(Press-News.org) SAN DIEGO – Women who have migraines with aura, which are often visual disturbances such as flashing lights, may be more likely to have problems with their heart and blood vessels, and those on newer contraceptives may be at higher risk for blood clots, according to two studies released today that will be presented at the American Academy of Neurology's 65th Annual Meeting in San Diego, March 16 to 23, 2013.
The first study showed that migraine with aura is a strong contributor to the development of major cardiovascular events such as heart attack and stroke. The Women's Health Study involved 27,860 women, 1,435 of whom had migraine with aura. During the 15-year study, there were 1,030 cases of heart attack, stroke or death from a cardiovascular cause. The study examined the relative contribution of various vascular risk factors to these major cardiovascular events.
"After high blood pressure, migraine with aura was the second strongest single contributor to risk of heart attacks and strokes," said study author Tobias Kurth, MD, ScD, of INSERM, the French National Institute of Health and Medical Research in Bordeaux and Brigham and Women's Hospital in Boston. Kurth is also a Fellow of the American Academy of Neurology. "It came ahead of diabetes, current smoking, obesity, and family history of early heart disease."
Kurth cautioned that while people with migraine with aura have an increased risk, it does not mean that everyone with migraine with aura will have a heart attack or stroke. He said people with migraine with aura can reduce their risk in the same ways others can, such as not smoking, keeping blood pressure low and weight down and exercising.
The second study looked at women with migraine who take hormonal contraceptives and the occurrence of blood clots. The study involved women with migraine with and without aura who were taking both newer contraceptives such as the contraceptive patch and ring and older contraceptives. Of the 145,304 women who used the contraceptives, 2,691 had migraine with aura and 3,437 had migraine without aura.
Women with migraine with aura were more likely to have experienced blood clot complications such as deep vein thrombosis with all types of contraceptives than women with migraine without aura. For example, 7.6 percent of women with migraine with aura who used a newer generation combined hormonal contraceptive had deep vein thrombosis compared to 6.3 percent of women with migraine without aura, but the timing of the two events is not clear. The occurrence of blood clot complications was also higher in women with migraine who took contraceptives than women taking the contraceptives who did not have migraine.
"Women who have migraine with aura should be sure to include this information in their medical history and talk to their doctors about the possible higher risks of newer contraceptives, given their condition," said study author Shivang Joshi, MD, MPH, RPh, of Brigham and Women's Falkner Hospital in Boston and a member of the American Academy of Neurology.
INFORMATION:
Learn more about migraine at http://www.aan.com/patients.
Kurth's study was supported by the National Institutes of Health. Joshi's study was supported by the Graham Headache Center Research Fund.
The American Academy of Neurology, an association of more than 25,000 neurologists and neuroscience professionals, is dedicated to promoting the highest quality patient-centered neurologic care. A neurologist is a doctor with specialized training in diagnosing, treating and managing disorders of the brain and nervous system such as Alzheimer's disease, stroke, migraine, multiple sclerosis, brain injury, Parkinson's disease and epilepsy.
For more information about the American Academy of Neurology, visit http://www.aan.com or find us on Facebook, Twitter, Google+ and YouTube.
Media Contacts:
Rachel Seroka, rseroka@aan.com, (612) 928-6129
Angela Babb, APR, ababb@aan.com, (612) 928-6102
END
CHICAGO – In a study that included nearly 1.3 million Medicare beneficiaries who were either first-time enrollees or enrollees switching plans, researchers found a positive association between enrollment and publicly reported Medicare Advantage star ratings reflecting plan quality, according to a study appearing in the January 16 issue of JAMA.
"To inform enrollment decisions and spur improvement in the Medicare Advantage marketplace, the U.S. Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) provides star ratings reflecting Medicare Advantage plan quality. A combined Part ...
PHILADELPHIA – Brain diseases associated with the misformed protein tau, including Alzheimer's disease and frontotemporal lobar degeneration with tau pathologies, are characterized by neurofibrillary tangles (NFTs) comprised of pathological tau filaments. Tau tangles are also found in progressive supranuclear palsy, cortical basal degeneration and other related tauopathies, including chronic traumatic encephalopathy due to repetitive traumatic brain injuries sustained in sports or on the battle field.
By using synthetic fibrils made from pure recombinant protein, Penn ...
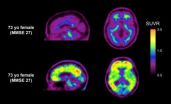
The amount of amyloid β (Aβ) in the brains of people with mild cognitive impairment (MCI) is contributing to early memory loss, and increases with severity of symptoms, finds a study in BioMed Central's open access journal Alzheimer's Research & Therapy. The non-invasive study which used 18F-florbetaben to find Aβ plaques in brain scans to also show that in MCI the affect of Aβ on memory loss is independent of other aspects of mental decline.
Positron emission tomography (PET) has previously relied on carbon-11 labeling of Aβ, however this ...
Research: Dietary sugars and body weight: a systematic review and meta-analyses of randomised controlled trials and cohort studies
Editorial: Science souring on sugar
Feature: Sugar and the heart: old ideas revisited
Reducing sugar intake has a small but significant effect on body weight in adults, finds a paper published on bmj.com today.
Although the effect is relatively small (an average reduction of 0.8 kg), the findings provide some support for international guidelines to cut sugar intake to less than 10% of total energy to help reduce the global obesity epidemic.
Excessive ...
Research: Incidence of pulmonary and venous thromboembolism in pregnancies after in vitro fertilisation: cross sectional study
In vitro fertilization (IVF) is associated with an increased risk of pulmonary embolism (blockage of the main artery of the lung) and venous thromboembolism (blood clots) during the first trimester of pregnancy, a study published today on bmj.com suggests.
IVF has been used since 1978 for the 10% of couples worldwide affected by infertility. Approximately five million individuals have so far been born after IVF.
It is well known that the ...
A virtual heart, developed at The University of Manchester, is revealing new information about one of the world's most common heart conditions.
Researchers at the School of Physics and Astronomy used cutting edge technology to build an advanced computational model of an anatomically correct sheep's heart. It was made by taking a series of very thin slices of the heart, imaging them in 2D and then using a computer programme to render them into a 3D model.
The reconstruction includes details of the complex fibre structure of the tissue, and the segmentation of the upper ...
Silicon wafers destined to become photovoltaic (PV) cells can take a bruising through assembly lines, as they are oxidized, annealed, purified, diffused, etched, and layered to reach their destinies as efficient converters of the sun's rays into useful electricity.
All those refinements are too much for 5% to 10% of the costly wafers. They have micro-cracks left over from incomplete wafer preparation, which causes them to break on the conveyers or during cell fabrication.
Scientists at the U.S. Department of Energy's National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) have ...
NEWPORT, Ore. – The $15 billion ornamental fish industry faces a global problem with antibiotic resistance, a new study concludes, raising concern that treatments for fish diseases may not work when needed – and creating yet another mechanism for exposing humans to antibiotic-resistant bacteria.
The risk to humans is probably minor unless they frequently work with fish or have compromised immune systems, researchers said, although transmission of disease from tropical fish has been shown to occur. More serious is the risk to this industry, which has grown significantly ...
PHILADELPHIA, January 15, 2013 -- Stage 3 Meaningful Use measures need to focus more on measuring improvements in patient health outcomes rather being than a large and growing collection of functional measures, the American College of Physicians (ACP) says in a letter submitted to the Health Information Technology Policy Committee (HITPC).
While praising the HITPC and its Meaningful Use Work Group for their diligence and hard work in developing recommendations for the Meaningful Use portion of the EHR Incentive Program, ACP noted that the proposed Stage 3 measures appear ...
HONOLULU — While the iconic Haleakalā silversword plant made a strong recovery from early 20th-century threats, it has now entered a period of substantial climate-related decline. New research published this week warns that global warming may have severe consequences for the silversword in its native habitat.
Known for its striking rosette, the silversword grows for 20-90 years before the single reproductive event at the end of its life, at which time it produces a large (up to six feet tall) inflorescence with as many as 600 flower heads. The plant was in jeopardy ...