(Press-News.org) Cyclone Evan is now far south of Fiji and wind shear and cooler sea surface temperatures have been taking their toll on the storm and weakening it. Infrared data from NASA's Aqua satellite has shown a quick decline in the storm's structure over one day.
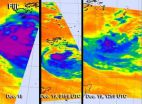
A time series of infrared images from the Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) instrument that flies aboard NASA's Aqua satellite showed changes in intense thunderstorms within Cyclone Evan between Dec. 18 and Dec. 19. Over a time period of 36 hours, Evan weakened from Cyclone strength to Tropical Storm strength. In an AIRS image captured on Dec. 18 there were two large areas of strong thunderstorms with very cold cloud top temperatures colder than -63 Fahrenheit (-52 Celsius).
By Dec. 19 at 0159 UTC (Dec. 18 at 8:59 p.m. EST/U.S.) the area of strong thunderstorms had become smaller, and the storm appeared less organized. In the AIRS infrared image from Dec. 19 at 1259 UTC (7:59 a.m. EST), the area of strongest thunderstorms had been reduced further and cloud top temperatures throughout the storm were warming, indicating cloud heights were falling because of less evaporation. Evan had moved over sea surface temperatures below the 80 degree Fahrenheit (26.6 degree Celsius) threshold, so evaporation and thunderstorm development had waned.
Wind shear had increased as well, pushing the bulk of the thunderstorm activity about 65 nautical miles (74.8 miles/120.4 km) to the southeast, according to the Joint Typhoon Warning Center. Northwesterly wind shear was very strong, blowing between 40 and 50 knots (46 and 57.5 mph/74 and 92.6 kph). Animated multi-spectral satellite imagery also showed the low-level circulation center remains fully exposed.
On Dec. 19 at 0900 UTC (4 a.m. EST/U.S.), Evan was a tropical storm with maximum sustained winds near 45 knots (51.7 mph/83.3 kph). It was located about 335 nautical miles (385.5 miles/620.4 km) south of Nadi, Fiji, near 23.7 south latitude and 178.3 east longitude. Evan was moving to the south-southeast at 7 knots (8 mph/13 kph).
Forecasters at the Joint Typhoon Warning Center noted that because of the strong wind shear and cooler sea surface temperatures, Evan may dissipate sometime on Dec. 20.
INFORMATION:
Time series of infrared NASA images show Cyclone Evan's decline
2012-12-20
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
NASA satellite finds an unusually tall storm-cell in Cyclone Evan
2012-12-20
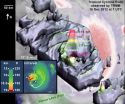
NASA's Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission or TRMM satellite found an unusually tall towering thunderstorm in Cyclone Evan.
According to Owen Kelley of the TRMM satellite team at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Md, the most startling feature of the December 16 overflight of Tropical Cyclone Evan was the extremely tall storm-cell in the north side of the eyewall. At the time TRMM passed overhead and captured an image of the storm, Evan was about to rake across the northern coast of the islands of Fiji.
The updrafts in this tower extended high enough ...
Why our backs can't read braille
2012-12-20
Johns Hopkins scientists have created stunning images of the branching patterns of individual sensory nerve cells. Their report, published online in the journal eLife on Dec. 18, details the arrangement of these branches in skin from the backs of mice. The branching patterns define ten distinct groups that, the researchers say, likely correspond to differences in what the nerves do and could hold clues for pain management and other areas of neurological study.
Each type of nerve cell that the team studied was connected at one end to the spinal cord through a thin, wire-like ...
NASA's Operation IceBridge data brings new twist to sea ice forecasting
2012-12-20
Shrinking Arctic sea ice grabbed the world's attention again earlier this year with a new record low minimum. Growing economic activity in the Arctic, such as fishing, mineral exploration and shipping, is emphasizing the need for accurate predictions of how much of the Arctic will be covered by sea ice. Every June, an international research group known as the Study of Environmental Arctic Change (SEARCH) publishes a summary of the expected September Arctic sea ice minimum known as the Sea Ice Outlook. The initial reports and monthly updates aim to give the scientific community ...
LSUHSC research discovery provides therapeutic target for ALS
2012-12-20
New Orleans, LA –Research led by Dr. Udai Pandey, Assistant Professor of Genetics at LSU Health Sciences Center New Orleans, has found that the ability of a protein made by a gene called FUS to bind to RNA is essential to the development of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS). This discovery identifies a possible therapeutic target for the fatal neurological disease. The research will be available online in the Advanced Access section of the journal Human Molecular Genetics website, posted by December 21, 2012. It will be published in an upcoming issue of the journal.
...
Small changes in eating prompts weight loss
2012-12-20
Making small easy changes to our eating habits on a consistent basis - 25 days or more per month - can lead to sustainable weight loss, according to research by Professor Brian Wansink in Cornell University's Food and Brand Lab. The challenge is to figure out which changes work for specific individuals and how to stick with changes long enough to make them second nature.
To explore this issue, Cornell researchers launched the National Mindless Eating Challenge (NMEC), an online healthy eating and weight loss program that focused on simple eating behavior changes, instead ...
MicroRNAs present exciting opportunities for cancer therapy and diagnosis
2012-12-20
Amsterdam, NL, December 19, 2012 – As many as 50 percent of all human protein-coding genes are regulated by microRNA (miRNA) molecules. While some miRNAs impact onset and progression of cancer, others can actually suppress the development of malignant tumors and are useful in cancer therapy. They can also serve as potential biomarkers for early cancer detection. In a new issue of Cancer Biomarkers, investigators report on non-coding miRNAs as appealing biomarkers for malignancy.
"MiRNA-based therapies are attractive partly due to the fact that these molecules can target ...
California's graduate students in environmental sciences lag behind in technology, computation
2012-12-20
RIVERSIDE, Calif. — Researchers at the University of California, Riverside have conducted a study showing that many skills and practices that could help scientists make use of technological and computational opportunities are only marginally being taught in California's formal graduate programs in the environmental sciences.
The researchers found, too, that graduate students in the state were, in general, not engaged in data management practices. Of the students surveyed who had already completed their graduate degree, only 29.3 percent had made their research data products ...
Delusions of gender: Men's insecurities may lead to sexist views of women
2012-12-20
He loves her, he loves her not.
A new study led by Joshua Hart, assistant professor of psychology, suggests that men's insecurities about relationships and conflicted views of women as romantic partners and rivals could lead some to adopt sexist attitudes about women.
The study was recently published in Personality and Social Psychology Bulletin, a peer-reviewed journal.
Hart and his co-authors, Jacqueline Hung '11, a former student of Hart's, and psychology professors Peter Glick of Lawrence University and Rachel Dinero of Cazenovia College, surveyed more than 400 ...
Young offenders who work, don't attend school may be more antisocial
2012-12-20
Many high school students work in addition to going to school, and some argue that employment is good for at-risk youths. But a new study has found that placing juvenile offenders in jobs without ensuring that they attend school may make them more antisocial.
The study, by researchers at the University of Pittsburgh, Temple University, and the University of California, Irvine, appears in the journal Child Development.
While evidence suggests that working long hours during the school year has negative effects on adolescent antisocial behavior among middle- and upper-income ...
Topics of teen sibling fights affect anxiety, depression, self-esteem
2012-12-20
Fights between siblings about simple things, like whose turn it is to empty the dishwasher, aren't harmless. Rather, such fights are about equality and fairness, and they can lead to depression, according to a new study.
The longitudinal research, by researchers at the University of Missouri, appears in the journal Child Development.
Although teen siblings fight about a lot of different issues, many of their fights can be categorized as being about equality and fairness (for example, whose turn it is to empty the dishwasher) or invasion of personal space (for example, ...