(Press-News.org) Alcoholic liver disease (ALD) is characterized by a fatty liver, hepatitis, fibrosis, and cirrhosis. Binge drinking is on the rise worldwide, and is particularly common in the U.S. A review of studies addressing the effects of binge drinking on the liver underscores the complex interactions among various immune, signaling pathways, epigenetic, and metabolic responses of the liver to binge drinking.
Results will be published in the April 2013 issue of Alcoholism: Clinical & Experimental Research and are currently available at Early View.
"The liver is the main metabolic site in the body," said Shivendra D. Shukla, Margaret Proctor Mulligan Professor at the University of Missouri, School of Medicine as well as corresponding author for the study. "It is involved in nutrient and drug metabolism and disposition, and in the production of a myriad of agents needed for the physiological functions of organs such as the heart, kidney, blood vessels, and brain. ALD-affected liver chemicals can also influence immunity, cardiovascular health, and coagulation. Thus, ALD can have a 'domino effect' on many organs."
"The liver is also the major organ for alcohol metabolism, and as such, is the first line of defense against excessive alcohol consumption," added Samir Zakhari, senior vice president in the Office of Science at Distilled Spirits Council of the United States. "The effects of binge drinking on the liver depend on whether binge drinking is superimposed on chronic heavy drinking, or is done on an empty stomach especially after a period of fasting or starvation."
"Binge abuse is on the rise globally," said Shukla. "For example, about 43 percent of college students have reported at least one binge episode during the previous months. It is therefore necessary to fully understand its consequences at molecular levels. This is the first review that highlights the molecular pharmacology of binge drinking and how this may offer insight into binge-induced injury and its wider implications."
Some of the review's key themes are:
Binge consumption of alcohol is implicated in the pathophysiology of ALD. New studies from both experimental animals and humans indicate that binge drinking has profound effects on immunological, signaling, and epigenetic parameters of the liver. This is in addition to the known metabolic effects of acute levels of alcohol.
"Chronic alcohol consumption renders the liver highly susceptible to binge-induced liver damage," said Shukla. "Binge-induced liver injury impacts other organs as well, a view rather poorly appreciated by the public."
Binge drinking alters the levels of several cellular components and dramatically amplifies liver injury in the chronically alcohol-exposed liver.
"This review, the first of its kind, emphasizes the importance of molecular and epigenetic mechanisms in binge-induced liver injury," said Shukla. "This review also sets the stage for additional investigations in this field. The cross-organ implications of binge-induced liver damage must be explored."
"Binge drinking influences all the mechanisms mentioned above, but can also cause mitochondrial damage, which may result in cell death and disturbances in bioenergetics," added Zakhari. "Therefore, people should not binge drink, especially on an empty stomach, and if they are chronic heavy drinkers, binge drinking will exacerbate liver injury, especially if comorbid conditions such as obesity, Hepatitis C, or HIV infection exist."
The authors stress the importance of additional molecular investigations into the binge effects of alcohol for a better understanding of ALD. They also suggest that future research address the development of therapeutic strategies to control binge drinking.
"Our review highlights the effects of ALD on multiple molecules that in turn have effects on various organs," said Shukla. "We hope this will encourage research and development of newer approaches and tools to control and ameliorate binge-induced health effects."
###Alcoholism: Clinical & Experimental Research (ACER) is the official journal of the Research Society on Alcoholism and the International Society for Biomedical Research on Alcoholism. Co-authors of the ACER paper, "Binge Alcohol and Liver: New Molecular Developments," were: Stephen B. Pruett of the Department of Basic Sciences at Mississippi State University; Gyongyi Szabo of the Department of Internal Medicine at the University of Massachusetts Medical School; and Gavin E. Arteel of the Department of Pharmacology & Toxicology at the University of Louisville Health Sciences Center. This release is supported by the Addiction Technology Transfer Center Network at http://www.ATTCnetwork.org.
Binge drinking can dramatically amplify damage to the liver
2013-01-23
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Reviewing alcohol's effects on normal sleep
2013-01-23
Sleep is supported by natural cycles of activity in the brain and consists of two basic states: rapid eye movement (REM) sleep and non-rapid eye movement (NREM) sleep. Typically, people begin the sleep cycle with NREM sleep followed by a very short period of REM sleep, then continue with more NREM sleep and more REM sleep, this 90 minute cycle continuing through the night. A review of all known scientific studies on the impact of drinking on nocturnal sleep has clarified that alcohol shortens the time it takes to fall asleep, increases deep sleep, and reduces REM sleep.
Results ...
The ability to 'hold one's liquor' indicates risk of developing alcohol problems
2013-01-23
Prior studies have shown that a low subjective response (SR) to alcohol is a risk factor for alcohol use disorders (AUDs). Research on moderate drinkers has shown that acquired tolerance is different from initial response, and is also significantly associated with drinking problems. A new study of linkages among early SR, acquired tolerance, alcohol use, and alcohol-related problems among problem drinkers has found that a low, early subjective response –an ability to "hold one's liquor" - may protect against problems in the short term, but likely becomes a risk factor ...
Will proposed DSM-5 changes to assessment of alcohol problems do any better?
2013-01-23
Proposed changes to the upcoming fifth edition of the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5) will affect the criteria used to assess alcohol problems. One change would collapse the two diagnoses of alcohol abuse (AA) and alcohol dependence (AD) into a single diagnosis called alcohol use disorder (AUD). A second change would remove "legal problems," and a third would add a criterion of "craving." A study of the potential consequences of these changes has found they are unlikely to significantly change the prevalence of diagnoses.
Results will ...
Alcohol use from adolescence to adulthood follows different, complex pathways
2013-01-23
Adolescence is often a time of novelty seeking and risk taking, including the initiation of drinking. While heavy drinking that begins in adolescence can lead to problematic alcohol use later in life, other risk factors are also involved in trajectories of alcohol use that may develop. A study of factors predicting alcohol use and patterns of use over time has identified six distinct trajectories that concern level of alcohol use, rate of increase in use during early adolescence, and persistence of use into adulthood.
Results will be published in the March 2013 issue ...
New test predicted presence of harmful BRCA mutations
2013-01-23
PHILADELPHIA — A new multiple gene expression profile test was able to predict the presence of harmful BRCA1 or BRCA2 mutations in otherwise healthy women carrying the mutations, according to data published in Cancer Prevention Research, a journal of the American Association for Cancer Research.
"This novel technology aims to provide a layer of information regarding the cell functionality aspect of BRCA mutations that could greatly enhance the doctor's ability to identify high-risk carriers," said Asher Y. Salmon, M.D., a breast cancer specialist at the Hadassah Hebrew ...
A brain protein called vimentin can indicate damage to the hippocampus following binge drinking
2013-01-23
Contact: Kimberly Nixon
kim-nixon@uky.edu
859-218-1025
The University of Kentucky
Contact: Fulton T. Crews
ftcrews@med.unc.edu
919-966-5678
University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
Alcoholism: Clinical & Experimental Research
A brain protein called vimentin can indicate damage to the hippocampus following binge drinking
Binge drinking is known to increase the risk of developing dementia and/or brain damage.
A new study used rodents to test markers of neurodegeneration to determine a threshold for brain damage.
The vimentin brain protein can ...
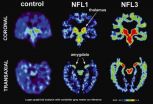
UCLA study first to image concussion-related abnormal brain proteins in retired NFL players
2013-01-23
Sports-related concussions and mild traumatic brain injuries have grabbed headlines in recent months, as the long-term damage they can cause becomes increasingly evident among both current and former athletes. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention estimates that millions of these injuries occur each year.
Despite the devastating consequences of traumatic brain injury and the large number of athletes playing contact sports who are at risk, no method has been developed for early detection or tracking of the brain pathology associated with these injuries.
Now, ...
Less tau reduces seizures and sudden death in severe epilepsy
2013-01-23
HOUSTON (Jan. 23, 2013) – Deleting or reducing expression of a gene that carries the code for tau, a protein associated with Alzheimer's disease, can prevent seizures in a severe type of epilepsy linked to sudden death, said researchers at Baylor College of Medicine and the Mayo Clinic in Jacksonville, Fla., in a report in the current issue of the Journal of Neuroscience.
A growing understanding of the link between epilepsy and some forms of inherited Alzheimer's disease led to the finding that could point the way toward new drugs for seizure disorders said Dr. Jeffrey ...
Beta carotene may protect people with common genetic risk factor for type-2 diabetes
2013-01-23
STANFORD, Calif. — Stanford University School of Medicine investigators have found that for people harboring a genetic predisposition that is prevalent among Americans, beta carotene, which the body converts to a close cousin of vitamin A, may lower the risk for the most common form of diabetes, while gamma tocopherol, the major form of vitamin E in the American diet, may increase risk for the disease.
The scientists used a "big data" approach to hunt down interactions between gene variants previously associated with increased risk for type-2 diabetes and blood levels ...
Emergency department use within 30 days of hospital discharge common
2013-01-23
CHICAGO – In a study that included more than 4 million patients, nearly 20 percent of hospitalizations resulted in at least 1 acute care encounter within the 30 days following discharge, with emergency department visits accounting for about 40 percent of post-discharge hospital-based acute care use, according to a study appearing in the January 23/30 issue of JAMA.
"Hospital readmissions within 30 days of discharge are common, costly, and often related to the index hospitalization," according to background information in the article. "Current efforts to improve health ...