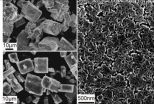
Modifications of a nanoparticle can change chemical interactions with cell membranes
2013-01-24
(Press-News.org) Researchers at Syracuse University's Department of Biomedical and Chemical Engineering at L.C. Smith College of Engineering and Computer Science are studying the toxicity of commonly used nanoparticles, particles up to one million times smaller than a millimeter that could potentially penetrate and damage cell membranes.
In a recent article published along with cover art in the leading journal Langmuir entitled "Effects of nanoparticle charge and shape anisotropy on translocation through cell membranes," researchers Shikha Nangia, assistant professor of biomedical and chemical engineering (BMCE), and Radhakrishna Sureshkumar, Department Chair of BMCE and professor of physics, showed how simple shape and charge modifications of a nanoparticle can cause tremendous changes in the chemical interactions between the nanoparticle and a cell membrane.
Nanomaterials, which are currently being used as drug carriers, also pose a legitimate concern, since no universal standards exist to educate and fully protect those who handle these materials. Nanoparticles are comparable to chemicals in their potential threat because they could easily penetrate the skin or be inhaled.
"Nanotechnology has immense potential that is starting to be being realized; a comprehensive understanding of toxicity of nanoparticles will help develop better safe handling procedures in nanomanufacturing and nano-biotechnology" says Sureshkumar and Nangia, In addition, the toxicity levels of various nanoparticles can be used to our advantage in targeting cancer cells and absorbing radiation during cancer therapy. Nanotoxicity is becoming a major concern as the use of nanoparticles in imaging, therapeutics, diagnostics, catalysis, sensing and energy harvesting continues to grow dramatically.
This research project has taken place over the past year utilizing a state of the art 448 core parallel computer nicknamed "Prophet" housed in Syracuse University's Green Data Center. The research was funded by the National Science Foundation.
INFORMATION:
Langmuir is a notable, interdisciplinary journal of American Chemical Society publishing articles in: colloids, interfaces, biological interfaces, nano-materials, electrochemistry and devices and applications. It can be found at: pubs.acs.org/journal/langd5.
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2013-01-24
What cancerous conditions lead to what kinds of bacterial infections? If doctors knew, they could predict which patients would likely benefit from pre-treatment with certain kinds of antibiotics. A University of Colorado Cancer Center study published in this month's issue of the International Journal of Infectious Diseases shows the answer: E. coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae are especially prevalent in patients with lung and GI cancers, more so for Klebsiella if these patients have been treated previously with aminopenicillins.
"These are really dangerous infections. You ...
2013-01-24
COLLEGE PARK, Md. – Filipinos have been an invisible minority in Annapolis, Maryland for more than a century. Now, researchers at the University of Maryland are using oral histories as a way to flesh out their life and times – documenting the incredible challenges they faced – and successes they celebrated.
After the Spanish-American War, the Philippines became a U.S. territory. Filipinos were brought to Annapolis – home of the Naval Academy – to serve as desk interns, fire fighters, construction laborers, messmen and stewards. In many cases, the Naval Academy replaced ...
2013-01-24
VIDEO:
This is a NASA TRMM satellite flyby of Tropical Cyclone Peta in the South Indian Ocean. TRMM revealed that rain was falling at a rate of up to 94 mm...
Click here for more information.
Infrared data from NASA's Aqua satellite has shown that soon after a low pressure system in northwestern West Australia became Tropical Storm Peta, it made landfall and started to fall apart.
Early on Jan. 22, the Joint Typhoon Warning Center (JTWC) gave System 93S a high chance for ...
2013-01-24
OAK RIDGE, Tenn., Jan. 23, 2013 -- Looking toward improved batteries for charging electric cars and storing energy from renewable but intermittent solar and wind, scientists at Oak Ridge National Laboratory have developed the first high-performance, nanostructured solid electrolyte for more energy-dense lithium ion batteries.
Today's lithium-ion batteries rely on a liquid electrolyte, the material that conducts ions between the negatively charged anode and positive cathode. But liquid electrolytes often entail safety issues because of their flammability, especially as ...
2013-01-24
Tropical Storm Oswald's heavy rains have caused flooding in Queensland, Australia and NASA's TRMM satellite measured almost two feet of rain fell in certain areas.
Tropical cyclone Oswald's sustained winds have never been greater than 35 knots (~40.2 mph) but the storm's extreme rainfall has resulted in widespread flooding in Australia over northern Queensland. Many roads have been reported flooded resulting in some communities being cut off.
NASA's Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission (TRMM) is a satellite that can measure rainfall from space. TRMM-based satellite precipitation ...
2013-01-24
The longstanding ethical framework for protecting human volunteers in medical research needs to be replaced because it is outdated and can impede efforts to improve health care quality, assert leaders in bioethics, medicine, and health policy in two companion articles in a Hastings Center Report special report, "Ethical Oversight of Learning Health Care Systems." One of the authors calling for a new approach is the main architect of the current ethical framework.
Seven commentaries in the publication, written by leaders with national responsibility for ethical oversight ...
2013-01-24
[EMBARGOED FOR JAN. 24, 2013] Pediatric rotavirus vaccination also indirectly protects unvaccinated adults from the highly contagious cause of severe diarrhea and vomiting, suggests a new study published in Clinical Infectious Diseases and available online. The findings suggest pediatric immunization against the virus may be more cost effective than previously thought, given rotavirus-related health care costs among adults.
Before the vaccine, rotavirus caused an estimated 24 million outpatient visits, 2.4 million hospitalizations, and 453,000 deaths in infants and young ...
2013-01-24
A Phase 3 clinical trial demonstrates that tofacitinib improves disease activity and inhibits progression of joint damage in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients who did not respond to methotrexate (MTX). Results of the 12-month interim analysis of the efficacy of tofacitinib appear in Arthritis & Rheumatism, a journal published by Wiley on behalf of the American College of Rheumatology (ACR).
RA is a chronic, autoimmune disease that causes inflammation, pain and swelling of the joints. Over time, RA may destroy joints, impair daily function, and lead to significant disability. ...
2013-01-24
The first ever review of abuse cases related to child death or serious injury in Northern Ireland will be launched at Queen's University today (24 January 2013). The review, Translating Learning into Action, was commissioned by the Department of Health, Social Services and Public Safety (DHSSPS) and was carried out by researchers at Queen's University and the NSPCC.
The Case Management Review (CMR) report – the first to be produced in Northern Ireland - analysed 24 case reviews relating to 45 children which resulted in death or serious injury in the period between 2003 ...
2013-01-24
Researchers at Moffitt Cancer Center and colleagues have investigated the safety, efficacy and the maximum tolerated dose of pomalidomide for patients with multiple myeloma who have disease relapsed after treatments with other drugs, such as bortezomib and lenalidomide. This phase I clinical trial enrolled 38 patients, and pomalidomide provided a minimal or better response for 42 percent of the patients, a partial response or better for 21 percent, and a complete response for 3 percent.
The study, a collaborative effort among researchers from Moffitt, Dana-Farber Cancer ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Modifications of a nanoparticle can change chemical interactions with cell membranes