each transistor contains three tiny nanowires made not of silicon, ...
NASA satellites analyze Typhoon Bopha inside and out
2012-12-06
Typhoon Bopha proved deadly to residents in the Mindanao region of the Philippines after ravaging islands in Micronesia. NASA's Aqua and TRMM satellites peered at the storm inside and out, providing forecasters with valuable data as the storm moved into the South China Sea.
On Dec. 5, 2012, Bopha crossed over Palawan and entered the South China Sea after crossing over the southern Philippines' Mindanao region, leaving death and destruction in its wake. According to Reuters news reports on Dec. 5, at least at total of 283 people were killed and hundreds remain missing ...
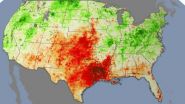
Plant stress paints early picture of drought
2012-12-06
In July 2012, farmers in the U.S. Midwest and Plains regions watched crops wilt and die after a stretch of unusually low precipitation and high temperatures. Before a lack of rain and record-breaking heat signaled a problem, however, scientists observed another indication of drought in data from NASA and NOAA satellites: plant stress.
Healthy vegetation requires a certain amount of water from the soil every day to stay alive, and when soil moisture falls below adequate levels, plants become stressed. Scientists with the U.S. Department of Agriculture's Agricultural Research ...
NASA investigates use of 'trailblazing' material for new sensors
2012-12-06
Tiny sensors -- made of a potentially trailblazing material just one atom thick and heralded as the "next best thing" since the invention of silicon -- are now being developed to detect trace elements in Earth's upper atmosphere and structural flaws in spacecraft.
Technologist Mahmooda Sultana, who joined NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Md., two years ago and has since emerged as Goddard's go-to expert in the development of graphene-based technology, has expanded her portfolio to include two new research and development efforts aimed at creating nano-sized ...
Site-specific, long-term research expanding understanding of climate change
2012-12-06
DURHAM, N.H., Dec. 5, 2012 – While science has often focused on big-scale, global climate change research, a study recently published in the journal Bioscience suggests that long-term, integrated and site-specific research is needed to understand how climate change affects multiple components of ecosystem structure and function, sometimes in surprising ways.
"Long-term ecological research is important to understanding the effects of a changing climate on our natural resources and so much more," said Michael T. Rains, Director of the Forest Service's Northern Research Station. ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Pekingese, Shih Tzu and Staffordshire Bull Terrier among twelve dog breeds at risk of serious breathing condition
Selected dog breeds with most breathing trouble identified in new study
Interplay of class and gender may influence social judgments differently between cultures
Pollen counts can be predicted by machine learning models using meteorological data with more than 80% accuracy even a week ahead, for both grass and birch tree pollen, which could be key in effective
Rewriting our understanding of early hominin dispersal to Eurasia
Rising simultaneous wildfire risk compromises international firefighting efforts
Honey bee "dance floors" can be accurately located with a new method, mapping where in the hive forager bees perform waggle dances to signal the location of pollen and nectar for their nestmates
Exercise and nutritional drinks can reduce the need for care in dementia
Michelson Medical Research Foundation awards $750,000 to rising immunology leaders
SfN announces Early Career Policy Ambassadors Class of 2026
Spiritual practices strongly associated with reduced risk for hazardous alcohol and drug use
Novel vaccine protects against C. diff disease and recurrence
An “electrical” circadian clock balances growth between shoots and roots
Largest study of rare skin cancer in Mexican patients shows its more complex than previously thought
Colonists dredged away Sydney’s natural oyster reefs. Now science knows how best to restore them.
Joint and independent associations of gestational diabetes and depression with childhood obesity
Spirituality and harmful or hazardous alcohol and other drug use
New plastic material could solve energy storage challenge, researchers report
Mapping protein production in brain cells yields new insights for brain disease
Exposing a hidden anchor for HIV replication
Can Europe be climate-neutral by 2050? New monitor tracks the pace of the energy transition
Major heart attack study reveals ‘survival paradox’: Frail men at higher risk of death than women despite better treatment
Medicare patients get different stroke care depending on plan, analysis reveals
Polyploidy-induced senescence may drive aging, tissue repair, and cancer risk
Study shows that treating patients with lifestyle medicine may help reduce clinician burnout
Experimental and numerical framework for acoustic streaming prediction in mid-air phased arrays
Ancestral motif enables broad DNA binding by NIN, a master regulator of rhizobial symbiosis
Macrophage immune cells need constant reminders to retain memories of prior infections
Ultra-endurance running may accelerate aging and breakdown of red blood cells
Ancient mind-body practice proven to lower blood pressure in clinical trial
[Press-News.org] Clinical trial tests rice bran to prevent cancerBioactive small molecules work synergistically, like a drug