Abuse during childhood linked to adult-onset asthma in African-American women
2012-12-07
(Press-News.org) (Boston) – According to a new study from the Slone Epidemiology Center (SEC) at Boston University, African-American women who reported suffering abuse before age 11 had a greater likelihood of adult-onset asthma compared to women whose childhood and adolescence were free of abuse.
The study, which is published online in the Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology, was led by Patricia Coogan, DSc, senior epidemiologist at SEC and associate professor of epidemiology at the Boston University School of Public Health.
This study followed 28,456 African-American women, all of whom are participants in the Black Women's Health Study, between 1995-2011. They completed health questionnaires and provided information on physical and sexual abuse during childhood up to age 11 and adolescence, ages 12-18.
The results indicate that the incidence of adult-onset asthma was increased by more than 20 percent among women who had been abused during childhood. The evidence was stronger for physical abuse than for sexual abuse. There was little indication, however, that abuse during adolescence was associated with the risk of adult-onset asthma.
"This is the first prospective study to show an association between childhood abuse and adult-onset asthma," said Coogan. "The results suggest that chronic stress contributes to asthma onset, even years later." The hypothesized mechanism linking childhood abuse to asthma incidence is stress and its physiological consequences, particularly effects on the immune system and on airway development.
According to 2010 statistics from the United States Department of Health and Human Service's (HHS) National Child Abuse and Neglect Data System, approximately 695,000 children aged 0-17 were identified as neglected or abused by state Child Protective Service agencies, and 22 percent of neglected or abused children were African-American. National statistics show that asthma is more prevalent in African-Americans.
"Given the high prevalence of asthma and of childhood abuse in the United States, the association is of significant public health importance," Coogan added.
###
The Black Women's Health Study (BWHS) is the largest follow-up study of the health of African American women in the United States. Led by researchers at the Slone Epidemiology Center, the BWHS has followed 59,000 African-American women through biennial questionnaires since 1995 and has led to a better understanding of numerous health conditions that disproportionately affect African-American women.
Funding for this study was provided by the National Institute of Health's National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (grant award #HL107314) and the National Cancer Institute (grant award #CA058420). END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2012-12-07
New Rochelle, NY, December 6, 2012—Enzymes play a crucial role as biocatalysts, increasing the speed and efficiency and decreasing the energy consumption of biochemical reactions in many industrial processes. The advantages of using compressed propane to enhance the biocatalytic activity of an industrial enzyme are described in an article published in Industrial Biotechnology, a peer-reviewed journal from Mary Ann Liebert, Inc., publishers (http://www.liebertpub.com). The article is available free on the Industrial Biotechnology website (http://www.liebertpub.com/ind). ...
2012-12-07
PHILADELPHIA — Periodontitis, a form of chronic gum disease that affects nearly half of the U.S. adult population, results when the bacterial community in the mouth becomes unbalanced, leading to inflammation and eventually bone loss. In its most severe form, which affects 8.5 percent of U.S. adults, periodontitis can impact systemic health.
By blocking a molecular receptor that bacteria normally target to cause the disease, scientists from the University of Pennsylvania have now demonstrated an ability in a mouse model to both prevent periodontitis from developing and ...
2012-12-07
Highlights
The incidence of the most severe form of acute kidney injury has increased 10% per year on average over the past decade.
Deaths associated with the condition have doubled during that time.
Washington, DC (December 6, 2012) — Acute kidney injury (AKI), an abrupt or rapid decline in kidney function, is a serious and increasingly prevalent condition that can occur after major infections, major surgery, or exposure to certain medications. The incidence rates of the most serious form of AKI—which requires dialysis—increased rapidly in all patient subgroups ...
2012-12-07
The catastrophic drought last year in the Horn of Africa affected millions of people but also caused the extremely late arrival into northern Europe of several migratory songbird species, a study from University of Copenhagen published today in Science shows. Details of the migration route was revealed by data collected from small back-packs fitted on birds showing that the delay resulted from an extended stay in the Horn of Africa.
The extensive 2011 drought in the Horn of Africa had significant consequences for European songbirds such as thrush nightingale and red-backed ...
2012-12-07
HOUSTON – (Dec. 7, 2012) – For much of her professional life, Dr. Susan Rosenberg (www.bcm.edu/genetics/?pmid=11034) has studied the puzzling response of bacteria to stress and the mutations that result. In the current issue of the journal Science (www.sciencemag.org), she puts together the pieces of that puzzle, describing most of the members of an elaborate gene network that functions in causing mutations during repair of double-stranded breaks in the DNA of stressed cells.
"We now know the 93 genes more than half of which are funneling into three nodes that go down ...
2012-12-07
Scientists from New Zealand, Austria and the UK have created the world's smallest reaction chamber, with a mixing volume that can be measured in femtolitres (million billionths of a litre).
Using this minuscule reaction chamber, lead researcher Peter Derrick, professor of chemical physics and physical chemistry and head of the Institute of Fundamental Sciences at Massey University in New Zealand, plans to study the kind of speedy, nanoscale biochemical reactions that take place inside individual cells. This work appears in the latest issue of the European Journal of Mass ...
2012-12-07
Antidepressants are the most widely used treatment for people with moderate to severe depression. However, up to two thirds of people with depression don't respond fully to this type of treatment. New findings, published in The Lancet, have shown cognitive behavioural therapy (CBT)*, provided in addition to usual care, can reduce symptoms of depression and help improve patients' quality of life.
This is the first large-scale trial to test the effectiveness of CBT — a type of talking psychotherapy — given in addition to usual care that includes antidepressants. The National ...
2012-12-07
The family of disorders known as ataxia can impair speech, balance and coordination, and have varying levels of severity. Scientists from the Universities of Oxford and Edinburgh have identified a new member of this group of conditions which is connected to 'Lincoln ataxia', so called because it was first found in the relatives of US President Abraham Lincoln. The results are published in the journal PLOS Genetics.
Lincoln ataxia affects the cerebellum, a crucial part of the brain controlling movement and balance. It is caused by an alteration in the gene for 'beta-III ...
2012-12-07
Women with higher circulating carotenoid levels are at a reduced risk of breast cancer according to a study published December 6 in the Journal of the National Cancer Institute
Carotenoids, which are micronutrients found in fruits and vegetables, have been found to have anticarcinogenic properties. Previous experimental studies have shown that carotenoids inhibit the tumor progression and reduce proliferation of estrogen receptor–positive (ER+) and estrogen receptor–negative (ER-) breast cancers. Despite the inverse association between carotenoids and breast cancer ...
2012-12-07
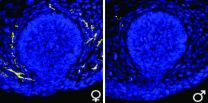
Johns Hopkins scientists have found a surprising mechanism that gives male sex hormones like testosterone control over the gender-specific absence or presence of mammary gland nerves that sense the amount of milk available in breast milk ducts.
In a Dec. 7 report on their discovery in Science, they say the hormones do the job by altering the availability of a nerve growth factor, called BDNF for short.
The most obvious differences between males and females involve the presence or absence of physical structures. Below the surface, however, these structures are penetrated ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Abuse during childhood linked to adult-onset asthma in African-American women