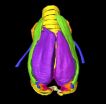
(Press-News.org) The question 'How do songbirds sing?' is addressed in a study published in BioMed Central's open access journal BMC Biology. High-field magnetic resonance imaging and micro-computed tomography have been used to construct stunning high resolution, 3D, images, as well as a data set "morphome" of the zebra finch (Taeniopygia guttata) vocal organ, the syrinx.
Like humans, songbirds learn their vocalizations by imitation. Since their songs are used for finding a mate and retaining territories, birdsong is very important for reproductive success.
The syrinx, located at the point where the trachea splits in two to send air to the lungs, is unique to birds and performs the same function as vocal cords in humans. Birds can have such a complete control over the syrinx, with sub-millisecond precision, that in some cases they are even able to mimic human speech.
Despite great inroads in uncovering the neural control of birdsong, the anatomy of the complex physical structures that generate sound have been less well understood.
The multinational team has generated interactive 3D PDF models of the syringeal skeleton, soft tissues, cartilaginous pads, and muscles affecting sound production. These models show in detail the delicate balance between strength, and lightness of bones and cartilage required to support and alter the vibrating membranes of the syrinx at superfast speeds.
Dr Coen Elemans, from the University of Southern Denmark, who led this study, explained, "This study provides the basis to analyze the micromechanics, and exact neural and muscular control of the syrinx. For example, we describe a cartilaginous structure which may allow the zebra finch to precisely control its songs by uncoupling sound frequency and volume." In addition, the researchers found a previously unrecognized Y-shaped structure on the sternum which corresponds to the shape of the syrinx and could help stabilize sound production.
INFORMATION:
Media Contact
Dr Hilary Glover
Scientific Press Officer
BioMed Central
Mob: 44-778-698-1967
Notes
1. The songbird syrinx morphome: a three-dimensional, high-resolution, interactive morphological map of the zebra finch vocal organ
Daniel N Düring, Alexander Ziegler, Christopher K Thompson, Andreas Ziegler, Cornelius Faber, Johannes Müller, Constance Scharff and Coen P H Elemans
BMC Biology (in press)
Please name the journal in any story you write. If you are writing for the web, please link to the article. All articles are available free of charge, according to BioMed Central's open access policy.
Article citation and URL available on request on the day of publication.
2. BMC Biology is the flagship biology journal of the BMC series, publishing peer-reviewed research and methodology articles of special importance and broad interest in any area of biology, as well as reviews, opinion pieces, comment and Q&As on topics of special or topical interest. @BMCBiology
3. Images are to be credited to Daniel N Düring, Alexander Ziegler, Christopher K Thompson, Andreas Ziegler, Cornelius Faber, Johannes Müller, Constance Scharff and Coen P H Elemans.
4. BioMed Central is an STM (Science, Technology and Medicine) publisher which has pioneered the open access publishing model. All peer-reviewed research articles published by BioMed Central are made immediately and freely accessible online, and are licensed to allow redistribution and reuse. BioMed Central is part of Springer Science+Business Media, a leading global publisher in the STM sector. @BioMedCentral
Songbird sings in 3D
2013-01-08
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
How do songbirds sing? In 3D!
2013-01-08
January 8, 2013 – A multinational team of researchers made a significant step forward in trying to understand how birds produce their beautiful songs. "We used cutting-edge 3D imaging techniques to understand the complicated structure of the vocal organ of songbirds, the syrinx", says Dr. Coen Elemans, from the University of Southern Denmark, the senior author on the study. Elemans and his colleagues are publishing their findings January 8, 2013 in BioMed Central's open access journal BMC Biology.
Communicating with sounds is central to the life of most animals and they ...
Costly breast cancer screenings don't add up to better outcomes
2013-01-08
Even though Medicare spends over $1 billion per year on breast cancer screenings such as a mammography, there is no evidence that higher spending benefits older women, researchers at Yale School of Medicine found in a study published Online First by JAMA Internal Medicine, a JAMA Network publication.
Led by Cary Gross, M.D., associate professor of internal medicine at Yale School of Medicine and director of the Cancer Outcomes, Public Policy, and Effectiveness Research (COPPER) Center at Yale, the study sought to provide a comprehensive understanding of breast cancer ...
Giant fossil predator provides insights into the rise of modern marine ecosystem structures
2013-01-08
An international team of scientists has described a fossil marine predator measuring 8.6 meters in length (about 28 feet) recovered from the Nevada desert in 2010 as representing the first top predator in marine food chains feeding on prey similar to its own size. A paper with their description will appear the week of January 7, 2013 in the EE (early electronic) issue of Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
Scientists who studied the fossil include lead author Dr. Nadia Fröbisch and Prof. Jörg Fröbisch (both at Museum für Naturkunde Leibniz-Institut für Evolutions- ...
Looming malpractice
2013-01-08
The average physician can expect to spend nearly 11 per cent of his or her career with a malpractice claim waiting to be resolved. Some specialists will spend nearly a third of their careers with open claims.
The length of time it takes to resolve a malpractice claim is a stress on patients, physicians and the legal system. The time spent with open claims may be even more distressing for physicians than the financial costs of malpractice claims.
"We believe that the time required to resolve malpractice claims may be a significant reason that physicians are so vocal ...
Centralization to fewer surgeons results in better survival after esophageal cancer surgery
2013-01-08
Patients who undergo surgery for oesophageal cancer have a much greater chance of long term survival if the operation is carried out by a surgeon who has performed this particular operation many times before. This according to a new, large-scale study conducted by researchers at Karolinska Institutet in Sweden, and published in the Journal of Clinical Oncology. In their article, the researchers conclude that oesophageal cancer surgery should be concentrated – or centralised – to fewer surgeons.
Surgery is the most widely established curative treatment for oesophageal ...
The reason we lose at games
2013-01-08
Writing in PNAS, a University of Manchester physicist has discovered that some games are simply impossible to fully learn, or too complex for the human mind to understand.
Dr Tobias Galla from The University of Manchester and Professor Doyne Farmer from Oxford University and the Santa Fe Institute, ran thousands of simulations of two-player games to see how human behaviour affects their decision-making.
In simple games with a small number of moves, such as Noughts and Crosses the optimal strategy is easy to guess, and the game quickly becomes uninteresting.
However, ...
High salt intake linked to social inequalities
2013-01-08
People from low socio-economic positions in Britain eat more salt than the well off, irrespective of where they live, states a paper led by Warwick Medical School published on Tuesday in the BMJ Open journal .
The research was carried out by the World Health Organization Collaborating Centre for Nutrition , based in the Division of Mental Health & Wellbeing of Warwick Medical School at the University of Warwick.
The study looked at the geographical distribution of habitual dietary salt intake in Britain and its association with manual occupations and educational attainments, ...
Modified antibodies trigger immune response, point to novel vaccine design strategies
2013-01-08
CAMBRIDGE, Mass. (January 7, 2013) – In an approach with the potential to aid therapeutic vaccine development, Whitehead Institute scientists have shown that enzymatically modified antibodies can be used to generate highly targeted, potent responses from cells of the immune system.
The approach, referred to as "sortagging," relies on the bacterial enzyme sortase A to modify antibodies to carry various payloads, such as peptides, lipids, fluorophores, and proteins. In this case, the scientists, whose findings are reported online this week in the journal PNAS, attached ...
Untreated Parkinson's disease patients no more likely to have impulse control disorders
2013-01-08
PHILADELPHIA - While approximately one in five Parkinson's disease patients experience impulse control disorder symptoms, the disease itself does not increase the risk of gambling, shopping, or other impulsivity symptoms, according to research from the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania. A new study is the first to show in a large sample that people with untreated Parkinson's were no more likely to have an increased impulsivity than people without the disease. Published in the January 8, 2013, print issue of Neurology®, the medical journal of ...
Comprehensive public health approach urged to curb gun violence in US
2013-01-08
Boston, MA -- In the wake of the horrific school shootings in Newtown, Conn. in December, three Harvard experts say the best way to curb gun violence in the U.S. is to take a broad public health approach, drawing on proven, evidence-based strategies that have successfully reduced other public health threats like smoking, car crashes, and accidental poisonings.
The authors make the case for a comprehensive public health approach to gun violence in a viewpoint article published online January 7, 2013 in the Journal of the American Medical Association (JAMA).
For instance, ...