(Press-News.org) Every day scientists learn more about how the world works at the smallest scales. While this knowledge has the potential to help others, it's possible that the same discoveries can also be used in ways that cause widespread harm.
A new article in the journal Nanomedicine, born out of a Federal Bureau of Investigation workshop held at the University of Notre Dame in September 2012, tackles this complex "dual-use" aspect of nanotechnology research.
"The rapid pace of breakthroughs in nanotechnology, biotechnology, and other fields, holds the promise of great improvements in areas such as medical diagnosis and treatment" says Kathleen Eggleson, a research scientist in Notre Dame's Center for Nano Science and Technology and the author of the study.
"But the risk of misuse of these breakthroughs rises along with the potential benefit. This is the essence of the 'dual-use dilemma.'"
The report examines the potential for nano-sized particles (which are measured in billionths of a meter) to breach the blood-brain barrier, the tightly knit layers of cells that afford the brain the highest level of protection—from microorganisms, harmful molecules, etc.—in the human body. Some neuroscientists are purposefully engineering nanoparticles that can cross the blood-brain barrier (BBB) so as to deliver medicines in a targeted and controlled way directly to diseased parts of the brain.
At the same time, the report notes, "nanoparticles designed to cross the BBB constitute a serious threat…in the context of combat." For example, it is theorized that "aerosol delivery" of some nano-engineered agent in "a crowded indoor space" could cause serious harm to many people at once.
The problem of dual-use research was highlighted last year when controversy erupted over the publication of findings that indicate how, with a handful modifications, the H5N1 influenza virus ("bird flu") can be altered in a way that would enable it to be transmitted between mammalian populations.
After a self-imposed one-year moratorium on this research, several laboratories around the world announced that they will restart the work in early 2013.
The FBI is actively responding to these developments in the scientific community.
"The law enforcement-security community seeks to strengthen the existing dialogue with researchers," William So of the FBI's Biological Countermeasures Unit says in the study.
"Science flourishes because of the open and collaborative atmosphere for sharing and discussing ideas. The FBI believes this model can do the same for our two communities…[and] create effective safeguards for science and national interests."
The scientists and engineers who conduct nanoscale research have the ability and responsibility to consider the public safety aspects of their research and to act to protect society when necessary, argues Eggleson.
"The relationship between science and society is an uneasy one, but it is undeniable on the whole and not something any individual can opt out of in the name of progress for humanity's benefit," she says.
"Thought about dual-use, and action when appropriate, is inherent to socially responsible practice of nanobiomedical science."
INFORMATION: END
CORVALLIS, Ore. – Dairy cows that are fed flaxseed produce more nutritious milk, according to a new study by Oregon State University.
Their milk contained more omega-3 fatty acids and less saturated fat, the study found.
Diets high in saturated fat can increase cholesterol and cause heart disease, while those rich in omega-3 and other polyunsaturated fatty acids may reduce the risk of heart disease, studies have shown.
Traditional cattle feed mixtures of corn, grains, alfalfa hay and grass silage result in dairy products with low concentrations of omega-3 and other ...
Ex-tropical cyclone Oswald doesn't know when to stop causing problems for Queensland, Australia, and now teamed up with a low pressure area, it continues to bring heavy rainfall. NASA's Aqua satellite passed over the remnants and saw Oswald hugging the southeastern Queensland coast.
Oswald has dropped a lot of rainfall throughout Queensland. An earlier rainfall analysis using NASA's TRMM satellite data showed Oswald and its remnants had dropped over 600 mm (~23.6 inches) of rain in areas of the Cape York Peninsula near the Gulf of Carpentaria. Higher rainfall totals have ...
VIDEO:
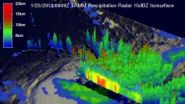
NASA's TRMM satellite saw tropical cyclone Garry moving through the open waters of the South Pacific Ocean on Jan. 25, 2013, at 0909 UTC. The heaviest rainfall (red) was occurring...
Click here for more information.
NASA's Aqua satellite identified powerful thunderstorms around the center of Cyclone Garry as the storm continued to intensify over warm waters of the South Pacific Ocean. Garry has prompted warnings for the southern group of the Cook Islands.
When NASA's ...
Railroad workers sue for asbestos and silica exposure injuries
In many respects, railroad work can be a dangerous job. Railroad workers are routinely exposed to risks that employees in other sectors do not encounter. The Federal Employers Liability Act aims to address these risks by providing injured railroad workers with the right to seek financial compensation for on-the-job injuries.
Occupational exposure claims -- for injuries or illnesses caused by repeated or prolonged exposure to hazardous substances -- are common FELA actions. Railroad workers who are injured ...
A felony conviction will haunt you
On May 23, 2012, 21-year-old University of Colorado Boulder graduate Zoey Ripple wandered drunk into a Boulder home at 3:30 a.m. The homeowners told police that Zoey came into their bedroom and approached their bed with some kind of light. They said she never said a word. The homeowners told her to leave several times and even warned her that they had a gun. When Zoey got about six feet from the couple, the husband shot her once in the hip.
Zoey not only suffered a fractured hip from the shot, but was charged with first-degree criminal ...
Freeh Report on Penn State Scandal Holds Corporate Governance Lessons
The recent indictment of former Penn State University President Graham Spanier alleges that Spanier engaged in a "conspiracy of silence" with other administrators to cover up the crimes of former football coach Jerry Sandusky. Although the media is likely to focus on the more salacious details of the Spanier indictment, it also holds important lessons for corporate boards.
One of the key points arising from the indictment of Spanier is the importance of the report of Judge Louis Freeh ...
Netflix Adopts Shareholder-Friendly Poison Pill
After Carl Icahn announced that he had acquired a 9.98 percent stake in Netflix, the company took steps to protect itself and its shareholders from a corporate takeover. The shareholder rights plan - also known as a poison pill - is intended to prevent Icahn from obtaining a controlling stake in the company. While the Netflix board sees its efforts as necessary to protect the company, Icahn claims that enacting the pill without a shareholder vote is an example of poor corporate governance.
The exact mechanism of the ...
An overview of workers' compensation in New York
It is an unfortunate reality that work can be dangerous. Of course, some professions are more hazardous than others, but nearly every job carries some risk of injury or illness.
A work-related injury can cause major disruptions in a person's life. At a minimum, there will be medical care to pay for. In some cases, the worker will need to take time off to recover. In others, he or she may be left with long-lasting disabilities.
When work injuries or illnesses happen, it is important for workers to avail themselves ...
The liability of drivers for pedestrian injuries in Pennsylvania
Two recent accidents in Pennsylvania highlight the often-tragic results of what happens when car meets pedestrian. Near North Belle Vernon, police are investigating an accident when a man was killed while walking along Interstate 70. Unfortunately, this tragedy was compounded when two other vehicles crashed while trying to avoid the pedestrian accident.
In a separate accident, a Baden man, who was driving without insurance and with a suspended license, struck a pedestrian in Ambridge, knocking him unconscious. ...
The possible future of search warrant detentions
In July 2005, Suffolk County, New York police obtained a warrant to search the apartment of Chunon Bailey. Specifically, officers were looking for a handgun described by a confidential informant. After obtaining the warrant, surveillance officers saw Bailey and another man drive away from the apartment and began to follow them. After those officers drove off, the SWAT team executed the search warrant and entered the apartment.
The officers followed Bailey for approximately one mile before pulling him over. Their only ...