(Press-News.org) New Rochelle, NY, January 15, 2013—A novel therapeutic approach called exon skipping involves bypassing a disease-causing mutation in a gene to restore normal gene expression and protein production. Two innovative examples of this strategy used to correct gene defects associated with muscular dystrophy are described in articles in Human Gene Therapy, a peer-reviewed journal from Mary Ann Liebert, Inc., publishers. The articles are available free on the Human Gene Therapy website.
Willem Hoogaars and a team of researchers from France, the Netherlands, Finland, and Germany evaluated a combination of an exon-skipping treatment delivered via an adeno-associated virus (AAV) vector and a compound that inhibits myostatin signaling in a mouse model of Duchenne muscular dystrophy. The dual treatments led to improved muscle force and a decrease in ineffective muscle contractions, as well as increased body weight, muscle mass, and muscle fiber size. They did not, however, improve the effects of each treatment given individually. The results are reported in the article "Combined Effect of AAV-U7-Induced Dystrophin Exon Skipping and Soluble Activin Type IIB Receptor in mdx Mice."
Francesca Gualandi and colleagues, University of Ferrara and University of Padua, Italy, used exon skipping to inactivate mutated RNA messages responsible for defective collagen structure and function in muscle tissue affected by Ullrich muscular dystrophy or Bethlem myopathy. The authors describe their approach in "Antisense-Induced Messenger Depletion Corrects a COL6A2 Dominant Mutation in Ullrich Myopathy."
"This combines two very promising therapeutic approaches in a relevant animal model of muscular dystrophy," says James M. Wilson, MD, PhD, Editor-in-Chief, and Director of the Gene Therapy Program, Department of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine, University of Pennsylvania Perelman School of Medicine, Philadelphia.
INFORMATION:
About the Journal
Human Gene Therapy, the Official Journal of the European Society of Gene and Cell Therapy, British Society for Gene and Cell Therapy, French Society of Cell and Gene Therapy, German Society of Gene Therapy, and five other gene therapy societies, is an authoritative peer-reviewed journal published monthly in print and online. Human Gene Therapy presents reports on the transfer and expression of genes in mammals, including humans. Related topics include improvements in vector development, delivery systems, and animal models, particularly in the areas of cancer, heart disease, viral disease, genetic disease, and neurological disease, as well as ethical, legal, and regulatory issues related to the gene transfer in humans. Its sister journal, Human Gene Therapy Methods, published bimonthly, focuses on the application of gene therapy to product testing and development, and Human Gene Therapy Clinical Development, launching in 2013, publishes data relevant to the regulatory review and commercial development of cell and gene therapy products. Tables of content for all three publications and a free sample issue may be viewed on the Human Gene Therapy website.
About the Publisher
Mary Ann Liebert, Inc., publishers is a privately held, fully integrated media company known for establishing authoritative peer-reviewed journals in many promising areas of science and biomedical research, including Nucleic Acid Therapeutics Tissue Engineering, Stem Cells and Development, and Cellular Reprogramming. Its biotechnology trade magazine, Genetic Engineering & Biotechnology News (GEN), was the first in its field and is today the industry's most widely read publication worldwide. A complete list of the firm's 70 journals, books, and newsmagazines is available on the Mary Ann Liebert, Inc., publishers website.
Mary Ann Liebert, Inc. 140 Huguenot St., New Rochelle, NY 10801-5215 www.liebertpub.com
Phone: (914) 740-2100 (800) M-LIEBERT Fax: (914) 740-2101
Exon skipping to restore gene expression is promising therapeutic strategy for muscular dystrophy
2013-01-16
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Western University researchers identify new genetic mutation for ALS
2013-01-16
Researchers at Western University in London, Canada, have identified a new genetic mutation for amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), opening the door to future targeted therapies. Dr. Michael Strong, a scientist with Western's Robarts Research Institute and Distinguished University Professor in Clinical Neurological Sciences at the Schulich School of Medicine & Dentistry, and colleagues found that mutations within the ARHGEF28 gene are present in ALS. When they looked across both familial and sporadic forms of the disease, they found that virtually all cases of ALS demonstrated ...
For sports fans, the story -- not the victor -- makes the difference in enjoyment
2013-01-16
CORVALLIS, Ore. – A new study has concluded that sports fans love to root for a hero and against a villain, but if the game is exciting, they'll enjoy it no matter who wins.
The research, recently published in the Journal of Media Psychology, examines emotional experiences, outcome satisfaction, and enjoyment of athletic events, particularly ones featuring individual athletes rather than team sports.
Lead author Colleen Bee, an assistant professor of marketing at Oregon State University, said the Olympics are a good example of an event where fans often cheer for little-known ...
Researchers identify ways to improve quality of care measurement from electronic health records
2013-01-16
NEW YORK (January 15, 2013) -- Health care providers and hospitals are being offered up to $27 billion in federal financial incentives to use electronic health records (EHRs) in ways that demonstrably improve the quality of care. The incentives are based, in part, on the ability to electronically report clinical quality measures. By 2014, providers nationwide will be expected to document and report care electronically, and by 2015, they will face financial penalties if they don't meaningfully use EHRs.
A new, federally-funded study by Weill Cornell Medical College in ...
International study: Where there's smoke or smog, there's climate change
2013-01-16
In addition to causing smoggy skies and chronic coughs, soot – or black carbon – turns out to be the number two contributor to global warming. It's second only to carbon dioxide, according to a four-year assessment by an international panel.
The new study concludes that black carbon, the soot particles in smoke and smog, contributes about twice as much to global warming as previously estimated, even by the 2007 Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change.
"We were surprised at its potential contribution to climate," said Sarah Doherty, a University of Washington atmospheric ...
New American Chemical Society podcast: Leaves of carob tree fight food-poisoning bacteria
2013-01-16
The latest episode in the American Chemical Society's (ACS') award-winning Global Challenges/Chemistry Solutions podcast series reports that an antibacterial extract from the leaves of the carob tree (the source of a popular chocolate substitute) could fight the microbe responsible for the serious form of food poisoning called listeriosis.
Based on a report by Pierluigi Caboni, Ph.D., Nadhem Aissani and colleagues in ACS' Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, the new podcast is available without charge at iTunes and from www.acs.org/globalchallenges.
In the ...
Novel approach to track migration of arctic-breeding avian species
2013-01-16
Animals move around the globe in billions, sometimes - like the snow bunting - one of the iconic Arctic-breeding species, covering huge distances and enduring the most extreme frigid weather conditions. In this conspicuously white sparrow-sized bird, animal migration epitomizes a stunning success of biological adaptation – with Snow Bunting representing the only songbird to breed as far north as the Arctic Circle. Indeed, there is nothing north of the snow bunting's breeding ground except the North Pole and the polar ice cap. These passerines thrive in chilly, alpine conditions, ...
Studies provide new insights into brain-behavior relationships
2013-01-16
Amsterdam, NL, January 15, 2013 – Approximately half a million individuals suffer strokes in the US each year, and about one in five develops some form of post-stroke aphasia, the partial or total loss of the ability to communicate. By comparing different types of aphasia, investigators have been able to gain new insights into the normal cognitive processes underlying language, as well as the potential response to interventions. Their findings are published alongside papers on hemispatial neglect and related disorders in the January, 2013 issue of.
The January issue of ...
NASA finds 2012 sustained long-term climate warming trend
2013-01-16
NASA scientists say 2012 was the ninth warmest of any year since 1880, continuing a long-term trend of rising global temperatures. With the exception of 1998, the nine warmest years in the 132-year record all have occurred since 2000, with 2010 and 2005 ranking as the hottest years on record.
NASA's Goddard Institute for Space Studies (GISS) in New York, which monitors global surface temperatures on an ongoing basis, released an updated analysis Tuesday that compares temperatures around the globe in 2012 to the average global temperature from the mid-20th century. The ...
Choline supplementation during pregnancy presents a new approach to schizophrenia prevention
2013-01-16
AURORA, Colo. (Jan. 15, 2013) — Choline, an essential nutrient similar to the B vitamin and found in foods such as liver, muscle meats, fish, nuts and eggs, when given as a dietary supplement in the last two trimesters of pregnancy and in early infancy, is showing a lower rate of physiological schizophrenic risk factors in infants 33 days old. The study breaks new ground both in its potentially therapeutic findings and in its strategy to target markers of schizophrenia long before the illness itself actually appears. Choline is also being studied for potential benefits ...
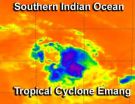
Infrared NASA imagery shows sinking air, elongation in Tropical Storm Emang
2013-01-16
The Atmospheric Infrared Sounder instrument that flies on NASA's Aqua satellite provides valuable data to tropical cyclone forecasters, and revealed sinking air, a small area of powerful thunderstorms, and a slightly elongated Tropical Storm Emang.
Infrared data on Tropical Storm Emang's cloud top temperatures was captured by the Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) instrument on Jan. 15 at 0823 UTC (3:23 a.m. EST). AIRS data showed that the largest area of powerful thunderstorms were in the northern half of the storm. That area showed cold cloud top temperatures of -63F ...