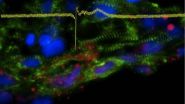
(Press-News.org) LA JOLLA, Calif., January 27, 2013 – Most patients with an inherited heart condition known as arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia/cardiomyopathy (ARVD/C) don't know they have a problem until they're in their early 20s. The lack of symptoms at younger ages makes it very difficult for researchers to study how ARVD/C evolves or to develop treatments. A new stem cell-based technology created by 2012 Nobel Prize winner Shinya Yamanaka, M.D., Ph.D., helps solve this problem. With this technology, researchers can generate heart muscle cells from a patient's own skin cells. However, these newly made heart cells are mostly immature. That raises questions about whether or not they can be used to mimic a disease that occurs in adulthood. In a paper published January 27 in Nature, researchers at Sanford-Burnham Medical Research Institute and Johns Hopkins University unveil the first maturation-based "disease in a dish" model for ARVD/C. The model was created using Yamanaka's technology and a new method to mimic maturity by making the cells' metabolism more like that in adult hearts. For that reason, this model is likely more relevant to human ARVD/C than other models and therefore better suited for studying the disease and testing new treatments.
"It's tough to demonstrate that a disease-in-a-dish model is clinically relevant for an adult-onset disease. But we made a key finding here—we can recapitulate the defects in this disease only when we induce adult-like metabolism. This is an important breakthrough considering that ARVD/C symptoms usually don't arise until young adulthood. Yet the stem cells we're working with are embryonic in nature," said Huei-Sheng Vincent Chen, M.D., Ph.D., associate professor at Sanford-Burnham and senior author of the study.
To establish this model, Chen teamed up with expert ARVD/C cardiologists Daniel Judge, M.D., Joseph Marine, M.D., and Hugh Calkins, M.D., at Johns Hopkins University. Johns Hopkins is home to one of the largest ARVD/C patient registries in the world.
"There is currently no treatment to prevent progression of ARVD/C, a rare disorder that preferentially affects athletes. With this new model, we hope we are now on a path to develop better therapies for this life-threatening disease," said Judge, associate professor and medical director of the Center for Inherited Heart Disease at the Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine.
Disease in a dish
To recreate a person's own unique ARVD/C in the lab, the team first obtained skin samples from ARVD/C patients with certain mutations believed to be involved in the disease. Next they performed Yamanaka's technique: adding a few molecules that dial back the developmental clock on these adult skin cells, producing embryonic-like induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs). The researchers then coaxed the iPSCs into producing an unlimited supply of patient-specific heart muscle cells. These heart cells were largely embryonic in nature, but carried along the original patient's genetic mutations.
However, for nearly a year, no matter what they tried, the team couldn't get their ARVD/C heart muscle cells to show any signs of the disease. Without actual signs of adult-onset ARVD/C, these young, patient-specific heart muscle cells were no use for studying the disease or testing new therapeutic drugs.
Speeding up time
Eventually, the team experienced the big "aha!" moment they'd been looking for. They discovered that metabolic maturity is the key to inducing signs of ARVD/C, an adult disease, in their embryonic-like cells. Human fetal heart muscle cells use glucose (sugar) as their primary source of energy. In contrast, adult heart muscle cells prefer using fat for energy production. So Chen's team applied several cocktails to trigger this shift to adult metabolism in their model.
After more trial and error, they discovered that metabolic malfunction is at the core of ARVD/C disease. Moreover, Chen's team tracked down the final piece of puzzle to make patient-specific heart muscle cells behave like sick ARVD/C hearts: the abnormal over-activation of a protein called PPAR. Scientists previously attributed ARVD/C to a problem in weakened connections between heart muscle cells, which occur only in half of the ARVD/C patients. With the newly established model, they not only replicated this adult-onset disease in a dish, but also presented new potential drug targets for treating ARVD/C.
What's next?
Chen's team was recently awarded a new grant from the California Institute for Regenerative Medicine to create additional iPSC-based ARVD/C models. With more ARVD/C models, they will determine whether or not all (or at least most) patients develop the disease via the same metabolic defects discovered in this current study.
Together with the Johns Hopkins team, Chen also hopes to conduct preclinical studies to find a new therapy for this deadly heart condition.
INFORMATION:
This research was funded by the California Institute of Regenerative Medicine (grants RS1-00171-1, RB2-01512, and RB4-06276) and the U.S. National Institutes of Health (National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute grant RO1HL105194).
The study was co-authored by Changsung Kim, Sanford-Burnham; Jianyan Wen, Sanford-Burnham and China-Japan Friendship Hospital; Johnson Wong, Sanford-Burnham; Shirong Wang, Sanford-Burnham; Cheng Wang, Sanford-Burnham; Sean Spiering, Sanford-Burnham; Natalia G. Kan, Sanford-Burnham; Sonia Forcales, Sanford-Burnham; Pier Lorenzo Puri, Sanford-Burnham; Teresa C. Leone, Sanford-Burnham; Joseph E. Marine, Johns Hopkins University; Hugh Calkins, Johns Hopkins University; Daniel P. Kelly, Sanford-Burnham; Daniel P. Judge, Johns Hopkins University; and Huei-Sheng Vincent Chen, Sanford-Burnham and University of California, San Diego.
About Sanford-Burnham Medical Research Institute
Sanford-Burnham Medical Research Institute is dedicated to discovering the fundamental molecular causes of disease and devising the innovative therapies of tomorrow. The Institute consistently ranks among the top five organizations worldwide for its scientific impact in the fields of biology and biochemistry (defined by citations per publication) and currently ranks third in the nation in NIH funding among all laboratory-based research institutes. Sanford-Burnham utilizes a unique, collaborative approach to medical research and has established major research programs in cancer, neurodegeneration, diabetes, and infectious, inflammatory, and childhood diseases. The Institute is especially known for its world-class capabilities in stem cell research and drug discovery technologies. Sanford-Burnham is a U.S.-based, non-profit public benefit corporation, with operations in San Diego (La Jolla), California and Orlando (Lake Nona), Florida. For more information, news, and events, please visit us at sanfordburnham.org.
Patients' own skin cells are transformed into heart cells to create 'disease in a dish'
Researchers use skin cells from patients with an inherited heart condition to recreate the adult-onset disease in a laboratory dish -- producing the first maturation-based disease model for testing new therapies
2013-01-28
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Demagnetization by rapid spin transport
2013-01-28
For purposes of their research, the scientists irradiated two separate layered systems with ultrashort laser pulses on the order of just one hundred femtoseconds (10-15 s). One sample consisted essentially of a single thin layer of ferromagnetic nickel. By contrast, a second sample of this same nickel material was coated with a non-magnetic layer of gold. Only a mere 30 nanometers (10-9 m) thick, the gold layer swallowed up the lion's share of the laser light so that barely any light ended up reaching the nickel layer. In spite of this, the nickel layer's magnetization ...
Accelerating neutral atoms on a table top
2013-01-28
Charged particle accelerators have become crucially important to modern day life, be it in health care for cancer treatment or for answering important fundamental scientific questions like the existence of the HIGGS boson, the so called 'God particle'. In a simple picture, charged particles like electrons and protons are accelerated between two end plates across which an electrical voltage is applied. High energies need high voltages (millions and billions of volts) and long acceleration paths in giant sized machines – for instance the trillion volt machine called the 'large ...
Rice technique points toward 2-D devices
2013-01-28
HOUSTON – (Jan. 28, 2013) – Rice University scientists have taken an important step toward the creation of two-dimensional electronics with a process to make patterns in atom-thick layers that combine a conductor and an insulator.
The materials at play – graphene and hexagonal boron nitride – have been merged into sheets and built into a variety of patterns at nanoscale dimensions.
Rice introduced a technique to stitch the identically structured materials together nearly three years ago. Since then, the idea has received a lot of attention from researchers interested ...
Cities affect temperatures for thousands of miles
2013-01-28
BOULDER – Even if you live more than 1,000 miles from the nearest large city, it could be affecting your weather.
In a new study that shows the extent to which human activities are influencing the atmosphere, scientists have concluded that the heat generated by everyday activities in metropolitan areas alters the character of the jet stream and other major atmospheric systems. This affects temperatures across thousands of miles, significantly warming some areas and cooling others, according to the study in Nature Climate Change.
The extra "waste heat" generated from ...
Stem cells aid recovery from stroke
2013-01-28
Stem cells from bone marrow or fat improve recovery after stroke in rats, finds a study published in BioMed Central's open access journal Stem Cell Research & Therapy. Treatment with stem cells improved the amount of brain and nerve repair and the ability of the animals to complete behavioural tasks.
Stem cell therapy holds promise for patients but there are many questions which need to be answered, regarding treatment protocols and which cell types to use. This research attempts to address some of these questions.
Rats were treated intravenously with stem cells or ...
Measuring the consequence of forest fires on public health
2013-01-28
Pollution from forest fires is impacting the health of people with asthma and other chronic obstructive lung diseases, finds a study in Biomed Central's open access journal Environmental Health. This study uses data from pharmacies and dispensaries to measure the increase in drugs needed to alleviate symptoms associated with pollution.
Forest fires burn nearly 1000 km2 of trees in British Columbia every year. The Ministry of Environment keeps a close watch on levels of particulate matter in the air caused by these fires but it is harder to measure the impact of this ...
Poor sleep in old age prevents the brain from storing memories
2013-01-28
The connection between poor sleep, memory loss and brain deterioration as we grow older has been elusive. But for the first time, scientists at the University of California, Berkeley, have found a link between these hallmark maladies of old age. Their discovery opens the door to boosting the quality of sleep in elderly people to improve memory.
UC Berkeley neuroscientists have found that the slow brain waves generated during the deep, restorative sleep we typically experience in youth play a key role in transporting memories from the hippocampus – which provides short-term ...
In breast cancer metastasis, researchers identify possible drug target
2013-01-28
The spread of breast cancer to distant organs within the body, an event that often leads to death, appears in many cases to involve the loss of a key protein, according to UC San Francisco researchers, whose new discoveries point to possible targets for therapy.
In the January 27, 2013 online edition of Nature Cell Biology, UCSF scientists describe for the first time how the protein, known as GATA3 — which is abnormal or absent in many cases of human breast cancer — normally acts downstream in biochemical pathways to prevent the distant spread of cancer, an event called ...
Less invasive treatment may increase survival in early stage breast cancer
2013-01-28
DURHAM, N.C. -- Patients with early stage breast cancer who are treated with lumpectomy plus radiation have a better chance of survival compared with those who undergo mastectomy, according to Duke Medicine research.
The study, which appears online Jan. 28, 2013, in the journal CANCER, demonstrates the effectiveness of breast-conserving therapies such as lumpectomy, where only the tumor and surrounding tissue are surgically removed.
"Our findings support the notion that less invasive treatment can provide superior survival to mastectomy in stage I or stage II breast ...
Better survival rates seen with lumpectomy compared with mastectomy for early breast cancer
2013-01-28
A new analysis has found that lumpectomy plus radiation for early breast cancer may provide patients with a better chance of survival than mastectomy. Published early online in CANCER, a peer-reviewed journal of the American Cancer Society, the results provide confidence in the efficacy of breast-conserving treatments even among patients with aggressive, early disease.
Lumpectomy combined with radiation is a good treatment choice for women with early breast cancer; however, over the past 10 years, a growing number of women have been choosing mastectomy even for very small ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
When safety starts with a text message
CSIC develops an antibody that protects immune system cells in vitro from a dangerous hospital-acquired bacterium
New study challenges assumptions behind Africa’s Green Revolution efforts and calls for farmer-centered development models
Immune cells link lactation to long-lasting health
Evolution: Ancient mosquitoes developed a taste for early hominins
Pickleball players’ reported use of protective eyewear
Changes in organ donation after circulatory death in the US
Fertility preservation in people with cancer
A universal 'instruction manual' helps immune cells protect our organs
Fifteen-year results from SWOG S0016 trial suggest follicular lymphoma is curable
The breasts of a breastfeeding mother may protect a newborn from the cold – researchers offer a new perspective on breast evolution
More organ donations now come from people who die after their heart stops beating
How stepping into nature affects the brain
Study: Cancer’s clues in the bloodstream reveal the role androgen receptor alterations play in metastatic prostate cancer
FAU Harbor Branch awarded $900,000 for Gulf of America sea-level research
Terminal ileum intubation and biopsy in routine colonoscopy practice
Researchers find important clue to healthy heartbeats
Characteristic genomic and clinicopathologic landscape of DNA polymerase epsilon mutant colorectal adenocarcinomas
Start school later, sleep longer, learn better
Many nations underestimate greenhouse emissions from wastewater systems, but the lapse is fixable
The Lancet: New weight loss pill leads to greater blood sugar control and weight loss for people with diabetes than current oral GLP-1, phase 3 trial finds
Pediatric investigation study highlights two-way association between teen fitness and confidence
Researchers develop cognitive tool kit enabling early Alzheimer's detection in Mandarin Chinese
New book captures hidden toll of immigration enforcement on families
New record: Laser cuts bone deeper than before
Heart attack deaths rose between 2011 and 2022 among adults younger than age 55
Will melting glaciers slow climate change? A prevailing theory is on shaky ground
New treatment may dramatically improve survival for those with deadly brain cancer
Here we grow: chondrocytes’ behavior reveals novel targets for bone growth disorders
Leaping puddles create new rules for water physics
[Press-News.org] Patients' own skin cells are transformed into heart cells to create 'disease in a dish'Researchers use skin cells from patients with an inherited heart condition to recreate the adult-onset disease in a laboratory dish -- producing the first maturation-based disease model for testing new therapies