(Press-News.org) URBANA – Every year farmers spend a lot of money trying to control corn rootworm larvae, which are a significant threat to maize production in the United States and, more recently, in Europe. University of Illinois researchers have been working on validating a model for estimating damage functions.
Nicholas Tinsley, a doctoral candidate in crop sciences, has refined a model developed in 2009 by researchers at the University of Wisconsin and in Brescia, Italy, to describe the relationship between root injury caused by these pests and yield loss. He used the equivalent of 19 years of data collected by personnel from the Insect Management and Insecticide Evaluation Program in the U of I Department of Crop Sciences.
"Every year we evaluate a number of different management tactics for corn rootworm; these include soil insecticides and Bt traits," Tinsley explained. "We do that at a number of different locations on university research farms."
Tinsley took more than 7,000 data points from field crop insect management trials at Urbana, Perry, Monmouth, and DeKalb for 2005-2011. These trials measured root injury on a 0-3 node-injury scale and mechanically harvested the center two rows of each plot after the crop reached maturity to calculate yield. The results suggested that yield was reduced by 15 percent for each node of roots lost.
Two components had a statistically significant effect variance in the data–location and experimental error. Year had no significant effect.
Tinsley attributes the location effect to differences in weather characteristics and in soil type. "The larva doesn't really burrow through the soil, it exploits existing soil pores. If you have smaller soil pores, it's not able to navigate through the soil and find those roots very well," he said.
The large experimental error indicates that a significant amount of the variability remains unexplained. Tinsley said that this is not surprising considering that yield and proportional yield loss in the experiments varied considerably, probably due to differences among hybrids in yield potential and response to environmental conditions. Other factors that may have contributed to the variability include planting date, planting population, crop emergence, moisture at harvest, and management tactics.
"This not a model that a farmer can use to say, 'What is my yield loss going to be like this year?'" said Tinsley. "You just don't know what some of these things that are affecting the error are going to do."
The model may, however, be useful to help economists to estimate the effect of corn rootworm. "That's when a model like this can become really handy," he continued.
Tinsley said that further directions for this research include developing collaborations with other states. "If we extend to the western Corn Belt where it may be drier, we might start to see differences between two different regions in the relationship," he said.
Another direction is to explicitly model heat stress and moisture stress into the model, perhaps as a covariate. Such an analysis would look at the effects of combinations of factors.
"For example, if I have one node of roots destroyed but I have 10 inches of moisture stress, what's going to happen as compared to what happens if I have one node of root injury but no moisture stress," he explained.
He noted that many studies have demonstrated that often, when there is neither moisture stress nor excessive heat stress, the injury from corn rootworm does not result in significant yield loss.
Another factor to consider is lodging, when plants with root injury fall over. Lodged plants are very difficult to harvest.
"Under certain circumstances, you can have not very much root injury but a lot of lodging and big yield losses," Tinsley said. "Under other circumstances, you can have what seems to be a lot of root injury but if there are no big storms and you don't have any lodging, there may be no yield loss." Future collaborations in the development of this damage function may include lodging in the model.
INFORMATION: The article, "The validation of a nested error component model to estimate damage cause by corn rootworm larvae," was published in Journal of Applied Entomology, which is available online at http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/j.1439-0418.2012.01736.x/abstract. Ronald Estes and Michael Gray, also in the Department of Crop Sciences, are co-authors.
END
DETROIT - Both nature and nurture appear to be significant factors in early antisocial behaviors of adopted children, a Wayne State University researcher believes.
Christopher Trentacosta, Ph.D., assistant professor of psychology in the College of Liberal Arts and Sciences, recently examined data from 361 linked triads (birth mother, adoptive parents, adopted child) in order to assess externalizing behavioral problems such as aggression and defiance when children were 18, 27 and 54 months of age.
The triads were part of the Early Growth and Development Study (EGDS), ...
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. — The small kerosene lamps that light millions of homes in developing countries have a dark side: black carbon – fine particles of soot released into the atmosphere.
New measurements show that kerosene wick lamps release 20 times more black carbon than previously thought, say researchers at the University of Illinois and the University of California, Berkeley. The group published its findings in the journal Environmental Science and Technology.
Black carbon is a hazard for human health and the environment, affecting air quality both indoors and out. ...
Young patients with an aggressive form of leukemia who are likely to relapse after chemotherapy treatment can significantly reduce those odds by receiving additional courses of chemotherapy, suggest the findings of a clinical trial led by investigators at Dana-Farber/Children's Hospital Cancer Center in Boston.
The trial leaders will present the results of the Dana-Farber Cancer Institute ALL Consortium study, which involved nearly 500 patients under age 18 with B-precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia (B-ALL), at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology ...
Over past decades, many areas of the forested Amazon basin have become a patchwork of farms, pastures and second-growth forest as people have moved in and cleared land--but now many are moving out, in search of economic opportunities in newly booming Amazonian cities. The resulting depopulation of rural areas, along with spreading road networks and increased drought are causing more and bigger fires to ravage vast stretches, say researchers in a new study. The study, focusing on the Peruvian Amazon, is the latest to suggest that land-use changes and other factors, including ...
Blood levels of an immunity-related protein, galectin-1, in patients with newly diagnosed Hodgkin lymphoma reflected the extent of their cancer and correlated with other predictors of outcome, scientists reported at the American Society of Hematology annual meeting.
In a study of 315 patients from a German database, researchers from Dana-Farber Cancer Institute found that serum galectin-1 levels "are significantly associated with tumor burden and additional adverse clinical characteristics in newly diagnosed Hodgkin lymphoma (HL) patients."
The measurements were made ...
When it comes to climate change, deforestation and toxic waste, the assumption has been that conservative views on these topics are intractable. But new research from the University of California, Berkeley, suggests that such viewpoints can be changed after all, when the messages about the need to be better stewards of the land are couched in terms of fending off threats to the "purity" and "sanctity" of Earth and our bodies.
A UC Berkeley study has found that while people who identified themselves as conservatives tend to be less concerned about the environment than ...
Violent acts in James Bond films were more than twice as common in Quantum of Solace (2008) than in the original 1962 movie Dr No, researchers from New Zealand's University of Otago have found.
The researchers analysed 22 official franchise films, which span 46 years, to test the hypothesis that popular movies are becoming more violent (The latest Bond film, Skyfall, was not included as it was unreleased at the time of the study).
They found that rates of violence increased significantly over the period studied and there was an even bigger increase in portrayals of ...
Infrared data from NASA's Aqua satellite have watched the strong thunderstorms in Typhoon Bopha fizzle and shrink in area over the weekend as wind shear increased. Bopha has now dissipated in the South China Sea, just west of Luzon, Philippines.
NASA's Aqua satellite has been providing data on Bopha since the day it formed on Nov. 26. In the storm's last days, Aqua's Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) instrument captured infrared data of the storm and showed that cloud top temperatures warmed from Dec. 8 through Dec. 9 as cloud heights fell and thunderstorms lost their ...
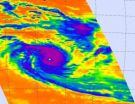
NASA's Aqua satellite got "eyeballed" from Cyclone Claudia in the Southern Indian Ocean when two instruments captured the storm's eye in infrared and visible light. Satellite data indicates that Claudia's eye is about 10 nautical miles wide.
On Dec. 10 at 0841 UTC (3:41 a.m. EST), NASA's Aqua satellite's Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) instrument captured an infrared view of Cyclone Claudia which showed a clear eye surrounded by powerful thunderstorms. The thunderstorms that surrounded the eye were high in the troposphere and cloud top temperatures topped -63 Fahrenheit ...
An experimental drug combination for preventing graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) was not significantly better than the standard regimen on key endpoints, according to a report of a phase 3 trial at the American Society of Hematology annual meeting.
The combination of two immunosuppressive compounds -- tacrolimus plus sirolimus -- did not provide a statistically significant, GVHD-free survival benefit over the long-used standard of care, tacrolimus plus methotrexate, said researchers from Dana-Farber Cancer Institute who led the multi-center trial.
However, there were ...