(Press-News.org) TORONTO, Jan. 24, 2013—Up to one-third of patients undergoing surgery in Ontario have a treatable form of anemia but are not optimally treated for it.
A paper published online today in the Canadian Journal of Anesthesia says that hospitals that do treat patients with anemia have better outcomes, including fewer blood transfusions and infections and shorter hospital stays.
A common option for management of anemia has been blood transfusion. But blood transfusions are expensive and are associated with higher death and complication rates.
Dr. Gregory Hare, an anesthesiologist at St. Michael's Hospital, reported in today's paper that hip and knee replacement patients who had blood transfusions stayed in hospital about two days longer than those who did not have transfusions. The stay was about three days longer for coronary artery bypass graft patients who had transfusions. The risk of infection more than doubled for patients who had transfusions.
Dr. Hare called anemia a "silent killer." Severe anemia can cause low oxygen levels in vital organs and may result in heart attacks, strokes and kidney failure. He said early diagnosis of anemia is important to give doctors sufficient time to treat it before surgery.
For example, 10.4 per cent of knee replacement patients diagnosed with anemia less than seven days before surgery required transfusions, compared to 7.3 per cent diagnosed more than 21 days in advance. He said 41.3 per cent of coronary artery bypass grafts patients needed blood transfusions if diagnosed with anemia less than seven days before surgery, compared with 22.8 per cent diagnosed more than 21 days in advance.
"If given time to treat anemia, we can avoid unnecessary transfusions and thereby improve quality of patient care," Dr. Hare said.
St. Michael's is developing a Centre of Excellence for Patient Blood Management, which would be one of the first of its kind in Canada and a global leader in patient care and in training, research and education for health care professionals.
Under patient blood management, physicians might prescribe certain drugs or dietary supplements to raise a patient's hemoglobin level before surgery.
During surgery, doctors may use a variety of state of-the-art technologies and techniques to minimize blood loss, such as minimally invasive surgery, electrocautery (using heat to stop vessels from bleeding), an argon beam coagulator, which coagulates or clots blood to minimize blood loss, or intravenous iron and erythropoietin, which stimulate bone marrow to produce red blood cells.
The number of patients requiring blood transfusions after undergoing knee replacement surgery in Ontario in 2011 was less than half the number in 2002.
2002 was when the provincial government set up the Ontario Transfusion Coordinators (ONTraC), a province-wide blood management program administered by St. Michael's Hospital. The goal of the program is to promote blood conservation and alternatives to transfusions for problems such as anemia, a condition where a person has a reduced number of red blood cells or hemoglobin, the part of the red blood cell that carries oxygen.
ONTraC figures published for the first time today show the number of patients requiring blood transfusions after undergoing knee surgery fell from 24.5 per cent in 2002 to 10.1 per cent in 2011. The number requiring transfusions after undergoing coronary artery bypass grafting fell from 60.2 per cent to 25.2 per cent in the same time.
INFORMATION:
The research was funded by the Canadian Anesthesiologists' Society, St. Michael's Departments of Anesthesia, Laboratory Medcine and Medicine. Dr. Hare has been supported by a Merit Award from the Department of Anesthesia, University of Toronto, with salary support from Johnson and Johnson Medical Companies.
About St. Michael's Hospital
St. Michael's Hospital provides compassionate care to all who enter its doors. The hospital also provides outstanding medical education to future health care professionals in more than 23 academic disciplines. Critical care and trauma, heart disease, neurosurgery, diabetes, cancer care, and care of the homeless are among the Hospital's recognized areas of expertise. Through the Keenan Research Centre and the Li Ka Shing International Healthcare Education Center, which make up the Li Ka Shing Knowledge Institute, research and education at St. Michael's Hospital are recognized and make an impact around the world. Founded in 1892, the hospital is fully affiliated with the University of Toronto.
For more information or to interview Dr. Hare, please contact:
Leslie Shepherd
Manager, Media Strategy
St. Michael's Hospital
Phone: 416-864-6094 or 647-300-1753
shepherdl@smh.ca
www.stmichaelshospital.com
Follow us on Twitter: http://www.twitter.com/stmikeshospital
END
COLUMBIA, Mo. – Health care practitioners now can access patients' data using electronic medical records, which often include information systems that assess individuals' medical histories and clinical research to facilitate doctors' diagnoses. A University of Missouri researcher says the increased use of computerized clinical decision support systems (CDSSs) leads to greater patient dissatisfaction and could increase noncompliance with preventative care and treatment recommendations.
Victoria Shaffer, an assistant professor of health sciences and psychological sciences, ...
ANN ARBOR—A new way of making crystalline silicon, developed by U-M researchers, could make this crucial ingredient of computers and solar cells much cheaper and greener.
Silicon dioxide, or sand, makes up about 40 percent of the earth's crust, but the industrial method for converting sand into crystalline silicon is expensive and has a major environmental impact due to the extreme processing conditions.
"The crystalline silicon in modern electronics is currently made through a series of energy-intensive chemical reactions with temperatures in excess of 2,000 degrees ...
PHILADELPHIA—Infectious diseases in Ghana tend to capture the most attention, but a quiet crisis may soon take over as the country's most threatening epidemic: cancer.
A new study published in January in the journal BMC Cancer, led by Kosj Yamoah, M.D., Ph.D., a resident in the Department of Radiation Oncology at Thomas Jefferson University and Hospital, takes aim at the issue by investigating prostate cancer diagnoses and treatment delivery in black men living in the West African region, in order to devise research strategies to help improve health outcomes.
Overall, ...
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. — A retailer's optimal store layout is the result of balancing the interests of two different types of markets – consumers and suppliers, says new research co-written by a University of Illinois business professor.
According to Yunchuan "Frank" Liu, a retailer's strategic manipulation of store layout is driven by an incentive to balance the shopping process of "fit-uncertain consumers" and the pricing behavior of upstream suppliers.
"Retailers face two different kinds of markets – the consumers who buy goods, and the manufacturers that supply goods," ...
Tropical Cyclone Garry is in a good environment to intensify and satellite imagery from NOAA's GOES-15 satellite helped confirm that the storm has become more organized.
NOAA's GOES-15 satellite captured an infrared image of Tropical Storm Garry when it was located about 330 nautical miles (379.8 miles/ 611.2 km) east of Pago Pago, American Samoa. The image, created by the NASA GOES Project at the NASA Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Md., was taken Jan. 24 at 1500 UTC (10 a.m. EST). The image showed a bright white circle of clouds that indicate strong thunderstorms ...
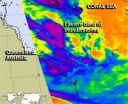
Infrared imagery from NASA's Aqua satellite revealed that a band of thunderstorms on the eastern side of Tropical Storm Oswald's remnants still contained some punch. Oswald's remnants have triggered severe weather warnings in parts of Queensland, Australia.
When NASA's Aqua satellite passed over the eastern side of the remnants of Tropical Cyclone Oswald the Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) instrument captured an infrared image of a powerful band of thunderstorms over the Coral Sea. The band of thunderstorms east of Oswald's center showed some strong convection and ...
Flying high over Antarctica, a NASA long duration balloon has broken the record for longest flight by a balloon of its size.
The record-breaking balloon, carrying the Super Trans-Iron Galactic Element Recorder (Super-TIGER) experiment, has been afloat for 46 days and is on its third orbit around the South Pole.
"This is an outstanding achievement for NASA's Astrophysics balloon team," said John Grunsfeld, associate administrator for the Science Mission Directorate at NASA Headquarters in Washington. "Keeping these huge balloons aloft for such long periods lets us do ...
Irvine, Calif. (Corrected version) — Exposing pregnant mice to low doses of the chemical tributyltin (TBT) – which was used in marine antifouling paints and is used as an antifungal agent in some paints, certain plastics and a variety of consumer products – can lead to obesity for multiple generations without subsequent exposure, a UC Irvine study has found.
After exposing pregnant mice to TBT at low concentrations, similar to those found in the environment and in humans, researchers observed increased body fat, liver fat and fat-specific gene expression in liver and ...
In a development that could lead to faster and more effective toxicity tests for airborne chemicals, scientists from Rice University and the Rice spinoff company Nano3D Biosciences have used magnetic levitation to grow some of the most realistic lung tissue ever produced in a laboratory.
The research is part of an international trend in biomedical engineering to create laboratory techniques for growing tissues that are virtually identical to those found in people's bodies. In the new study, researchers combined four types of cells to replicate tissue from the wall of ...
Pulsars—tiny spinning stars, heavier than the sun and smaller than a city—have puzzled scientists since they were discovered in 1967.
Now, new observations by an international team, including University of Vermont astrophysicist Joanna Rankin, make these bizarre stars even more puzzling.
The scientists identified a pulsar that is able to dramatically change the way in which it shines. In just a few seconds, the star can quiet its radio waves while at the same time it makes its X-ray emissions much brighter.
The research "challenges all proposed pulsar emission theories," ...