(Press-News.org) ANN ARBOR -- A review of the available evidence underscores the safety of the federal childhood immunization schedule, according to a report released today by the Institute of Medicine. University of Michigan population ecologist Pejman Rohani served on the 13-person committee that wrote the report.
Roughly 90 percent of American children receive most childhood vaccines advised by the federal immunization schedule by the time they enter kindergarten, the committee noted. However, some parents choose to spread out their children's immunizations over a different time frame than recommended by the schedule, and a small fraction object to having their children immunized at all.
Their concerns arise in part from the number of doses that children receive. The schedule entails 24 immunizations by age 2, given in amounts ranging from one to five injections during a pediatric visit.
"We reviewed the available data and concur with studies that have repeatedly shown the health benefits associated with the recommended schedule, including fewer illnesses, deaths and hospital stays," said Rohani, a professor of ecology and evolutionary biology, a professor of complex systems and a professor of epidemiology at the School of Public Health.
"Every new vaccine is tested for safety and evaluated in the context of the entire schedule before it is added. And the systems designed to detect possible harmful effects of immunization have worked well at discovering occasional problems with individual vaccines."
Until newer and bigger data collection systems can be harnessed, the Vaccine Safety Datalink (VSD) is the best available tool for exploring questions about the immunization schedule should the need arise, the committee concluded. This database contains information on the immunization histories of more than 9 million people covered by nine participating managed care organizations.
Researchers can identify individuals who were vaccinated according to alternative schedules as well as any diagnoses, medical procedures and outcomes they have experienced. VSD also contains data on race, age, gender and other factors that help researchers do better comparisons and account for factors that might affect participants' health. Already a research team has tapped VSD to explore patterns among children in the Kaiser Permanente Colorado system who are defined as under-vaccinated.
However, VSD tracks people from only eight states and looks at a smaller percentage of low-income and minority people than is in the U.S. population as a whole. Moreover, VSD's usefulness depends on the continuing involvement of participating health plans. The U.S. Department of Health and Human Services and its partners should maintain their commitment to funding VSD and consider bringing in additional health plan members to enhance the data and make it more representative of the full U.S. population, the report states.
Some critics of immunization policies have called for studies comparing health outcomes among vaccinated and unvaccinated children and for research to determine if subgroups exist that are predisposed to experiencing harmful health effects from the vaccines.
Although randomized controlled trials are the gold standard for clinical research, such a trial cannot be safely and efficiently performed to compare health outcomes among vaccinated and unvaccinated or differently immunized children, the committee concluded. Among other reasons, children placed in the study group that does not receive vaccines in a timely fashion would be exposed to greater risk for contracting illnesses. Many parents who refuse immunization may object to their children being randomly assigned to the group that gets vaccines.
Some people have suggested comparing vaccinated children with children in "naturally occurring" populations of unimmunized individuals, such as certain religious communities. With less than 1 percent of the American population refusing all immunizations, however, it would be very difficult to recruit enough willing unvaccinated participants, the committee concluded.
It can take tens of thousands of study participants to discover uncommon health problems. Moreover, these populations tend to be much less diverse ethnically, racially, socioeconomically and genetically than the general population. Because such factors can influence health, it would be difficult to determine if differences between the study groups are the result of vaccines or these other factors, the committee concluded.
"The costs of conducting this kind of study, or a randomized controlled trial, likely would be prohibitive," Rohani said.
Newer data collection and surveillance systems offer great potential to monitor rare adverse events that may be associated with the childhood immunization schedule, the committee said. When fully implemented, the Sentinel Initiative program being developed by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration to monitor the safety of approved drugs and other medical products will complement existing passive vaccine surveillance systems, the report says. FDA's new Post-License Rapid Immunization Safety Monitoring Program is amassing a large amount of health data, offering the potential to analyze vaccine exposures and adverse events with a greater degree of statistical power.
INFORMATION:
The report, "The Childhood Immunization Schedule and Safety: Stakeholder Concerns, Scientific Evidence, and Future Studies," was sponsored by the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. Established in 1970 under the charter of the National Academy of Sciences, the Institute of Medicine provides objective, evidence-based advice to policymakers, health professionals, the private sector and the public. The Institute of Medicine, National Academy of Sciences, National Academy of Engineering and National Research Council together make up the private, nonprofit National Academies.
WASHINGTON -- A review of the available evidence underscores the safety of the federal childhood immunization schedule, says a new report from the Institute of Medicine. Should signals indicate the need for investigation of the schedule, however, the report offers a framework for conducting safety research using existing or new data collection systems.
Roughly 90 percent of American children receive most childhood vaccines advised by the federal immunization schedule by the time they enter kindergarten, noted the committee that wrote the report. However, some parents ...
Philadelphia, Pa. (January 16, 2013) – With the rapidly expanding use of brain and spinal cord stimulation therapy (neuromodulation), new "remote presence" technologies may help to meet the demand for experts to perform stimulator programming, reports a study in the January issue of Neurosurgery, official journal of the Congress of Neurological Surgeons. The journal is published by Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, a part of Wolters Kluwer Health.
The preliminary study by Dr. Ivar Mendez of Queen Elizabeth II Health Sciences Centre in Halifax, Nova Scotia, Canada, supports ...
PHILADELPHIA -- In the first study to examine discussion of drug side effects on Internet message boards, researchers from the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania found that breast cancer survivors taking the commonly prescribed adjuvant therapy known as aromatase inhibitors (AIs) often detailed in these forums troublesome symptoms resulting from the drugs, and they were apt to report discontinuing the treatment or switching to a different drug in the same class. The findings are published online this week in the journal Pharmacoepidemiology and ...
Fashionable people may turn up their noses at jute — the cheap fiber used to make burlap, gunny sacks, twine and other common products — but new research is enhancing jute's appeal as an inexpensive, sustainable reinforcement for mortar and concrete. The study appears in ACS' journal Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research.
Subhasish B Majumder and colleagues note that there has been a resurgence of interest in using economical, sustainable natural fibers, rather than steel or synthetic fibers, to reinforce the cement compositions used to make concrete and mortar, ...
Scientists are reporting development of the first practical way to make large amounts of a promising new anti-cancer substance that kills cancer cells differently than existing medicines. Their article on synthesis of the substance, and tests demonstrating its effectiveness in the laboratory, appears in ACS' Journal of Medicinal Chemistry.
Isamu Shiina and colleagues explain that the substance, AMF-26, showed promise against certain forms of cancer in laboratory studies, fostering excitement about its potential for development as a new anti-cancer drug. That excitement ...
Philadelphia, Pa. (January 16, 2012) – Efforts to correct false beliefs about health care reform may backfire, depending on individuals' political views and level of knowledge, suggests a study in the February issue of Medical Care. The journal is published by Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, a part of Wolters Kluwer Health.
In the study, more politically knowledgeable people with positive views of Sarah Palin were likely to harden their opposition to the Affordable Care Act (ACA) when presented with information debunking Palin's "death panel" claim, according to the study ...
Philadelphia, Pa. (January 16, 2013) – Researchers using sophisticated genetic testing techniques have identified a promising new biomarker for diagnosis of glioma—the most common type of malignant brain tumor, reports the January issue of Neurosurgery, official journal of the Congress of Neurological Surgeons. The journal is published by Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, a part of Wolters Kluwer Health.
The biomarker ELTD1 "may serve as an additional biomarker for gliomas in preclinical and clinical diagnosis of gliomas," according to the study by Rheal A. Towner of Oklahoma ...
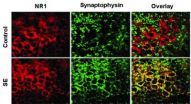
LOS ANGELES (Jan. 16, 2013) – In a promising finding for epileptic patients suffering from persistent seizures known as status epilepticus, researchers reported today that new medication could help halt these devastating seizures. To do so, it would have to work directly to antagonize NMDA receptors, the predominant molecular device for controlling synaptic activity and memory function in the brain.
"Despite the development of new medications to prevent seizures, status epilepticus remains a life-threatening condition that can cause extensive brain damage in the patients ...
RIVERSIDE, Calif. (www.ucr.edu) — An assistant professor at the University of California, Riverside's Bourns College of Engineering is using the teeth of a marine snail found off the coast of California to create less costly and more efficient nanoscale materials to improve solar cells and lithium-ion batteries.
The most recent findings by David Kisailus, an assistant professor of chemical and environmental engineering, details how the teeth of chiton grow. The paper was published today (Jan. 16) in the journal Advanced Functional Materials. It was co-authored by several ...
Researchers of the Catalan Institute of Oncology (ICO) at the Bellvitge Biomedical Research Institute (IDIBELL) have developed and validated a new method to diagnose hereditary breast and ovarian cancer syndrome based on mass sequencing of BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes. The model is based on a genetic and bioinformatic analysis which has been proved very effective. The new protocol has been described in an article published in the European Journal of Human Genetics.
In recent years, new advances in sequencing techniques have involved the development of new platforms for nucleic ...