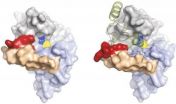
(Press-News.org) After you eat, your liver switches from producing glucose to storing it. At the same time, a cellular signaling pathway known as the unfolded protein response (UPR) is transiently activated, but it is not clear how this pathway contributes to the liver's metabolic switch. In this issue of the Journal of Clinical Investigation, researchers led by Phillip Scherer at the University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center report that activation of the UPR triggers the expression of Xbp1s, a protein that regulates genes needed for the metabolic switch. Scherer and colleagues found that they could induce changes in liver metabolism just by increasing expression of Xbps1. These results suggest that Xbps1 could play a role in metabolic disease.
TITLE:
The Xbp1s/GalE axis links ER stress to postprandial hepatic metabolism
AUTHOR CONTACT:
Philipp E. Scherer
The University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, TX, USA
Phone: (214) 648-8715; Fax: (214) 648-8720; E-mail: philipp.scherer@utsouthwestern.edu
View this article at: http://www.jci.org/articles/view/62819?key=17adb760d62c3d29b6fb
### END
The X factor in liver metabolism
2012-12-21
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Ironing out the link between H. pylori infection and gastric cancer
2012-12-21
H. pylori frequently causes gastric ulcers and is also one of the greatest risk factors for gastric cancer. H. pylori infection is also associated with another gastric cancer risk factor, iron deficiency. In this issue of the Journal of Clinical Investigation, researchers led by Richard Peek at Vanderbilt University investigated the influence of iron on H. pylori-induced gastric cancer. Peek and colleagues found that low iron accelerated the development of H. pylori-associated cancerous lesions in gerbils. Further, H. pylori strains isolated from a human population at high ...
A new type of nerve cell found in the brain
2012-12-21
Scientists at Karolinska Institutet in Sweden, in collaboration with colleagues in Germany and the Netherlands, have identified a previously unknown group of nerve cells in the brain. The nerve cells regulate cardiovascular functions such as heart rhythm and blood pressure. It is hoped that the discovery, which is published in the Journal of Clinical Investigation, will be significant in the long term in the treatment of cardiovascular diseases in humans.
The scientists have managed to identify in mice a previously totally unknown group of nerve cells in the brain. These ...
Thomas Jefferson University researchers discover new pathways that drive metastatic prostate cancer
2012-12-21
PHILADELPHIA—Elevated levels of Cyclin D1b could function as a novel biomarker of lethal metastatic disease in prostate cancer patients, according to a pre-clinical study published ahead of print on December 21 in the Journal of Clinical Investigation by researchers at the Kimmel Cancer Center at Jefferson.
The group, headed by Karen E. Knudsen, Ph.D., Professor and Hilary Koprowski Chair, Departments of Cancer Biology, Urology, and Radiation Oncology at Thomas Jefferson University and Deputy Director for Basic Science at the KCC, found that Cyclin D1b, a variant of the ...
Hawaiian Islands are dissolving, study says
2012-12-21
Someday, Oahu's Koolau and Waianae mountains will be reduced to nothing more than a flat, low-lying island like Midway.
But erosion isn't the biggest culprit. Instead, scientists say, the mountains of Oahu are actually dissolving from within.
"We tried to figure out how fast the island is going away and what the influence of climate is on that rate," said Brigham Young University geologist Steve Nelson. "More material is dissolving from those islands than what is being carried off through erosion."
The research pitted groundwater against stream water to see which ...
miR-205 can be responsible for breast cancer
2012-12-21
Over the past couple of years research into miRNAs has become increasingly diversified and attracted a great number of research articles across genetics and medicine. This should hardly come as a surprise to any scientist in the field, especially since it has become clear that miRNAs, a recently discovered class of non-coding RNAS, are represented in nearly all cellular functions and molecular pathways. A growing list of reports demonstrates that microRNAs play a critical role in cancer initiation and progression, and that miRNA alterations are ubiquitous in human cancers. ...
May the force be with the atomic probe
2012-12-21
Theoretical physicist Elad Eizner from Ben Gurion University, Israel, and colleagues created models to study the attractive forces affecting atoms located at a wide range of distances from a surface, in the hundreds of nanometers range. Their results, about to be published in EPJ D, show that these forces depend on electron diffusion, regardless of whether the surface is conducting or not. Ultimately, these findings could contribute to designing minimally invasive surface probes.
Bombarding a surface with atoms helps us understand the distribution of its electrons and ...
Carin Göring's remains identified by researchers at Uppsala University
2012-12-21
The putative remains of Carin Göring, wife of Nazi leader Herman Göring, were found in 1991 at a site close to where she had been buried. In a recently published article, Maria Allen, professor of forensic genetics at Uppsala University, Sweden, and her associates present evidence supporting that it is Carin Göring's remains that have been identified.
The Swedish Carin Göring was married to the well-known Nazi leader Herman Göring. When she died in 1931 she was buried in Stockholm, but three years later Herman Göring had her remains moved to his residence Karinhall outside ...
Fighting sleeping sickness with X-ray lasers
2012-12-21
This press release is available in German.
Using the world's most powerful X-ray free-electron laser, an international team of researchers, including scientists of the Max Planck Institute for Medical Research in Heidelberg, has obtained new insight into the structure of a medicinally important protein that may serve as a blueprint for the development of drugs to fight sleeping sickness. Science magazine have chosen the experimental study as one of the top ten scientific breakthroughs of the year.
Sleeping sickness is caused by the unicellular organism Trypanosoma ...
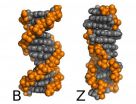
New calculations solve an old problem with DNA
2012-12-21
In a recent publication, researchers achieved new accuracy in the ability to measure energy differences between states of molecules, thus predicting which states will be observed.
It has been known since the seventies that excessive salt causes DNA to reverse its twist, from a right-handed spiral to a left-handed one. DNA in the Z form is treated by our natural repair enzymes as damaged, and is therefore usually deleted from the cell. Deletion of genetic material can lead to cancer or to other problems, so the B-Z transition is no mere curiosity. However such is the ...
Ups and downs of biodiversity after mass extinction
2012-12-21
The climate after the largest mass extinction so far 252 million years ago was cool, later very warm and then cool again. Thanks to the cooler temperatures, the diversity of marine fauna ballooned, as paleontologists from the University of Zurich have reconstructed. The warmer climate, coupled with a high CO2 level in the atmosphere, initially gave rise to new, short-lived species. In the longer term, however, this climate change had an adverse effect on biodiversi-ty and caused species to become extinct.
Until now, it was always assumed that it took flora and fauna ...