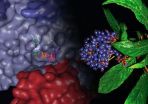
(Press-News.org) LA JOLLA, CA – December 23, 2012 – The mysterious inner workings of Chang Shan—a Chinese herbal medicine used for thousands of years to treat fevers associated with malaria—have been uncovered thanks to a high-resolution structure solved at The Scripps Research Institute (TSRI).
Described in the journal Nature this week, the structure shows in atomic detail how a two-headed compound derived from the active ingredient in Chang Shan works. Scientists have known that this compound, called halofuginone (a derivative of the febrifugine), can suppress parts of the immune system—but nobody knew exactly how.
The new structure shows that, like a wrench in the works, halofuginone jams the gears of a molecular machine that carries out "aminoacylation," a crucial biological process that allows organisms to synthesize the proteins they need to live. Chang Shan, also known as Dichroa febrifuga Lour, probably helps with malarial fevers because traces of a halofuginone-like chemical in the herb interfere with this same process in malaria parasites, killing them in an infected person's bloodstream.
"Our new results solved a mystery that has puzzled people about the mechanism of action of a medicine that has been used to treat fever from a malaria infection going back probably 2,000 years or more," said Paul Schimmel, PhD, the Ernest and Jean Hahn Professor and Chair of Molecular Biology and Chemistry and member of The Skaggs Institute for Chemical Biology at TSRI. Schimmel led the research with TSRI postdoctoral fellow Huihao Zhou, PhD.
Halofuginone has been in clinical trials for cancer, but the high-resolution picture of the molecule suggests it has a modularity that would make it useful as a template to create new drugs for numerous other diseases.
The Process of Aminoacylation and its Importance to Life
Aminoacylation is a crucial step in the synthesis of proteins, the end products of gene expression. When genes are expressed, their DNA sequence is first read and transcribed into RNA, a similar molecule. The RNA is then translated into proteins, which are chemically very different from DNA and RNA but are composed of chains of amino acid molecules strung together in the order called for in the DNA.
Necessary for this translation process are a set of molecules known as transfer RNAs (tRNAs), which shuttle amino acids to the growing protein chain where they are added like pearls on a string. But before the tRNAs can move the pearls in place, they must first grab hold of them.
Aminoacylation is the biological process whereby the amino acid's pearls are attached to these tRNA shuttles. A class of enzymes known as aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases is responsible for attaching the amino acids to the tRNAs, and Schimmel and his colleagues have been examining the molecular details of this process for years. Their work has given scientists insight into everything from early evolution to possible targets for future drug development.
Over time what has emerged as the picture of this process basically involves three molecular players: a tRNA, an amino acid and the aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase enzyme that brings them together. A fourth molecule called ATP is a microscopic form of fuel that gets consumed in the process.
The new work shows that halofuginone gets its potency by interfering with the tRNA synthetase enzyme that attaches the amino acid proline to the appropriate tRNA. It does this by blocking the active site of the enzyme where both the tRNA and the amino acid come together, with each half of the halofuginone blocking one side or the other.
Interestingly, said Schimmel, ATP is also needed for the halofuginone to bind. Nothing like that has ever been seen in biochemistry before.
"This is a remarkable example where a substrate of an enzyme (ATP) captures an inhibitor of the same enzyme, so that you have an enzyme-substrate-inhibitor complex," said Schimmel.
INFORMATION:
The article, "ATP-Directed Capture of Bioactive Herbal-Based Medicine on Human tRNA Synthetase," by Huihao Zhou, Litao Sun, Xiang-Lei Yang and Paul Schimmel was published in the journal Nature on December 23, 2012
This work was supported by the National Institutes of Health through grants #GM15539, #23562 and #88278 and by a fellowship from the National Foundation for Cancer Research.
Chinese medicine yields secrets to scientists at The Scripps Research Institute
Atomic mechanism of 2-headed molecule derived from Chang Shan, a traditional Chinese herb, is shown in unprecedented detail
2012-12-24
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
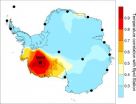
Study shows rapid warming on the West Antarctic Ice Sheet
2012-12-24
COLUMBUS, Ohio—In a discovery that raises further concerns about the future contribution of Antarctica to sea level rise, a new study finds that the western part of the ice sheet is experiencing nearly twice as much warming as previously thought.
The temperature record from Byrd Station, a scientific outpost in the center of the West Antarctic Ice Sheet (WAIS), demonstrates a marked increase of 4.3 degrees Fahrenheit (2.4 degrees Celsius) in average annual temperature since 1958—that is, three times faster than the average temperature rise around the globe.
This temperature ...
Fat influences decisions taken by brain cells for production and survival
2012-12-24
Scientists at Karolinska Institutet in Sweden have identified two molecules that play an important role in the survival and production of nerve cells in the brain, including nerve cells that produce dopamine. The discovery, which is published in the journal Nature Chemical Biology, may be significant in the long term for the treatment of several diseases, such as Parkinson's disease.
The same scientists have previously shown that receptors known as "liver X receptors" or LXR, are necessary for the production of different types of nerve cells, or neurons, in the developing ...
Understanding cell organization to tackle cancer
2012-12-24
Scientists at The University of Manchester have identified how cells know which way up they need to be. The discovery could help in the fight against cancer because in the early stages of the disease the cells become disorganised.
Professor Charles Streuli and Dr Nasreen Akhtar of the Wellcome Trust Centre for Cell-Matrix Research have conducted new research that leads to a better understanding of cell polarity. Properly organised tissues are vital to maintaining functional organs and a healthy body. Part of being organised includes cells being in the correct position ...
Research sheds new light on mechanisms of T-ALL, a form of leukemia that primarily affects children
2012-12-24
Acute lymphatic leukemia (ALL) is the most common cancer in children under the age of 14 years. With optimum treatment, approximately 75 % of children are currently cured, but the treatment consists of severe chemotherapy with many side effects. In collaboration with international research teams, scientists at VIB, KU Leuven and UZ Leuven have identified new genetic mutations that lead to T-ALL, a variant of ALL. They have unmasked the ribosome – the molecular machine in the cell that is involved in the production of proteins – as a weak spot in leukemia cells. Their research ...
Neuroscientists find excessive protein synthesis linked to autistic-like behaviors
2012-12-24
Autistic-like behaviors can be partially remedied by normalizing excessive levels of protein synthesis in the brain, a team of researchers has found in a study of laboratory mice. The findings, which appear in the latest issue of Nature, provide a pathway to the creation of pharmaceuticals aimed at treating autism spectrum disorders (ASD) that are associated with diminished social interaction skills, impaired communication ability, and repetitive behaviors.
"The creation of a drug to address ASD will be difficult, but these findings offer a potential route to get there," ...
3 new genetic links to colorectal cancer
2012-12-24
Vanderbilt-Ingram Cancer Center investigators have identified three new genetic "hotspots" linked to colorectal cancer.
These variants, reported Dec. 23 in an Advanced Online Publication in Nature Genetics, provide new insight into the biology of colorectal cancer – and could represent new therapeutic targets for the disease.
Colorectal cancer is one of the most commonly diagnosed cancers worldwide – and rates are particularly high in the United States and other developed countries. Genetics plays an important role in both sporadic and familial (inherited) forms of ...
OpGen announces sequence assembly and finishing of first reference genome of domestic goat
2012-12-24
Gaithersburg, Md.—December 23, 2012— OpGen, Inc. today announced its ARGUS® Whole Genome Mapping System technology was used in combination with next-generation sequencing (NGS) to produce the first, high-quality reference genome of the domestic goat. The study, which was led by BGI-Shenzhen and Kunming Institute of Zoology, Chinese Academy of Sciences was published online today in Nature Biotechnology. The paper, titled Sequencing and automated whole-genome optical mapping of the genome of a domestic goat (Capra hircus), demonstrates the value, efficiency and cost effectiveness ...
Study turns parasite invasion theory on its head
2012-12-24
Current thinking on how the Toxoplasma gondii parasite invades its host is incorrect, according to a study published today in Nature Methods describing a new technique to knock out genes. The findings could have implications for other parasites from the same family, including malaria, and suggest that drugs that are currently being developed to block this invasion pathway may be unsuccessful.
Toxoplasma gondii is a parasite that commonly infects cats but is also carried by other warm-blooded animals, including humans. Up to a third of the UK population are chronically ...
The first goat genome sets a good example for facilitating de novo assembly of large genomes
2012-12-24
December 23, 2012, Shenzhen, China – In a collaborative study published online today in Nature Biotechnology, researchers from Kunming Institute of Zoology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, BGI, and other institutes, have completed the first genome sequence of domestic goat by a robust approach integrated with next-generation sequencing (NGS) and whole-genome mapping (WGM) technologies. The goat genome is the first reference genome for small ruminant animals and may help to advance the understanding of distinct ruminants' genomic features from non-ruminant species. This work ...
Gout study offers genetic insight into 'disease of kings'
2012-12-24
Scientists have shed light on why some people are more susceptible to gout than others. A study has identified 18 new genetic variations that increase levels of uric acid in the blood, which is the main cause of the disease.
High levels of uric acid form small crystals in joints and tissues, causing pain and swelling – the main symptoms of the condition once known as the 'disease of kings'.
Gout is the most common form of inflammatory arthritis, affecting up to two per cent of the world's population.
Understanding how these common genetic variants increase uric ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Study: Reported crop yield gains from breeding may be overstated
Stem cells from human baby teeth show promise for treating cerebral palsy
Chimps’ love for crystals could help us understand our own ancestors’ fascination with these stones
Vaginal estrogen therapy not linked to cancer recurrence in survivors of endometrial cancer
How estrogen helps protect women from high blood pressure
Breaking the efficiency barrier: Researchers propose multi-stage solar system to harness the full spectrum
A new name, a new beginning: Building a green energy future together
From algorithms to atoms: How artificial intelligence is accelerating the discovery of next-generation energy materials
Loneliness linked to fear of embarrassment: teen research
New MOH–NUS Fellowship launched to strengthen everyday ethics in Singapore’s healthcare sector
Sungkyunkwan University researchers develop next-generation transparent electrode without rare metal indium
What's going on inside quantum computers?: New method simplifies process tomography
This ancient plant-eater had a twisted jaw and sideways-facing teeth
Jackdaw chicks listen to adults to learn about predators
Toxic algal bloom has taken a heavy toll on mental health
Beyond silicon: SKKU team presents Indium Selenide roadmap for ultra-low-power AI and quantum computing
Sugar comforts newborn babies during painful procedures
Pollen exposure linked to poorer exam results taken at the end of secondary school
7 hours 18 mins may be optimal sleep length for avoiding type 2 diabetes precursor
Around 6 deaths a year linked to clubbing in the UK
Children’s development set back years by Covid lockdowns, study reveals
Four decades of data give unique insight into the Sun’s inner life
Urban trees can absorb more CO₂ than cars emit during summer
Fund for Science and Technology awards $15 million to Scripps Oceanography
New NIH grant advances Lupus protein research
New farm-scale biochar system could cut agricultural emissions by 75 percent while removing carbon from the atmosphere
From herbal waste to high performance clean water material: Turning traditional medicine residues into powerful biochar
New sulfur-iron biochar shows powerful ability to lock up arsenic and cadmium in contaminated soils
AI-driven chart review accurately identifies potential rare disease trial participants in new study
Paleontologist Stephen Chester and colleagues reveal new clues about early primate evolution
[Press-News.org] Chinese medicine yields secrets to scientists at The Scripps Research InstituteAtomic mechanism of 2-headed molecule derived from Chang Shan, a traditional Chinese herb, is shown in unprecedented detail