(Press-News.org) RIVERSIDE, Calif. (www.ucr.edu) — An assistant professor at the University of California, Riverside's Bourns College of Engineering is using the teeth of a marine snail found off the coast of California to create less costly and more efficient nanoscale materials to improve solar cells and lithium-ion batteries.
The most recent findings by David Kisailus, an assistant professor of chemical and environmental engineering, details how the teeth of chiton grow. The paper was published today (Jan. 16) in the journal Advanced Functional Materials. It was co-authored by several of his current and former students and scientists at Harvard University in Cambridge Mass., Chapman University in Orange, Calif. and Brookhaven National Laboratory in Upton, NY.
The paper is focused on the gumboot chiton, the largest type of chiton, which can be up to a foot-long. They are found along the shores of the Pacific Ocean from central California to Alaska. They have a leathery upper skin, which is usually reddish-brown and occasionally orange, leading some to give it the nickname "wandering meatloaf."
Over time, chitons have evolved to eat algae growing on and within rocks using a specialized rasping organ called a radula, a conveyer belt-like structure in the mouth that contains 70 to 80 parallel rows of teeth. During the feeding process, the first few rows of the teeth are used to grind rock to get to the algae. They become worn, but new teeth are continuously produced and enter the "wear zone" at the same rate as teeth are shed.
Kisailus, who uses nature as inspiration to design next generation engineering products and materials, started studying chitons five years ago because he was interested in abrasion and impact-resistant materials. He has previously determined that the chiton teeth contain the hardest biomineral known on Earth, magnetite, which is the key mineral that not only makes the tooth hard, but also magnetic.
In the just-published paper, "Phase transformations and structural developments in the radular teeth of Cryptochiton stelleri," Kisailus set out to determine how the hard and magnetic outer region of the tooth forms.
His work revealed this occurs in three steps. Initially, hydrated iron oxide (ferrihydrite) crystals nucleate on a fiber-like chitinous (complex sugar) organic template. These nanocrystalline ferrihydrite particles convert to a magnetic iron oxide (magnetite) through a solid-state transformation. Finally, the magnetite particles grow along these organic fibers, yielding parallel rods within the mature teeth that make them so hard and tough.
"Incredibly, all of this occurs at room temperature and under environmentally benign conditions," Kisailus said. "This makes it appealing to utilize similar strategies to make nanomaterials in a cost-effective manner."
Kisailus is using the lessons learned from this biomineralization pathway as inspiration in his lab to guide the growth of minerals used in solar cells and lithium-ion batteries. By controlling the crystal size, shape and orientation of engineering nanomaterials, he believes he can build materials that will allow the solar cells and lithium-ion batteries to operate more efficiently. In other words, the solar cells will be able to capture a greater percentage of sunlight and convert it to electricity more efficiently and the lithium-ion batteries could need significantly less time to recharge.
Using the chiton teeth model has another advantage: engineering nanocrystals can be grown at significantly lower temperatures, which means significantly lower production costs.
While Kisailus is focused on solar cells and lithium-ion batteries, the same techniques could be used to develop everything from materials for car and airplane frames to abrasion resistant clothing. In addition, understanding the formation and properties of the chiton teeth could help to create better design parameters for better oil drills and dental drill bits.
###Co-authors of the Advanced Functional Materials paper were: Qianqian Wang, Michiko Nemoto, Dongsheng Li, Garrett W. Milliron, Brian Weden, Leslie R. Wood, all of whom are current or former undergraduate and graduate students at UC Riverside; James C. Weaver, a former post-doc of Kisailus, now at Harvard University; John Stegemeier and Christopher S. Kim, of Chapman University; and Elaine DiMasi, of Brookhaven National Laboratory.
Using snail teeth to improve solar cells and batteries
Assistant professor David Kisailus studies the chiton, a marine snail found off the coast of California, to develop nanoscale materials for energy applications
2013-01-16
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Developed new method to diagnose hereditary breast and ovarian cancer
2013-01-16
Researchers of the Catalan Institute of Oncology (ICO) at the Bellvitge Biomedical Research Institute (IDIBELL) have developed and validated a new method to diagnose hereditary breast and ovarian cancer syndrome based on mass sequencing of BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes. The model is based on a genetic and bioinformatic analysis which has been proved very effective. The new protocol has been described in an article published in the European Journal of Human Genetics.
In recent years, new advances in sequencing techniques have involved the development of new platforms for nucleic ...
Dynamic Motivational Author, Speaker & Veteran Deborah L. Parker Keynotes Leesburg Virginia's Martin Luther King March & Program, "Moving the Dream Forward For All of Us" January 21
2013-01-16
Deborah L. Parker remembers the evening of April 4, 1968. In her rural Waverly Virginia home with no indoor plumbing, on the way to the laundromat with her mother, it seemed as if the world stopped. The headline of the evening news: Dr. Martin Luther King Jr. has been assassinated. What happens to the dream? Deborah wondered. She was poor, black, and a good student in a segregated Sussex County. Her mother was a single parent of four and they lived with her maternal grandparents in a shotgun style house on a wooded back road. But her mother was determined and her grandparents ...
Migraine with aura may lead to heart attack, blood clots for women
2013-01-16
SAN DIEGO – Women who have migraines with aura, which are often visual disturbances such as flashing lights, may be more likely to have problems with their heart and blood vessels, and those on newer contraceptives may be at higher risk for blood clots, according to two studies released today that will be presented at the American Academy of Neurology's 65th Annual Meeting in San Diego, March 16 to 23, 2013.
The first study showed that migraine with aura is a strong contributor to the development of major cardiovascular events such as heart attack and stroke. The Women's ...
Higher quality rating for Medicare Advantage plan linked with increased likelihood of enrollment
2013-01-16
CHICAGO – In a study that included nearly 1.3 million Medicare beneficiaries who were either first-time enrollees or enrollees switching plans, researchers found a positive association between enrollment and publicly reported Medicare Advantage star ratings reflecting plan quality, according to a study appearing in the January 16 issue of JAMA.
"To inform enrollment decisions and spur improvement in the Medicare Advantage marketplace, the U.S. Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) provides star ratings reflecting Medicare Advantage plan quality. A combined Part ...
Transmission of tangles in Alzheimer's mice provides more authentic model of tau pathology
2013-01-16
PHILADELPHIA – Brain diseases associated with the misformed protein tau, including Alzheimer's disease and frontotemporal lobar degeneration with tau pathologies, are characterized by neurofibrillary tangles (NFTs) comprised of pathological tau filaments. Tau tangles are also found in progressive supranuclear palsy, cortical basal degeneration and other related tauopathies, including chronic traumatic encephalopathy due to repetitive traumatic brain injuries sustained in sports or on the battle field.
By using synthetic fibrils made from pure recombinant protein, Penn ...
Tracing the impact of amyloid beta in mild cognitive impairment
2013-01-16
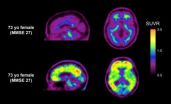
The amount of amyloid β (Aβ) in the brains of people with mild cognitive impairment (MCI) is contributing to early memory loss, and increases with severity of symptoms, finds a study in BioMed Central's open access journal Alzheimer's Research & Therapy. The non-invasive study which used 18F-florbetaben to find Aβ plaques in brain scans to also show that in MCI the affect of Aβ on memory loss is independent of other aspects of mental decline.
Positron emission tomography (PET) has previously relied on carbon-11 labeling of Aβ, however this ...
Cutting down on sugar has a small but significant effect on body weight
2013-01-16
Research: Dietary sugars and body weight: a systematic review and meta-analyses of randomised controlled trials and cohort studies
Editorial: Science souring on sugar
Feature: Sugar and the heart: old ideas revisited
Reducing sugar intake has a small but significant effect on body weight in adults, finds a paper published on bmj.com today.
Although the effect is relatively small (an average reduction of 0.8 kg), the findings provide some support for international guidelines to cut sugar intake to less than 10% of total energy to help reduce the global obesity epidemic.
Excessive ...
Blood clots and artery blockage more likely during IVF pregnancies
2013-01-16
Research: Incidence of pulmonary and venous thromboembolism in pregnancies after in vitro fertilisation: cross sectional study
In vitro fertilization (IVF) is associated with an increased risk of pulmonary embolism (blockage of the main artery of the lung) and venous thromboembolism (blood clots) during the first trimester of pregnancy, a study published today on bmj.com suggests.
IVF has been used since 1978 for the 10% of couples worldwide affected by infertility. Approximately five million individuals have so far been born after IVF.
It is well known that the ...
Virtual heart sheds new light on heart defect
2013-01-16
A virtual heart, developed at The University of Manchester, is revealing new information about one of the world's most common heart conditions.
Researchers at the School of Physics and Astronomy used cutting edge technology to build an advanced computational model of an anatomically correct sheep's heart. It was made by taking a series of very thin slices of the heart, imaging them in 2D and then using a computer programme to render them into a 3D model.
The reconstruction includes details of the complex fibre structure of the tissue, and the segmentation of the upper ...
Device tosses out unusable PV wafers
2013-01-16
Silicon wafers destined to become photovoltaic (PV) cells can take a bruising through assembly lines, as they are oxidized, annealed, purified, diffused, etched, and layered to reach their destinies as efficient converters of the sun's rays into useful electricity.
All those refinements are too much for 5% to 10% of the costly wafers. They have micro-cracks left over from incomplete wafer preparation, which causes them to break on the conveyers or during cell fabrication.
Scientists at the U.S. Department of Energy's National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) have ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
RESPIN launches new online course to bridge the gap between science and global environmental policy
[Press-News.org] Using snail teeth to improve solar cells and batteriesAssistant professor David Kisailus studies the chiton, a marine snail found off the coast of California, to develop nanoscale materials for energy applications