(Press-News.org) Contact: David Hosansky
hosansky@ucar.edu
303-497-8611
Zhenya Gallon, NCAR/UCAR Media Relations
zhenya@ucar.edu
303-497-8607
National Center for Atmospheric Research/University Corporation for Atmospheric Research
New system for aircraft forecasts potential storm hazards over oceans
BOULDER—The National Center for Atmospheric Research (NCAR) has developed a prototype system to help flights avoid major storms as they travel over remote ocean regions. The 8-hour forecasts of potentially dangerous atmospheric conditions are designed for pilots, air traffic controllers, and others involved in transoceanic flights.
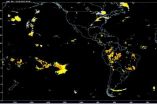
The NCAR-based system, developed with funding from NASA's Applied Sciences Program, combines satellite data and computer weather models to produce maps of storms over much of the world's oceans. The system is based on products that NCAR has developed to alert pilots and air traffic controllers about storms and related hazards, such as turbulence and lightning, over the continental United States.
Development of the forecasts was spurred in part by the 2009 crash of Air France Flight 447, which encountered a complex of thunderstorms over the Atlantic Ocean. NCAR worked with the Massachusetts Institute of Technology's Lincoln Laboratory, the Naval Research Laboratory, and the University of Wisconsin-Madison to create the system.
"These new forecasts can help fill an important gap in our aviation system," says NCAR's Cathy Kessinger, the lead researcher on the project. "Pilots have had limited information about atmospheric conditions as they fly over the ocean, where conditions can be severe. By providing them with a picture of where significant storms will be during an eight-hour period, the system can contribute to both the safety and comfort of passengers on flights over the ocean."
The forecasts, which continue to be tested and modified, can be viewed at http://www.rap.ucar.edu/projects/ocn/realtime_sys/global_extrap/. They cover most of the Atlantic and Pacific oceans, where NCAR has real-time access to geostationary satellite data. The forecasts are updated every three hours.
-----Flying with limited information-----
Pilots of transoceanic flights currently get preflight briefings and, in certain cases involving especially intense storms, in-flight weather updates every four hours. They also have onboard radar.
The information, however, is of limited value for strategic flight planning while en route. Pinpointing turbulence associated with storms over the oceans is far more challenging than over land because geostationary satellites, unlike ground-based radar, cannot see within the clouds. Thunderstorms may develop quickly and move rapidly, rendering the briefings and weather updates obsolete. Onboard radars lack the power to see long distances or through dense clouds.
As a result, pilots often must choose between detouring hundreds of miles around potentially stormy areas or flying through a region that may or may not contain intense weather. Storms may be associated with hazardous windshear and icing conditions, in addition to lightning, hail, and potentially severe turbulence.
"Turbulence is the leading cause of injuries in commercial aviation," says John Haynes, Applied Sciences Program manager at NASA Headquarters in Washington. "This prototype system is of crucial importance to pilots and is another demonstration of the practical benefit of NASA's Earth observations."
To create the forecasts, Kessinger and her colleagues first turned to geostationary satellite measurements to identify regions of the atmosphere that met two conditions: particularly high cloud tops and water vapor at high altitudes. Those two conditions are a sign of strong updrafts that can buffet an aircraft and are also correlated with powerful storms. They then used fuzzy logic and data fusion techniques to home in on storms of particular concern, and applied object tracking techniques and simulations of wind fields to predict storm locations at hourly intervals out to eight hours.
Researchers verified the forecasts using observations from the NASA Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission (TRMM) satellite.
"These advanced techniques enable us to inform pilots about the potential for violent downdrafts and turbulence, even over the middle of the ocean where we don't have land-based radar or other tools to observe storms in detail," Kessinger says.
INFORMATION:
The University Corporation for Atmospheric Research manages the National Center for Atmospheric Research under sponsorship by the National Science Foundation. Any opinions, findings and conclusions, or recommendations expressed in this publication are those of the author(s) and do not necessarily reflect the views of the National Science Foundation.
On the Web
Oceanic convection forecasting system
http://www.rap.ucar.edu/projects/ocn/realtime_sys/global_extrap/
News releases, visuals, and more:
www.ucar.edu/atmosnews
New system for aircraft forecasts potential storm hazards over oceans
2012-12-11
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Does changing the price of medicine influence consumers' perceived health risk?
2012-12-11
Consumers assume their risk of getting a serious illness is higher when medications are cheaper because they believe that prices for life-saving products are based on need and not profit, according to a new study in the Journal of Consumer Research.
"When consumers see lower prices for a life-saving product, they infer a higher need and thereby a greater risk that they can contract the disease. On the other hand, higher prices signal that a drug or treatment is inaccessible and thus the risk of getting a disease must not be all that great," write authors Adriana Samper ...
Eating or spending too much? Blame it on Facebook
2012-12-11
Participating in online social networks can have a detrimental effect on consumer well-being by lowering self-control among certain users, according to a new study in the Journal of Consumer Research.
"Using online social networks can have a positive effect on self-esteem and well-being. However, these increased feelings of self-worth can have a detrimental effect on behavior. Because consumers care about the image they present to close friends, social network use enhances self-esteem in users who are focused on close friends while browsing their social network. This ...
Who are you calling old? How elderly consumers negotiate their identities
2012-12-11
Caregivers view elderly consumers as "old" when they can no longer perform everyday consumption activities on their own regardless of their actual age, according to a new study in the Journal of Consumer Research.
"Consumption activities such as shopping, preparing meals, doing housework, going to the doctor, taking medications, and managing money serve as a means of identifying someone as old and a venue for working through conflicts that arise when older consumers who do not identify as old are treated as an 'old person' by family members and service providers," write ...
The current state of lung cancer treatment
2012-12-11
A review in the December issue of the journal Archives of Pathology & Laboratory Medicine by Paul Bunn Jr, MD, University of Colorado Cancer Center investigator and past president of ASCO, IASLC and AACI describes the current state of lung cancer care.
"We're in a new paradigm in which we realize this top cause of cancer deaths is actually a number of related diseases, each potentially with its own cause and cure," Bunn says.
The review describes the shift from blanketing lung cancer with radiation and chemotherapy, to targeting the specific genetic mutations that cause ...
Battling brittle bones... with broccoli and spinach?
2012-12-11
Troy, N.Y. – A new study from engineering researchers at Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute shows, for the first time, how the little-understood protein osteocalcin plays a significant role in the strength of our bones. The findings could lead to new strategies and therapeutics for fighting osteoporosis and lowering the risk of bone fracture.
Funded by the U.S. National Institutes of Health, the study details how fractures in healthy bones begin with the creation of incredibly tiny holes, each measuring only about 500 atoms in diameter, within the bone's mineral structure. ...
Reports assess global student achievement in math, science and reading literacy
2012-12-11
CHESTNUT HILL, Mass. (12-11-12)—Students from East Asian countries, in addition to a select group of European countries, outperformed students around the world in mathematics, science and reading at both the fourth and eighth grades, according to results released Dec. 11 by Lynch School of Education Professors Ina V.S. Mullis and Michael O. Martin, executive directors of the TIMSS & PIRLS International Study Center.
The Trends in International Mathematics and Science Study (TIMSS) is the first global assessment of mathematics and science to provide data about trends over ...
Holiday shopping madness: When do consumers seek to punish fellow shoppers for behaving badly?
2012-12-11
Consumers seek to punish fellow consumers who violate social norms while shopping but also make exceptions depending on the situation, according to a new study in the Journal of Consumer Research.
"Punishment is a complex decision for consumers to make as it is difficult to punish someone but also difficult to look the other way. Consumers do not seem to make these decisions lightly, and a number of interesting factors influence consumer punishment decisions," write authors Lily Lin, Darren W. Dahl (both University of British Columbia), and Jennifer J. Argo (University ...
How do stay-at-home dads seek greater social acceptance?
2012-12-11
In order to avoid the stigma and loss of status posed by their lifestyle choice, stay-at-home fathers are mobilizing to build greater legitimacy for their marginalized gender identity, according to a new study in the Journal of Consumer Research.
"Stay-at-home fathers aggressively pursue recognition by and acceptance from mainstream institutions, with a particular emphasis on the mass market and iconic household and family-oriented brands. Accordingly, they vigilantly watch for mass media representations and advertisements that positively acknowledge their collective ...
Need to move soon? Don't trust your emotions
2012-12-11
Consumers are more likely to make emotional instead of objective assessments when the outcomes are closer to the present time than when they are further away in the future, according to a new study in the Journal of Consumer Research.
"The proximity of a decision's outcome increases consumer reliance on feelings when making decisions. Feelings are relied upon more when the outcome is closer in time because these feelings appear to be more informative in such situations," write authors Hannah H. Chang (Singapore Management University) and Michel Tuan Pham (Columbia University).
From ...
Value or attention: Why do consumers prefer familiar products?
2012-12-11
Consumers are more likely to purchase a product if they have previously focused their attention on it but are less likely to purchase a product they have previously ignored, according to a new study in the Journal of Consumer Research.
"It's generally assumed that consumers will choose products that provide the greatest value. But prior consideration of a product makes it easier to process the product when it's encountered later and this influences whether or not consumers like the product, regardless of the benefits it provides. The act of attending to a product increases ...