(Press-News.org) You might expect dung beetles to keep their "noses to the ground," but they are actually incredibly attuned to the sky. A report published online on January 24 in Current Biology, a Cell Press publication, shows that even on the darkest of nights, African ball-rolling insects are guided by the soft glow of the Milky Way.
While birds and humans are known to navigate by the stars, the discovery is the first convincing evidence for such abilities in insects, the researchers say. It is also the first known example of any animal getting around by the Milky Way as opposed to the stars.
"Even on clear, moonless nights, many dung beetles still manage to orientate along straight paths," said Marie Dacke of Lund University in Sweden. "This led us to suspect that the beetles exploit the starry sky for orientation—a feat that had, to our knowledge, never before been demonstrated in an insect."
Dacke and her colleagues found that dung beetles do transport their dung balls along straight paths under a starlit sky but lose the ability under overcast conditions. In a planetarium, the beetles stayed on track equally well under a full starlit sky and one showing only the diffuse streak of the Milky Way.
That makes sense, the researchers explain, because the night sky is sprinkled with stars, but the vast majority of those stars should be too dim for the beetles' tiny compound eyes to see.
The findings raise the possibility that other nocturnal insects might also use stars to guide them at night. On the other hand, dung beetles are pretty special. Upon locating a suitable dung pile, the beetles shape a piece of dung into a ball and roll it away in a straight line. That behavior guarantees them that they will not return to the dung pile, where they risk having their ball stolen by other beetles.
"Dung beetles are known to use celestial compass cues such as the sun, the moon, and the pattern of polarized light formed around these light sources to roll their balls of dung along straight paths," Dacke said. "Celestial compass cues dominate straight-line orientation in dung beetles so strongly that, to our knowledge, this is the only animal with a visual compass system that ignores the extra orientation precision that landmarks can offer."
INFORMATION:
Current Biology, Dacke et al.: "Dung beetles use the Milky Way for orientation."
Dung beetles follow the Milky Way
2013-01-24
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Dung beetles use stars for orientation
2013-01-24
An insect with a tiny brain and minimal computing power has become the first animal proven to use the Milky Way for orientation. Scientists from South Africa and Sweden have published findings showing the link between dung beetles and the spray of stars which comprises our galaxy.
Although their eyes are too weak to distinguish individual constellations, dung beetles use the gradient of light to dark provided by the Milky Way to ensure they keep rolling their balls in a straight line and don't circle back to competitors at the dung pile.
"The dung beetles don't care which ...
Discovering the secrets of tumor growth
2013-01-24
Scientists at the University of Copenhagen's Center for Healthy Ageing have identified a compound that blocks the expression of a protein without which certain tumours cannot grow. This compound has the potential as an anticancer agent according to the research published in the journal CHBIOL: Chemistry and Biology this week.
The BLM protein is also known to be important in maintaining stability in cells when they multiply, thus preventing cancer. However, certain types of tumour need BLM to grow. This is typical of osteosarcomas - aggressive malignant tumours often seen ...
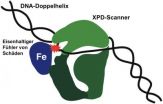
A scanner for hereditary defects
2013-01-24
Our DNA is constantly under attack from UV light, toxins and metabolic processes. Proteins and enzymes continually repair the damaged DNA. Unrecognized and therefore unrepaired damage to the genetic material, however, accelerates aging and causes cancer and genetic disorders. A team headed by veterinary pharmacologist and toxicologist Hanspeter Nägeli has now discovered that the protein XPD plays a key role in locating damaged DNA.
XPD protein as scanner
Genetic information is stored on approximately three billion base pairs of adenine/thymine or cytosine/guanine in ...
Research ties lightning to onset of headache, migraines
2013-01-24
CINCINNATI—University of Cincinnati (UC) researchers have found that lightning may affect the onset of headache and migraines.
These results, published in the Jan. 24, 2013 online edition of the journal Cephalalgia, are the first tying lightning to headache and could help chronic sufferers more efficiently anticipate headache and migraine arrival and begin preventive treatment immediately.
Geoffrey Martin, fourth-year medical student at UC, and his father Vincent Martin, MD, professor in the division of general internal medicine, UC Health physician and headache expert, ...
False beliefs persist, even after instant online corrections
2013-01-24
COLUMBUS, Ohio - It seems like a great idea: Provide instant corrections to web-surfers when they run across obviously false information on the Internet.
But a new study suggests that this type of tool may not be a panacea for dispelling inaccurate beliefs, particularly among people who already want to believe the falsehood.
"Real-time corrections do have some positive effect, but it is mostly with people who were predisposed to reject the false claim anyway," said R. Kelly Garrett, lead author of the study and assistant professor of communication at Ohio State University.
"The ...
Liquid crystal's chaotic inner dynamics
2013-01-24
Liquid crystal displays are ubiquitous. Now, Polish physicists have demonstrated that the application of a very strong alternating electric field to thin liquid crystal cells leads to a new distinct dynamic effect in the response of the cells. The theory of spatio-temporal chaos explains this effect. It was elucidated by Wojciech Jeżewski and colleagues from the Institute of Molecular Physics, Polish Academy of Sciences, in Poznań, Poland, and is about to be published in EPJ E. This effect has implications for the operation of liquid-crystal devices because their ...
Adolescent sexual and reproductive health priorities identified
2013-01-24
Quality sexual and reproductive health care is an essential component of public health. However, there are insufficient evidence-based policies related to adolescent sexual and reproductive health in low- and middle-income countries. In an effort to address the research gap, faculty from the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health led a project to identify research priorities for adolescent sexual and reproductive health in these countries. The results, which are based on input from nearly 300 experts and highlight key focus areas, are featured in the January issue ...
Some minority students may fare better than whites when working part time, new research finds
2013-01-24
WASHINGTON - African-American and Hispanic students may be less likely than non-Hispanic white students to hold a job during the school year, but when they do, they tend to work somewhat longer hours and seem less likely to see their grades suffer than non-Hispanic white students with jobs, according to new research published by the American Psychological Association.
A study involving nearly 600,000 students from around the country also found that among high school students who work long hours at a part-time job, black and Hispanic students from lower income households ...
Researchers uncover gene's role in rheumatoid arthritis, findings pave way for new treatments
2013-01-24
ANN ARBOR, Mich. — University of Michigan research sheds new light on why certain people are more likely to suffer from rheumatoid arthritis – paving the way to explore new treatments for both arthritis and other autoimmune diseases.
The new UMHS research in mice identifies how a specific group of genes works behind the scenes to activate the bone-destroying cells that cause severe rheumatoid arthritis, a debilitating health issue for millions of Americans.
"We believe this could be a significant breakthrough in our understanding of why certain genes are associated ...
Climate change beliefs of independent voters shift with the weather, UNH study finds
2013-01-24
DURHAM, N.H. – There's a well-known saying in New England that if you don't like the weather here, wait a minute. When it comes to independent voters, those weather changes can just as quickly shift beliefs about climate change.
New research from the University of New Hampshire finds that the climate change beliefs of independent voters are dramatically swayed by short-term weather conditions. The research was conducted by Lawrence Hamilton, professor of sociology and senior fellow at the Carsey Institute, and Mary Stampone, assistant professor of geography and the New ...