(Press-News.org) New Haven, Conn.—By examining the type of rock in which dinosaur fossils were embedded, an often unappreciated part of the remains, scientists have determined that different species of North American dinosaurs from the Late Cretaceous period 65 million years ago occupied different environments separated by just a few miles.
Hadrosaurs or duck-billed dinosaurs, along with the small ornithopod Thescelosaurus, preferred to live along the edge of rivers, according to the research. Ceratopsians, on the other hand, which include the well-known Triceratops, preferred to be several miles inland.
The findings, which appear in the online edition of the Proceedings of the Royal Society B, give scientists a more complete picture of the distribution of different species and help explain how several large herbivores managed to coexist.
Tyler Lyson of Yale University and the Marmarth Research Foundation, along with Yale researcher Nicholas Longrich, analyzed more than 300 fossils representing more than half a dozen dinosaur species from Western Canada, Montana, Wyoming and surrounding areas.
After several years of fieldwork, Lyson began to notice a pattern to the geographical distribution of different species. He and Longrich also searched through museum collections of fossils, some of which contained information about the type of rock in which the fossils were found, and some of which still had pieces of rock attached to them that were large enough for the researchers to recognize as either sandstone or mudstone.
"We're using what paleontologists usually throw away when excavating the fossils as clues to where these different species spent most of their time," Lyson said.
As the sole large carnivore in the region, Tyrannosaurs rex appears to have roamed both habitats, most likely feeding on large herbivores. However, the team discovered that hadrosaurs and Thescelosaurus fossils were more often found in sandstone, which occurs along riverbanks, whereas ceratopsians were likely to be embedded in mudstone from the floodplains.
"We didn't really think about distribution between different species before now,"
Longrich said. "But depending on what type of rock you look at, you get a very different picture of the community that lived there."
The study also shows that the dinosaurs had specialized eating habits (something about which very little is known), and likely fed on different types of plants found in each environment, Longrich said.
"This opens up the possibility of finding new species if we search different types of rock," Longrich said. "It also emphasizes the importance of recording data about the rock in which fossils are preserved, which can give us important clues as to the paleoecology of these animals."
INFORMATION:
Citation: doi:10.1098/rspb.2010.1444
Using discards, scientists discover different dinosaurs' stomping grounds
2010-10-17
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Small BMI change in overweight children could have big blood pressure impact
2010-10-17
Small changes in weight can make bigger differences in the blood pressure for overweight children, compared to those at normal weight, according to a new study.
Researchers tracked blood pressure, height and weight of 1,113 children over time, with the longest follow-up exceeding 10 years. They then compared the children's body mass index (BMI, a measure of body weight) to national charts adjusted for age, sex and height. Kids with BMIs in the 85th percentile or higher are considered overweight.
"Below the 85th percentile, BMI effects on blood pressure appear to be fairly ...
Team of chemists produces biodiesel at their university, using used cooking oil as a basis
2010-10-17
The cafeterias at the Catering School on the Leioa campus of the University of the Basque Country (UPV/EHU) use litres upon litres of oil for cooking, given that many students, research workers, lecturers and ancillary staff eat there. Currently a truck takes away all the waste. However, a number of Chemistry Faculty lecturers have demonstrated that this oil can be used and revalued at the university itself, having managed to produce biodiesel from the used oil. According to lecturer Ms Eneritz Anakabe, "we have shown that it can be done on a small scale, that biodiesel ...
First babies born from genetic screening study
2010-10-17
Two women taking part in the world's first controlled study of a comprehensive genetic screening test before IVF have given birth to healthy babies. The babies, twin girls born in Germany in June and a singleton boy born in Italy in September, are the first deliveries in a pilot study of comparative genomic hybridisation (CGH) by microarray, a new method of screening oocytes for IVF for a full range of chromosomal disorders.
Dr Cristina Magli, embryologist at the SISMER Centre in Bologna, one of the two centres taking part in the trial, said: " All the babies and their ...
Paper highlights blood pressure risk in overweight children
2010-10-17
Sophia Antipolis, 15 October 2010: The European Society of Cardiology (ESC) welcomes the findings of a paper presented today at the American Heart Association's High Blood Pressure Research 2010 Scientific Sessions (HBPR 2010) held in Washington, DC, USA. The paper details research into the relationship between body mass index (BMI) and blood pressure in children. It concludes that an increase in BMI in already overweight children risks a far greater rise in blood pressure than would the same increase in BMI in normal-weight children.
Commenting on the paper, ESC spokesperson ...
Small business success spotlighted by USDA at conference
2010-10-17
ChoiceBatter's® transformation from a federal laboratory bench technology to a grocery shelf product is among topics that will be discussed here today by U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA) officials and other participants attending the 17th annual conference of the National Association of Seed and Venture Funds (NASVF).
ChoiceBatter®, the brand name for a line of low oil-uptake batters marketed by CrispTek, LLC, of Columbia, Md., is based on a rice-flour formulation created by Fred Shih and Kim Daigle, chemists with the Agricultural Research Service (ARS), USDA's principal ...
2 studies present new data on effects of alcohol during pregnancy
2010-10-17
Scientific data continue to indicate that higher intake of alcohol during pregnancy adversely affects the fetus, and could lead to very severe developmental or other problems in the child. However, most recent publications show little or no effects of occasional or light drinking by the mother during pregnancy. The studies also demonstrate how socio-economic, education, and other lifestyle factors of the mother may have large effects on the health of the fetus and child; these must be considered when evaluating the potential effects of alcohol during pregnancy.
A ...
Eat safer: Novel approach detects unknown food pathogens
2010-10-17
INDIANAPOLIS – Technologies for rapid detection of bacterial pathogens are crucial to maintaining a secure food supply.
Researchers from the School of Science at Indiana University-Purdue University Indianapolis (IUPUI) and the Bindley Bioscience Center at Purdue University have developed a novel approach to automated detection and classification of harmful bacteria in food. The investigators have designed and implemented a sophisticated statistical approach that allows computers to improve their ability to detect the presence of bacterial contamination in tested samples. ...
New beam source for Brookhaven accelerators
2010-10-17
UPTON, NY - A new source of ions will soon be the starting point for the beams entering two major research facilities at the U.S. Department of Energy's (DOE) Brookhaven National Laboratory - the Relativistic Heavy Ion Collider (RHIC - http://www.bnl.gov/rhic), where physicists are recreating conditions of the early universe to learn more about the forces that hold matter together, and the NASA Space Radiation Laboratory (NSRL: http://www.bnl.gov/medical/NASA/NSRL_description.asp), where scientists study the effects of space radiation to help find ways to protect astronauts. ...
Focus on dementia
2010-10-17
Alzheimer's disease is not the only type of dementia. Two particular forms are dementia with Lewy bodies and Parkinson's disease dementia. In both forms, the diagnosis is of vital importance because the treatment for these dementias differs from that for Alzheimer's dementia, as Brit Mollenhauer and co-authors explain in the dementia theme issue of Deutsches Ärzteblatt International (Dtsch Arztebl Int 2010; 107[39]: 684-91).
In more than 75% of patients, the memory impairments are due to Alzheimer's disease. In Lewy body dementia, which is accompanied by cognitive and/or ...
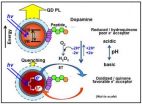
NRL scientists unravel complex quantum dot-dopamine interactions
2010-10-17
Scientists at the Naval Research Laboratory (NRL) in conjunction with the Scripps Research Institute in La Jolla, Ca., recently reported a detailed study of the interactions of water soluble semi-conductor quantum dots (QDs) with the electro-active neuro-transmitter dopamine. These biocompatible QD-dopamine nano-assemblies may be used as the active component for sensors that are used to detect a wide variety of target analytes ranging from sugars to peroxides.
According to NRL's Dr. Michael Stewart, a member of the research team "The nature of the QD-dopamine ...