(Press-News.org) Blood levels of an immunity-related protein, galectin-1, in patients with newly diagnosed Hodgkin lymphoma reflected the extent of their cancer and correlated with other predictors of outcome, scientists reported at the American Society of Hematology annual meeting.
In a study of 315 patients from a German database, researchers from Dana-Farber Cancer Institute found that serum galectin-1 levels "are significantly associated with tumor burden and additional adverse clinical characteristics in newly diagnosed Hodgkin lymphoma (HL) patients."
The measurements were made possible by a new laboratory test called a "sandwich ELISA" devised by the Dana-Farber team, led by Margaret Shipp, MD, director of the lymphoma program at Dana-Farber. Galectin-1 is a protein which, when overexpressed by Hodgkin lymphoma cells, allows them to evade the body's immune response that normally would detect the cancer and attack it with cell-killing lymphocytes. The Shipp group developed antibodies that recognize the galectin-1 protein and were used in developing the sandwich ELISA assay.
Since the protein is secreted into the bloodstream, the investigators hypothesized that measuring relative levels of galectin-1 in newly diagnosed, untreated Hodgkin patients could help to assess likely outcomes in those patients. Such predictions, in turn, could help physicians decide how aggressively to treat the lymphoma, Shipp explained. With further development, she added, the assay could become "an objective test that might help make decisions on which way to treat patients."
The Dana-Farber scientists collaborated with researchers of the German Hodgkin Study Group (GHSG) at the University Hospital of Cologne. Shipp said that the GHSG has "probably the largest, most comprehensive data on clinical trials of patient with well-defined Hodgkin lymphoma." The 315 patients whose blood levels of galactin-1 were tested in the study had been enrolled in three different clinical trials – one for early-stage disease, a second for early-stage disease with additional less-favorable risk factors, and the third for patients with bulky localized or advanced-stage disease.
Using the sandwich ELISA assay, the Dana-Farber investigators found that blood galectin-1 levels in Hodgkin lymphoma patients were significantly higher than in normal control patients. They also found that relative galectin-1 levels were correlated with the risk factors that had been used to assign the 315 patients to the three different clinical trials. Direct comparisons of the galectin-1 levels with patient outcomes are awaiting the completion of one of the clinical trials, the researchers noted.
Beyond the potential for a clinical test, galectin-1 holds promise as a therapeutic target, said Shipp, whose group has made a "neutralizing" antibody to block the protein. She said the antibody, which is produced in mice, would need to be "humanized," or genetically modified to be compatible with human patients, and then undergo rigorous testing for safety and efficacy. This is under discussion with potential industrial partners, said Shipp.
INFORMATION:
The first author of the report is Jing Ouyang, PhD, a postdoc in the Shipp laboratory.
The research was supported by the Leukemia and Lymphoma Society and by the Miller Family Research Fund.
About Dana-Farber Cancer Institute
Dana-Farber Cancer Institute is a principal teaching affiliate of the Harvard Medical School and is among the leading cancer research and care centers in the United States. It is a founding member of the Dana-Farber/Harvard Cancer Center (DF/HCC), designated a comprehensive cancer center by the National Cancer Institute. It provides adult cancer care with Brigham and Women's Hospital as Dana-Farber/Brigham and Women's Cancer Center and it provides pediatric care with Boston Children's Hospital as Dana-Farber/Children's Hospital Cancer Center. Dana-Farber is the top ranked cancer center in New England, according to U.S. News & World Report, and one of the largest recipients among independent hospitals of National Cancer Institute and National Institutes of Health grant funding. Follow Dana-Farber on Facebook: www.facebook.com/danafarbercancerinstitute and on Twitter: @danafarber.
END
When it comes to climate change, deforestation and toxic waste, the assumption has been that conservative views on these topics are intractable. But new research from the University of California, Berkeley, suggests that such viewpoints can be changed after all, when the messages about the need to be better stewards of the land are couched in terms of fending off threats to the "purity" and "sanctity" of Earth and our bodies.
A UC Berkeley study has found that while people who identified themselves as conservatives tend to be less concerned about the environment than ...
Violent acts in James Bond films were more than twice as common in Quantum of Solace (2008) than in the original 1962 movie Dr No, researchers from New Zealand's University of Otago have found.
The researchers analysed 22 official franchise films, which span 46 years, to test the hypothesis that popular movies are becoming more violent (The latest Bond film, Skyfall, was not included as it was unreleased at the time of the study).
They found that rates of violence increased significantly over the period studied and there was an even bigger increase in portrayals of ...
Infrared data from NASA's Aqua satellite have watched the strong thunderstorms in Typhoon Bopha fizzle and shrink in area over the weekend as wind shear increased. Bopha has now dissipated in the South China Sea, just west of Luzon, Philippines.
NASA's Aqua satellite has been providing data on Bopha since the day it formed on Nov. 26. In the storm's last days, Aqua's Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) instrument captured infrared data of the storm and showed that cloud top temperatures warmed from Dec. 8 through Dec. 9 as cloud heights fell and thunderstorms lost their ...
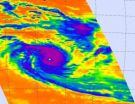
NASA's Aqua satellite got "eyeballed" from Cyclone Claudia in the Southern Indian Ocean when two instruments captured the storm's eye in infrared and visible light. Satellite data indicates that Claudia's eye is about 10 nautical miles wide.
On Dec. 10 at 0841 UTC (3:41 a.m. EST), NASA's Aqua satellite's Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) instrument captured an infrared view of Cyclone Claudia which showed a clear eye surrounded by powerful thunderstorms. The thunderstorms that surrounded the eye were high in the troposphere and cloud top temperatures topped -63 Fahrenheit ...
An experimental drug combination for preventing graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) was not significantly better than the standard regimen on key endpoints, according to a report of a phase 3 trial at the American Society of Hematology annual meeting.
The combination of two immunosuppressive compounds -- tacrolimus plus sirolimus -- did not provide a statistically significant, GVHD-free survival benefit over the long-used standard of care, tacrolimus plus methotrexate, said researchers from Dana-Farber Cancer Institute who led the multi-center trial.
However, there were ...
Public opinion on environmental issues such as climate change, deforestation, and toxic waste seems to fall along increasingly partisan lines. But new research suggests that environmental messages framed in terms of conservative morals — describing environmental stewardship in terms of fending off threats to the "purity" and "sanctity" of Earth and our bodies — may help to narrow the partisan gap.
A study from researchers at UC Berkeley has found that while people who identified themselves as conservatives tend to be less concerned about the environment than their liberal ...
COLUMBIA, Mo. – Medication reconciliation is a safety practice in which health care professionals review patients' medication regimens when patients transition between settings to reduce the likelihood of adverse drug effects. It is among the most complex clinical tasks required of physicians, nurses and pharmacists, who must work cooperatively to minimize discrepancies and inappropriate medication orders. Now, a University of Missouri gerontologiccal nursing expert suggests that acknowledging practitioners' varying perspectives on the purpose of medication reconciliation ...
ATLANTA - A two-prong approach combining ibrutinib and rituximab (Rituxin®) to treat aggressive chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) produced profound responses with minor side effects in a Phase 2 clinical trial at the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center.
Researchers presented the results today at the 54th annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology (ASH).
"This is a patient population with a great need for more targeted therapies," said Jan Burger, M.D., Ph.D., associate professor in MD Anderson's Department of Leukemia. Burger was lead author of ...
Physicians associated with "patient philanthropy" – financial donations from grateful patients to a medical institution – are concerned with how these contributions might affect their own behavior and attitudes, and how they might impact the doctor-patient relationship. A new study¹ by Scott Wright, MD and Joseph A. Carrese, MD, MPH of Johns Hopkins University, and colleagues, explores this topic. The paper considers the perspectives of internal medicine physicians working in an academic medical center who have had experiences with these situations. Their findings appear ...
OAK BROOK, Ill. – Some stroke patients may benefit from cerebral angioplasty and stent placement, according to a new study published online in the journal Radiology.
"As many as 70 percent of ischemic stroke patients could have positive clinical outcomes with the additional use of intra-arterial revascularization using stents," said Martin Roubec, M.D., Ph.D., a neurologist in the Comprehensive Stroke Center at the University Hospital Ostrava in the Czech Republic.
Ischemic stroke, the most common form of stroke, occurs when blockage in an artery—often from a blood ...