(Press-News.org) New York children participating in a federal nutrition program had healthier eating behaviors and lower rates of obesity two years after improvements to the program were undertaken, according to a study published online today in Obesity, the official journal of the Obesity Society.
In 2009 all 50 states rolled out sweeping changes to the menu of foods available through the Special Supplemental Nutrition Program for Women, Infants, and Children, or WIC, which reaches nearly half of all infants born in the United States. New York was the first state in the nation to roll out the new package of food vouchers, which added vegetables, fruits, and whole grains, substituted low-fat for whole milk, and reduced fruit juices. The New York State WIC program also added healthy lifestyle promotion, such as increasing physical activity and reducing screen time, as a core service.
To assess the impact of the changes, researchers analyzed 3.5 million New York State WIC records from before and after the January 2009 changes in the food package. The study was conducted by researchers from Columbia University's Mailman School of Public Health, the New York State Department of Health, and Public Health Solutions, a New York-based nonprofit.
Most encouraging for those concerned about reversing the childhood obesity epidemic were the observed differences in the proportion of obese children. After the changes in WIC programming, there was a 6% decline in obesity among 1 year-olds, from 15.1 to 14.2%, and 3% among 2-4 year-olds, from 14.6 to 14.2%.
"The new WIC food package was designed to promote healthier eating choices for children and we are excited by results that show it is helping to reduce pediatric obesity," State Health Commissioner Nirav R. Shah, MD, MPH, said. "New York was the first state to implement the new WIC food package and is the first to report that changing the foods provided to children under the program helped to improve their eating behavior and achieve healthier weights. Changing WIC foods does change what children eat."
When compared to children in the "old" WIC, children in the "new" WIC had more healthy behaviors and were less likely to be overweight or obese. For instance:
Low/nonfat milk consumption was up by 4.5% in 2-4 year-old children.
Steady increases in daily consumption of any fruits, vegetables, and whole grains were seen in 1-4-year-olds.
Proportions of 2-4-year-olds with 2 or fewer hours of television or other screen time increased by 2.5%, while the proportion of children under age 2 with no screen time increased by 33%.
Mothers who initiated breastfeeding jumped by 7%, from 72.2 to 77.5%.
"In the two years after the changes to WIC were rolled out in New York State, an estimated 2,300 more New York children were normal weight, not overweight or obese," says first author Mary Ann Chiasson, DrPH, Vice President of Research and Evaluation at Public Health Solutions; and Associate Professor of Clinical Epidemiology (in Medicine) at Columbia's Mailman School of Public Health and the College of Physicians and Surgeons.
While early childhood obesity levels had plateaued before the new changes in the WIC program, these results suggest that the new WIC food package may be contributing to further reductions in obesity risk.
"The new WIC food package appears to be having the hoped for effect of promoting healthy eating, building a foundation for healthy choices about diet, exercise, and other healthful habits," says Sally Findley, PhD, Professor of Clinical Population and Family Health and Sociomedical Sciences at Columbia's Mailman School.
"If you help keep kids at normal weight during early childhood, they are much more likely to stay at normal weight throughout childhood and beyond," continues Dr. Findley, adding that preventing obesity in young children is especially important given that it is linked with risk for adult obesity and a constellation of related health problems from diabetes to cardiovascular disease.
The study results are part of a larger assessment of the impact of New York's changes to WIC in 2009. Ongoing studies include elements such as control for background characteristics of enrolled children and for the potential additional effects of other city or state programs affecting healthy eating or exercise patterns in this age group.
INFORMATION:
Additional co-authors include Jackson Sekhobo, PhD, Director of Research and Evaluation, Division of Nutrition, New York State Department of Health, and Lynn Edmunds, DrPH, Senior Research Scientist, Evaluation and Analysis Unit, Division of Nutrition, New York State Department of Health; Roberta Scheinmann, MPH, and Adefunke Faly, MPH, at Public Health Solutions; and Natasha McLeod of Columbia's Mailman School.
Funding for the study was provided by the Robert Wood Johnson Foundation and the New York State Health Foundation. The authors declare no competing interests.
More data about New York's WIC program is available at http://www.nyhealth.gov/prevention/nutrition/wic/.
END
A new American Chemical Society (ACS) video provides a behind-the-scenes-look at the DayGlo Color Corp. factory, producer of the fluorescent paints that light up traffic cones, black light posters, hula-hoops and other products. The video, the latest episode of the award-winning Bytesize Science series from the world's largest scientific society, is at www.BytesizeScience.com.
Inside DayGlo opens with a brief history of the company, which has been designated as an ACS National Historic Chemical Landmark, and continues with an in-depth look inside its main production ...
With the first explosions of atomic bombs, the world became witness to one of the most important and consequential principles in physics: Energy and mass, fundamentally speaking, are the same thing and can, in fact, be converted into each other.
This was first demonstrated by Albert Einstein's Theory of Special Relativity and famously expressed in his iconic equation, E=mc2, where E stands for energy, m for mass and c for the speed of light (squared).
Although physicists have since validated Einstein's equation in countless experiments and calculations, and many technologies ...
VIDEO:
This is a computer simulation of one octant of a core collapse supernova, using SNSPH.
Click here for more information.
Two University of Texas at Arlington researchers want to bridge the gap between what is known about exploding stars and the remnants left behind thousands of years later. So they're trying something new – using SNSPH, a complex computer code developed at Los Alamos National Laboratory.
On Tuesday, Carola I. Ellinger, a post-doctoral researcher at ...
By taking a "bottom-up" approach, researchers at the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign have observed for the first time that "size does matter" in regards "pyroelectricity"—the current/voltage developed in response to temperature fluctuations that enables technologies such as infrared sensors, night-vision, and energy conversion units, to name a few.
"Controlling and manipulating heat for applications such as waste heat energy harvesting, integrated cooling technologies, electron emission, and related functions is an exciting field of study today," explained ...
HERSHEY, Pa. -- While the number of overweight and obese Americans has increased, the amount of weight counseling offered by primary care physicians has decreased -- especially for patients with high blood pressure and diabetes -- according to Penn State College of Medicine researchers.
More than 145 million adult Americans are overweight or obese.
Researchers analyzed data from the National Ambulatory Medical Care Survey for the years 1995-1996 and 2007-2008. This national survey collects information about the provision and use of outpatient medical care services in ...
Our Milky Way is a spiral galaxy - a pinwheel-shaped collection of stars, gas and dust. It has a central bar and two major spiral arms that wrap around its disk. Since we view the Milky Way from the inside, its exact structure is difficult to determine.
Astronomers have identified a new structure in the Milky Way: a long tendril of dust and gas that they are calling a "bone."
"This is the first time we've seen such a delicate piece of the galactic skeleton," says lead author Alyssa Goodman of the Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics (CfA). Goodman presented the ...
ROCHESTER, Minn. -- A combination of the drugs pazopanib and paclitaxel shows promise in slowing anaplastic thyroid cancer (ATC), according to a Mayo Clinic-led study published in the journal Science Translational Medicine. The two drugs together resulted in greater anti-cancer activity in ATC than either drug alone, says lead researcher Keith Bible, M.D., Ph.D., a Mayo Clinic oncologist.
Anaplastic thyroid cancer is a rare but devastating form of thyroid cancer that typically strikes men and women in their 60s and 70s. It is very aggressive, with a median survival ...
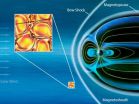
The sun ejects a continuous flow of electrically charged particles and magnetic fields in the form of the solar wind -- and this wind is hotter than it should be. A new study of data obtained by European Space Agency's Cluster spacecraft may help explain the mystery.
The solar wind is made of an electrically-charged gas called plasma. One theory about the wind's puzzling high temperatures is that irregularities in the flow of charged particles and magnetic fields in the plasma create turbulence, which, in turn, dissipates and adds heat to its surroundings. Using two separate ...
The eighth tropical cyclone to form during the Southern Indian Ocean cyclone season formed from low pressure System 98S and became Tropical Cyclone Narelle. NASA's TRMM satellite passed over System 98S and saw the hallmark "hot towers" that indicated the storm would soon likely intensify into Tropical Storm Narelle.
NASA's Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission (TRMM) satellite passed over System 98S on Jan. 7 at 0901 UTC (4:01 a.m. EST/U.S.) hours before it intensified into Tropical Storm Narelle.
TRMM's Precipitation Radar instrument captured estimates of rainfall occurring ...
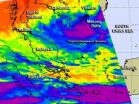
Tropical Depression Sonamu has been consistently slow moving over the last couple of days, and that has not changed. NASA's Aqua satellite captured an infrared image of the stubborn storm lingering in the South China Sea, and it still contained some strong thunderstorms.
When NASA's Aqua satellite passed over Tropical Depression Sonamu on Jan. 8 at 0641 UTC (1:41 a.m. EST/U.S.), the Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) instrument aboard took an infrared look at the storm. AIRS data showed that Sonamu still contained some very cold cloud top temperatures of -63F (-52C) ...