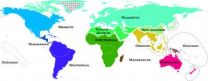
(Press-News.org) Until today, Alfred Russell Wallace's century old map from 1876 has been the backbone for our understanding of global biodiversity. Thanks to advances in modern technology and data on more than 20,000 species, scientists from University of Copenhagen have now produced a next generation map depicting the organisation of life on Earth. Published online in Science Express today, the new map provides fundamental information regarding the diversity of life on our planet and is of major significance for future biodiversity research.
An essential question in understanding life on Earth is why species are distributed the way they are across the planet. This new global map shows the division of nature into 11 large biogeographic realms and shows how these areas relate to each other. It is the first study to combine evolutionary and geographical information for all known mammals, birds and amphibians, a total of over 20,000 species.
Based on the work at the Center for Macroecology, Evolution and Climate at the University of Copenhagen involving 15 international researchers and 20 years of data compilation, the study is published today in Science Express.
The first attempt to describe the natural world in an evolutionary context was made in 1876 by Alfred Russel Wallace, the co-discoverer of the theory of natural selection, along with Charles Darwin. "Our study is a long overdue update of one of the most fundamental maps in natural sciences. For the first time since Wallace's attempt we are finally able to provide a broad description of the natural world based on incredibly detailed information for thousands of vertebrate species," says co-lead-author, Dr. Ben Holt from the Center for Macroecology, Evolution and Climate.
The new map can be split into finer geographical details for each class of animals. It is made freely available to contribute to a wide range of biological sciences, as well as conservation planning and management of biodiversity.
Hundreds of thousands of records
Modern technology like DNA sequencing and a tremendous compilation of hundreds of thousands of distribution records on mammals, birds and amphibians across the globe has made it possible to produce the map.
"The map provides important baseline information for future ecological and evolutionary research. It also has major conservation significance in light of the on-going biodiversity crisis and global environmental change. Whereas conservation planners have been identifying priority areas based on the uniqueness of species found in a given place, we can now begin to define conservation priorities based on millions of years of evolutionary history," says Dr. Jean-Philippe Lessard, the other co-lead-author from the Copenhagen center, who is currently based at McGill University, Canada.
Senior author Carsten Rahbek, director of the Center for Macroecology, Evolution and Climate adds:
"Despite the incredible advances of natural science, we are still battling to understand the underlying laws that govern life on the planet. This holistic description of the natural world that we provide could be a new cornerstone in fundamental biology."
INFORMATION:
Further information:
The release url will be available when the embargo is lifted.
Link to maps: www.macroecology.ku.dk/resources/wallace/ (available on the day of the press release)
Link to Center for Macroecology, Evolution and Climate: www.macroecology.ku.dk
Contact:
Dr. Ben Holt
+44 7866862865;
bholt@bio.ku.dk
Director Carsten Rahbek
+45 38794860;
crahbek@bio.ku.dk
Wallace's century-old map of natural world updated
2012-12-21
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Unlocking new talents in nature
2012-12-21
PASADENA, Calif.—Protein engineers at the California Institute of Technology (Caltech) have tapped into a hidden talent of one of nature's most versatile catalysts. The enzyme cytochrome P450 is nature's premier oxidation catalyst—a protein that typically promotes reactions that add oxygen atoms to other chemicals. Now the Caltech researchers have engineered new versions of the enzyme, unlocking its ability to drive a completely different and synthetically useful reaction that does not take place in nature.
The new biocatalysts can be used to make natural products—such ...
To outsmart malarial drug resistance, research team develops new whole-plant strategy
2012-12-21
AMHERST, Mass. – Malaria brings misery and death to millions in the developing world each year, and fighting it keeps medical researchers up at night because the mosquito-borne parasite Plasmodium falciparum, which causes the deadliest form of the disease, has developed resistance to every drug thrown at it. Resistance has cut short the useful life of nearly every therapy tried so far, experts say.
But now molecular parasitologist Stephen Rich at the University of Massachusetts Amherst has led a research team who report a promising new low-cost combined therapy with a ...
New MRI analysis useful in predicting stroke complications caused by clot-busters
2012-12-21
Johns Hopkins researchers have developed a new way of looking at standard MRI scans that more accurately measures damage to the blood-brain barrier in stroke victims, a process they hope will lead to safer, more individualized treatment of blood clots in the brain and better outcomes.
The blood-brain barrier is a unique shielding of blood vessels that limits the passage of molecules from the blood stream into the brain. Without it, the brain is open to infection, inflammation and hemorrhage. Ischemic stroke patients are at risk of bleeding into the brain when there is ...
Research reveals new drug target urgently needed for tuberculosis therapy
2012-12-21
One third of the world is infected with the bacterium that causes tuberculosis (TB), a disease that is increasingly difficult to treat because of wide spread resistance to available drugs. Researchers from the Institute of Pharmacology and Structural Biology (CNRS, Université de Toulouse) in Toulouse (France) have identified a fresh target to develop new drugs for TB. The study, published in the Open Access journal PLOS Pathogens, shows why the target will be important in developing new TB treatments.
The deadliest form of human tuberculosis is caused by Mycobacterium ...
Brain imaging insight into cannabis as a pain killer
2012-12-21
The pain relief offered by cannabis varies greatly between individuals, a brain imaging study carried out at the University of Oxford suggests.
The researchers found that an oral tablet of THC, the psychoactive ingredient in cannabis, tended to make the experience of pain more bearable, rather than actually reduce the intensity of the pain.
MRI brain imaging showed reduced activity in key areas of the brain that substantiated the pain relief the study participants experienced.
'We have revealed new information about the neural basis of cannabis-induced pain relief,' ...
Microevolutionary analysis of Clostridium difficile genomes to investigate transmission
2012-12-21
Over recent years, hospital-acquired Clostridium difficile infections have been a significant problem in UK hospitals and globally. There have been concerns that infections may be due to transmission between symptomatic patients, either directly, or indirectly via hospital staff; these concerns were strengthened when enhanced infection control was introduced in England in 2007, and the incidence of C. difficile infection declined. A recent study published in the open access journal Genome Biology, published by BioMed Central, took a genomics approach to assess the incidence ...
Newborn baby screening for fragile X syndrome
2012-12-21
A study into newborn screening for fragile X syndrome (FXS) demonstrates that testing for mutations in the gene FMR1 can be done on a large scale. The research, published in BioMed Central's open access journal Genome Medicine, shows that the number of carrier babies who carry the form of the gene known as the "premutation" is higher than previously estimated.
Three large hospitals in the USA participated in this study, testing more than 14,000 newborns, including children of different ethnic backgrounds. While only one child was identified with the full mutation, the ...
Cancer diagnosis later in life poses significant risk to offspring
2012-12-21
Relatives of family members diagnosed with cancer are still at risk of the disease even if the diagnosis came at an older age, suggests a paper published on bmj.com today.
It is known that early onset cancer cases carry more hereditary risk than late onset cases, but little is known about whether any familial component exists in cancer at a very old age.
Researchers from the German Cancer Research Centre and Lund University in Sweden therefore took data from the Swedish Family-Cancer Database (the largest one of its kind) on just under eight million offspring and their ...
Genetic differences may influence sensitivity to pain, according to new study
2012-12-21
The study, published in PLOS Genetics on 20 December, adds to growing evidence that particular genes are involved in chronic pain and highlights this pathway as a potential target for more effective pain relief treatments for patients.
The collaborative study between King's, Pfizer Ltd and the Beijing Genomics Institute (BGI), used a new method to study and compare DNA, called 'exome sequencing', to identify genetic variations relating to pain sensitivity.
Lead author Dr Frances Williams, from the Department of Twin Research and Genetic Epidemiology at King's College ...
New whole plant therapy shows promise as an effective and economical treatment for malaria
2012-12-21
Worcester, Mass. – In the worldwide battle to curtail malaria, one of the most prevalent and deadly infectious diseases of the developing world, drug after drug has fallen by the wayside as the malaria parasite has become resistant to it. Only artemisinin, derived from the sweet wormwood plant, Artemisia annua, remains as an effective treatment, but it is expensive to produce (particularly when combined with other antimalarial medications to make it less prone to resistance) and is frequently in short supply.
A new study by scientists at Worcester Polytechnic Institute ...