(Press-News.org) MINNEAPOLIS – Parkinson's disease itself does not increase the risk of impulse control problems such as compulsive gambling and shopping that have been seen in people taking certain drugs for Parkinson's disease, according to new research published in the January 8, 2013, print issue of Neurology®, the medical journal of the American Academy of Neurology.
"We've known for some time that these behaviors are more common in people taking certain Parkinson's medications, but we haven't known if the disease itself leads to an increased risk of these behaviors," said study author Daniel Weintraub, MD, of the University of Pennsylvania Perelman School of Medicine in Philadelphia.
The study involved 168 people who had recently been diagnosed with Parkinson's disease and had not yet taken any medications for the disease. They were compared to 143 people of similar ages who did not have the disease.
The participants were given a questionnaire asking how often they had impulse control symptoms such as compulsive gambling, shopping, sexual behavior or eating. Participants were also asked about aimless wandering, punding (which is excessive repetition of non-goal directed activity, such as continual handling and sorting of common objects) and hobbyism (the compulsive pursuit of a hobby such as collecting, cleaning or excessive Internet use).
Those with Parkinson's disease were no more or less likely to have the impulse control symptoms than those without the disease, with about 20 percent of each group having symptoms.
"These results provide further evidence that impulse control disorders that occur in people with Parkinson's disease are related to the exposure to the dopamine-related drugs, not just the disease itself," Weintraub said. "More long-term studies are needed to determine if the 20 percent of people who have some symptoms of these disorders are more likely to develop impulse control disorders once they start treatment for Parkinson's."
###
The study was supported by the Parkinson's Progression Markers Initiative, a public-private partnership funded by the Michael J. Fox Foundation for Parkinson's Research and funding partners including Abbott, Biogen Idec., F. Hoffman-La Roche Ltd., GE Healthcare, Genentech and Pfizer Inc.
To learn more about Parkinson's disease, visit http://www.aan.com/patients.
The American Academy of Neurology, an association of more than 25,000 neurologists and neuroscience professionals, is dedicated to promoting the highest quality patient-centered neurologic care. A neurologist is a doctor with specialized training in diagnosing, treating and managing disorders of the brain and nervous system such as Alzheimer's disease, stroke, migraine, multiple sclerosis, brain injury, Parkinson's disease and epilepsy.
For more information about the American Academy of Neurology, visit http://www.aan.com or find us on Facebook, Twitter, Google+ and YouTube.
Media Contacts:
Rachel Seroka, AAN
Angela Babb, APR, ababb@aan.com, 612-928-6102
Despite wide investments nationally in electronic medical records and related tools, the cost-saving promise of health information technology has not been reached because the systems deployed are neither interconnected nor easy to use, according to a new RAND Corporation analysis.
The potential of health information technology to both improve patient care and reduce spending are unlikely to be realized until health care providers reengineer their processes to focus on the benefits that can be achieved, according to the paper published in the January edition of Health ...
PHILADELPHIA – In the first study of its kind, a team of researchers led by faculty at the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania and the Baylor College of Medicine, has analyzed data on the impact of prolonged operational confinement on sleep, performance, and mood in astronauts from a groundbreaking international effort to simulate a 520-day space mission to Mars. The findings, published online-first in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, revealed alterations of life-sustaining sleep patterns and neurobehavioral consequences for ...
SAN DIEGO – People taking the blood pressure drugs called beta blockers may be less likely to have changes in the brain that can be signs of Alzheimer's disease and other types of dementia, according to a study released today that will be presented at the American Academy of Neurology's 65th Annual Meeting in San Diego, March 16 to 23, 2013.
The study involved 774 elderly Japanese-American men who took part in the Honolulu-Asia Aging Study. Autopsies were performed on the men after their death. Of the 774 men, 610 had high blood pressure or were being treated with medication ...
More than a third of U.S. physicians responding to a national survey indicated they often or sometimes prescribed brand-name drugs when appropriate generic substitutes were available simply because patients requested the brand-name drug. Survey respondents who had marketing relationships with industry were more likely to fulfill such patient requests than were those without those relationships. The report from investigators at the Mongan Institute for Health Policy (MIHP) at Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) will appear in JAMA Internal Medicine (formerly Archives ...
Despite the decline in cancer death rates in the U.S., there is an increase in incidence rates for cancers associated with human papillomavirus (HPV) infection and more efforts are needed to increase HPV vaccination coverage levels to prevent the occurrence of these cancers in the future according to a study published January 7 in the Journal of the National Cancer Institute.
The American Cancer Society (ACS), the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), the National Cancer Institute (NCI), and the North American Association of Central Cancer Registries (NAACCR) ...
A metanalysis published in BioMed Central's open access journal BMC Medicine has confirmed that polymorphisms (SNP) in the gene coding for interleukin-28 (IL28B) influence natural hepatitis C viral (HCV) clearance and response to pegylated interferon-α plus ribavirin (PEG-IFN/RBV). Information about IL28B genotype could be used to provide personalized medicine and target treatment options effectively.
Over 200 million people worldwide are chronically infected with hepatitis C virus (HCV) and about a quarter of these will go on to develop cirrhosis of the liver. Treatment ...
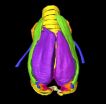
The question 'How do songbirds sing?' is addressed in a study published in BioMed Central's open access journal BMC Biology. High-field magnetic resonance imaging and micro-computed tomography have been used to construct stunning high resolution, 3D, images, as well as a data set "morphome" of the zebra finch (Taeniopygia guttata) vocal organ, the syrinx.
Like humans, songbirds learn their vocalizations by imitation. Since their songs are used for finding a mate and retaining territories, birdsong is very important for reproductive success.
The syrinx, located at the ...
January 8, 2013 – A multinational team of researchers made a significant step forward in trying to understand how birds produce their beautiful songs. "We used cutting-edge 3D imaging techniques to understand the complicated structure of the vocal organ of songbirds, the syrinx", says Dr. Coen Elemans, from the University of Southern Denmark, the senior author on the study. Elemans and his colleagues are publishing their findings January 8, 2013 in BioMed Central's open access journal BMC Biology.
Communicating with sounds is central to the life of most animals and they ...
Even though Medicare spends over $1 billion per year on breast cancer screenings such as a mammography, there is no evidence that higher spending benefits older women, researchers at Yale School of Medicine found in a study published Online First by JAMA Internal Medicine, a JAMA Network publication.
Led by Cary Gross, M.D., associate professor of internal medicine at Yale School of Medicine and director of the Cancer Outcomes, Public Policy, and Effectiveness Research (COPPER) Center at Yale, the study sought to provide a comprehensive understanding of breast cancer ...
An international team of scientists has described a fossil marine predator measuring 8.6 meters in length (about 28 feet) recovered from the Nevada desert in 2010 as representing the first top predator in marine food chains feeding on prey similar to its own size. A paper with their description will appear the week of January 7, 2013 in the EE (early electronic) issue of Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
Scientists who studied the fossil include lead author Dr. Nadia Fröbisch and Prof. Jörg Fröbisch (both at Museum für Naturkunde Leibniz-Institut für Evolutions- ...