(Press-News.org) The sun's energy is virtually limitless, but harnessing its electricity with today's single-crystal silicon solar cells is extremely expensive — 10 times pricier than coal, according to some estimates. Organic solar cells — polymer solar cells that use organic materials to absorb light and convert it into electricity — could be a solution, but current designs suffer because polymers have less-than-optimal electrical properties.
Researchers at Northwestern University have now developed a new design for organic solar cells that could lead to more efficient, less expensive solar power. Instead of attempting to increase efficiency by altering the thickness of the solar cell's polymer layer — a tactic that has preciously garnered mixed results — the researchers sought to design the geometric pattern of the scattering layer to maximize the amount of time light remained trapped within the cell.
Using a mathematical search algorithm based on natural evolution, the researchers pinpointed a specific geometrical pattern that is optimal for capturing and holding light in thin-cell organic solar cells.
The resulting design exhibited a three-fold increase over the Yablonovitch Limit, a thermodynamic limit developed in the 1980s that statistically describes how long a photon can be trapped in a semiconductor.
A paper about the results, "Highly Efficient Light-Trapping Structure Design Inspired by Natural Evolution," was published January 3 in Scientific Reports, a publication of Nature.
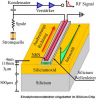
In the newly designed organic solar cell, light first enters a 100-nanometer-thick "scattering layer," a geometrically-patterned dielectric layer designed to maximize the amount of light transmitted into the cell. The light is then transmitted to the active layer, where it is converted into electricity.
"We wanted to determine the geometry for the scattering layer that would give us optimal performance," said Cheng Sun, assistant professor of mechanical engineering in Northwestern's McCormick School of Engineering and Applied Science and co-author of the paper. "But with so many possibilities, it's difficult to know where to start, so we looked to laws of natural selection to guide us."
The researchers employed a genetic algorithm, a search process that mimics the process of natural evolution, explained Wei Chen, Wilson-Cook Professor in Engineering Design and professor of mechanical engineering at McCormick and co-investigator of the research.
"Due to the highly nonlinear and irregular behavior of the system, you must use an intelligent approach to find the optimal solution," Chen said. "Our approach is based on the biologically evolutionary process of survival of the fittest."
The researchers began with dozens of random design elements, then "mated" and analyzed their offspring to determine their particular light-trapping performance. This process was carried out over more than 20 generations and also accounted for evolutionary principles of crossover and genetic mutation.
The resulting pattern will be fabricated with partners at Argonne National Laboratory.
###
Also co-authoring the paper were co-lead authors Chen Wang and Shuangcheng Yu, graduate students in McCormick's Department of Mechanical Engineering. END
Evolution inspires more efficient solar cell design
Geometric pattern maximizes time light is trapped in solar cell
2013-01-25
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Quantum communication: Each photon counts
2013-01-25
This press release is available in German.
The detector combines near-unity detection efficiency with high timing resolution and has a very low error rate. The results have been published by Nature Communications (doi:10.1038/ncomms2307).
Ultrafast, efficient, and reliable single-photon detectors are among the most sought-after components in photonics and quantum communication, which have not yet reached maturity for practical application. Physicist Dr. Wolfram Pernice of the Karlsruhe Institute of Technology (KIT), in cooperation with colleagues at Yale University, ...
NIST's 'nanotubes on a chip' may simplify optical power measurements
2013-01-25
The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) has demonstrated a novel chip-scale instrument made of carbon nanotubes that may simplify absolute measurements of laser power, especially the light signals transmitted by optical fibers in telecommunications networks.
The prototype device, a miniature version of an instrument called a cryogenic radiometer, is a silicon chip topped with circular mats of carbon nanotubes standing on end.* The mini-radiometer builds on NIST's previous work using nanotubes, the world's darkest known substance, to make an ultraefficient, ...
Analysis of Greenland ice cores adds to historical record and provide glimpse into climate's future
2013-01-25
A new study that provides surprising details on changes in Earth's climate from more than 100,000 years ago indicates that the last interglacial--the period between "ice ages"--was warmer than previously thought and may be a good analog for future climate, as greenhouse gases increase in the atmosphere and global temperatures rise.
The research findings also indicate that melting of the massive West Antarctic ice sheet may have contributed more to sea-level rise at that time than melting of the Greenland ice sheet.
The new results from the North Greenland Eemian Ice ...
Emotional stress reduces effectiveness of prostate cancer therapies in animal model
2013-01-25
WINSTON-SALEM, N.C. – Jan. 25, 2013 – Not surprisingly, a cancer diagnosis creates stress. And patients with prostate cancer show higher levels of anxiety compared to other cancer patients.
A new study by researchers at Wake Forest Baptist Medical Center indicates that stress is not just an emotional side effect of the diagnosis; it also can reduce the effectiveness of prostate cancer drugs and accelerate the development of prostate cancer.
The findings are published in the February issue of the Journal of Clinical Investigation.
The Wake Forest Baptist team, headed ...
INRS develops a nanohybrid with remarkable properties using a new laser-plasma process
2013-01-25
Montreal, January 25, 2013 – By achieving the synthesis of a novel nanohybrid structure by means of the pulsed laser ablation (PLA) technique, Professor My Ali El Khakani and his team paved the way for a new generation of optoelectronic materials. The combination of carbon nanotubes and lead sulfide (PbS) nanoparticles was performed using an effective and relatively simple process that offers considerable latitude for creating other nanohybrids for a variety of applications. The INRS Énergie Matériaux Télécommunications Research Centre researcher's work, published in the ...
No more 'empty nest:' middle-aged adults face family pressure on both sides
2013-01-25
CORVALLIS, Ore. – The "empty nest" of past generations, in which the kids are grown up and middle-aged adults have more time to themselves, has been replaced in the United States by a nest that's full – kids who can't leave, can't find a job and aging parents who need more help than ever before.
According to a new study by researchers at Oregon State University, what was once a life stage of new freedoms, options and opportunities has largely disappeared.
An economic recession and tough job market has made it hard on young adults to start their careers and families. ...
New tool for mining bacterial genome for novel drugs
2013-01-25
Vanderbilt biochemists have discovered that the process bacteria undergo when they become drug resistant can act as a powerful tool for drug discovery.
Their findings – reported this week in the Online Early Edition of the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences – should give a major boost to natural products drug discovery – the process of finding new drugs from compounds isolated from living organisms – by substantially increasing the number of novel compounds that scientists can extract from individual microorganisms.
Bacteria have traditionally been the ...
New suite of chemicals seen causing disease generations later
2013-01-25
PULLMAN, Wash.—Washington State University researchers have lengthened their list of environmental toxicants that can negatively affect as many as three generations of an exposed animal's offspring.
Writing in the online journal PLOS ONE, scientists led by molecular biologist Michael Skinner document reproductive disease and obesity in the descendants of rats exposed to the plasticizer bisephenol-A, or BPA, as well DEHP and DBP, plastic compounds known as phthalates.
In a separate article in the journal Reproductive Toxicology, they report the first observation of cross-generation ...
Breast feeding okay for mothers taking immunosuppressant drug
2013-01-25
Highlights
The breast milk of mothers taking the immunosuppressant tacrolimus contains only very low levels of the drug.
Women taking tacrolimus who wish to breast-feed after appropriate counseling should not be discouraged from doing so.
Increasing numbers of pregnant women are taking tacrolimus after organ transplantation and for other conditions.
Washington, DC (January 24, 2013) — Women taking the immunosuppressant tacrolimus can rest assured that breast feeding will not elevate their babies' exposure to the drug, according to a study appearing in an upcoming ...
Kidney disease accounts for most of the increased risk of dying early among diabetics
2013-01-25
Highlights
Among people without diabetes or kidney disease, 10-year mortality was 7.7%.
Among individuals with diabetes but without kidney disease, mortality was 11.5%.
Among those with both diabetes and kidney disease, mortality was 31.1%.
26 million people in the US and 340 million people in the world have type 2 diabetes.
Washington, DC (January 24, 2013) — One in every 10 Americans has diabetes, and a third or more of those with the condition will develop kidney disease. It may be possible to live a long and healthy life with diabetes, but once kidney disease ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
White House autism briefing linked to swift shifts in prescribing patterns, study finds
Specialist palliative care can save the NHS up to £8,000 per person and improves quality of life
New research warns charities against ‘AI shortcut’ to empathy
Cannabis compounds show promise in fighting fatty liver disease
Study in mice reveals the brain circuits behind why we help others
Online forum to explore how organic carbon amendments can improve soil health while storing carbon
Turning agricultural plastic waste into valuable chemicals with biochar catalysts
Hidden viral networks in soil microplastics may shape the future of sustainable agriculture
Americans don’t just fear driverless cars will crash — they fear mass job losses
Mayo Clinic researchers find combination therapy reduces effects of ‘zombie cells’ in diabetic kidney disease
Preventing breast cancer resistance to CDK4/6 inhibitors using genomic findings
Carbon nanotube fiber ‘textile’ heaters could help industry electrify high-temperature gas heating
Improving your biological age gap is associated with better brain health
Learning makes brain cells work together, not apart
Engineers improve infrared devices using century-old materials
Physicists mathematically create the first ‘ideal glass’
Microbe exposure may not protect against developing allergic disease
Forest damage in Europe to rise by around 20% by 2100 even if warming is limited to 2°C
Rapid population growth helped koala’s recovery from severe genetic bottleneck
CAR-expressing astrocytes target and clear amyloid-β in mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease
Unique Rubisco subunit boosts carbon assimilation in land plants
Climate change will drive increasing forest disturbances across Europe throughout the next century
Enhanced brain cells clear away dementia-related proteins
This odd little plant could help turbocharge crop yields
Flipped chromosomal segments drive natural selection
Whole-genome study of koalas transforms how we understand genetic risk in endangered species
Worcester Polytechnic Institute identifies new tool for predicting Alzheimer’s disease
HSS studies highlight advantages of osseointegration for people with an amputation
Buck Institute launches Healthspan Horizons to turn long-term health data into Actionable healthspan insights
University of Ottawa Heart Institute, the University of Ottawa and McGill University launch ARCHIMEDES to advance health research in Canada
[Press-News.org] Evolution inspires more efficient solar cell designGeometric pattern maximizes time light is trapped in solar cell